Literal vs. Nonliteral Language Worksheets for Grade 3

Literal language represents words and phrases that mean exactly what they say, while nonliteral language adds depth and creativity through figures of speech.
As students progress through their reading and writing journey, it’s essential for them to understand the difference between literal vs non-literal language. Third grade is an ideal time to introduce and reinforce this concept, as students are developing their comprehension skills and learning to interpret texts more deeply.
How can I Help My Third-grade Students Distinguish Between Literal and Non-literal Language?
One effective way to help students distinguish between literal and non-literal language is to use targeted worksheets and activities. Worksheets that present sentences or short passages containing both literal and non-literal phrases can help students practice identifying the differences. Encourage students to use context clues to determine whether a phrase is meant to be taken literally or figuratively.
Consider the Below Literal vs. Nonliteral Language Worksheets for Grade 3
Worksheet 1: Literal vs Nonliteral Language
This engaging worksheet, designed to address CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.L.3.5, helps third-grade students demonstrate their understanding of figurative language and word meanings by distinguishing between literal and nonliteral language in context. Students will read sentences containing bolded phrases and determine whether each phrase is used literally or nonliterally, using context clues to guide their decisions.

The worksheet features a variety of common idioms and figurative expressions, such as “hit the books,” “spill the beans,” and “butterflies in the stomach,” alongside literal phrases to provide a balanced and comprehensive assessment of the student’s ability to identify and differentiate between literal and nonliteral language. By completing this worksheet, students will develop a stronger understanding of how context influences the meaning of words and phrases, enhancing their overall reading comprehension skills.
What are Some Examples of Non-literal Language or Figures of Speech Commonly Used in Everyday Language?
Non-literal language, or figurative language, is used frequently in everyday speech and writing.
Some common examples include:
- Idioms: “It’s raining cats and dogs,” “a piece of cake,” “cost an arm and a leg”
- Similes: “as quiet as a mouse,” “as brave as a lion,” “as sweet as honey”
- Metaphors: “time is money,” “life is a rollercoaster,” “the world is a stage”
- Personification: “the wind whispered,” “the sun smiled down on us,” “the flowers danced in the breeze”
- Hyperbole: “I’ve told you a million times,” “I’m so hungry I could eat a horse,” “this backpack weighs a ton”
Introducing these figures of speech to your third-graders and providing examples will help them recognize non-literal language when they encounter it in texts.
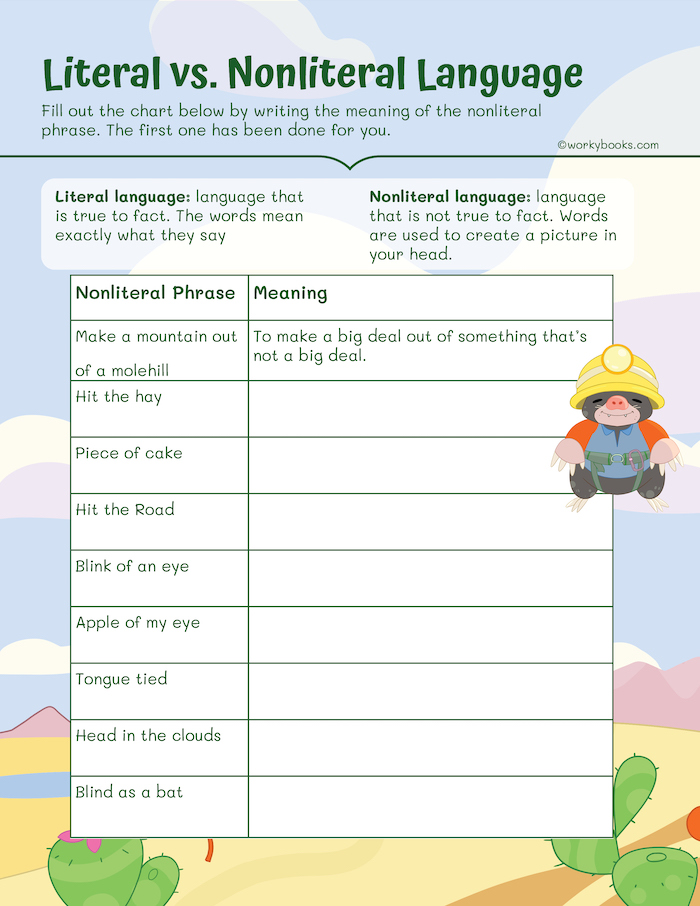
Worksheet 2: Nonliteral Language Meanings
This worksheet on nonliteral language will help students to learn several examples of nonliteral phrases. They will be asked to fill in all of the meanings that they already know, and can work with a partner or as a class to complete the remaining unknown phrases.
How Can I Teach Grade 3 Students to Identify and Understand Nonliteral Language in Stories and Poems?
Teaching Strategies for Identifying Non-literal Language:
- Guided Practice: Provide guided practice activities where students identify and underline non-literal language in texts, such as finding similes or metaphors.
- Writing Activities: Encourage students to create their own examples of non-literal language through writing prompts or poetry exercises.
- Reading stories and poems that contain non-literal language is an excellent way to help students identify and understand figurative expressions in context. Here are a few suggestions for third-grade level texts:
“Owl Moon” by Jane Yolen (picture book) – This beautifully illustrated story contains examples of similes, metaphors, and personification.

“Where the Sidewalk Ends” by Shel Silverstein (poetry collection) – Silverstein’s humorous and imaginative poems are filled with figurative language that will engage young readers.
The Giving Tree” by Shel Silverstein – This classic story uses personification to convey its message of love and selflessness.This classic tale contains rich examples of personification and metaphor, allowing students to explore deeper meanings beyond the literal text.

By combining engaging texts with targeted worksheets and activities, you can help your third-grade students develop a strong foundation in understanding and interpreting non-literal language. This skill will serve them well as they continue to grow as readers and writers in the years to come.