Climate - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the patterns that shape our planet's weather over time
What is Climate?
Climate is the average weather conditions in a place over a long period of time - usually 30 years or more. While weather changes every day, climate describes the pattern of weather we expect in different parts of the world.
For example, the climate of a desert is hot and dry, while the climate near the North Pole is cold and snowy. Climate includes patterns of temperature, rainfall, humidity, wind, and seasons. Scientists study climate to understand our planet and how it might change in the future.
Climate Fact!
The word "climate" comes from the Greek word "klima," which means "slope" or "inclination," referring to how the sun's rays hit Earth at different angles.
Weather vs Climate
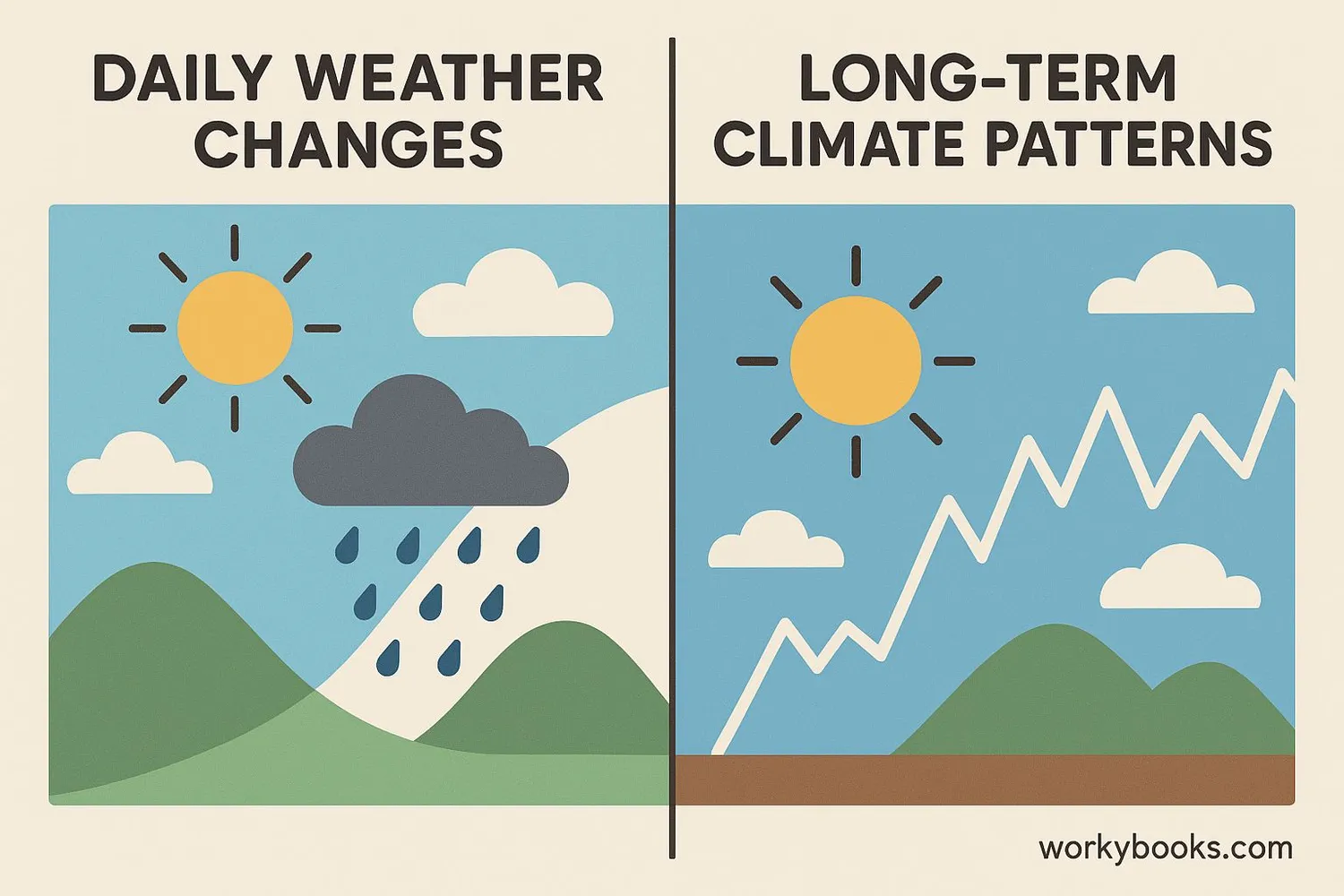
It's easy to mix up weather and climate, but they're different! Here's how:
Weather describes the conditions outside right now - whether it's sunny, rainy, hot, or cold today. Weather can change quickly, sometimes in just minutes.
Climate describes the typical weather patterns in an area over many years. While it might rain today (weather), the climate of a rainforest means it rains a lot throughout the year.
| Feature | Weather | Climate |
|---|---|---|
| Time period | Minutes, hours, days | Years, decades, centuries |
| Changes | Changes quickly | Changes slowly over time |
| Describes | Current conditions | Long-term patterns |
| Examples | Today's temperature, this week's rain | Average summer rainfall, typical winter temperatures |
Remember This!
A simple way to remember: "Climate is what you expect, weather is what you get!"
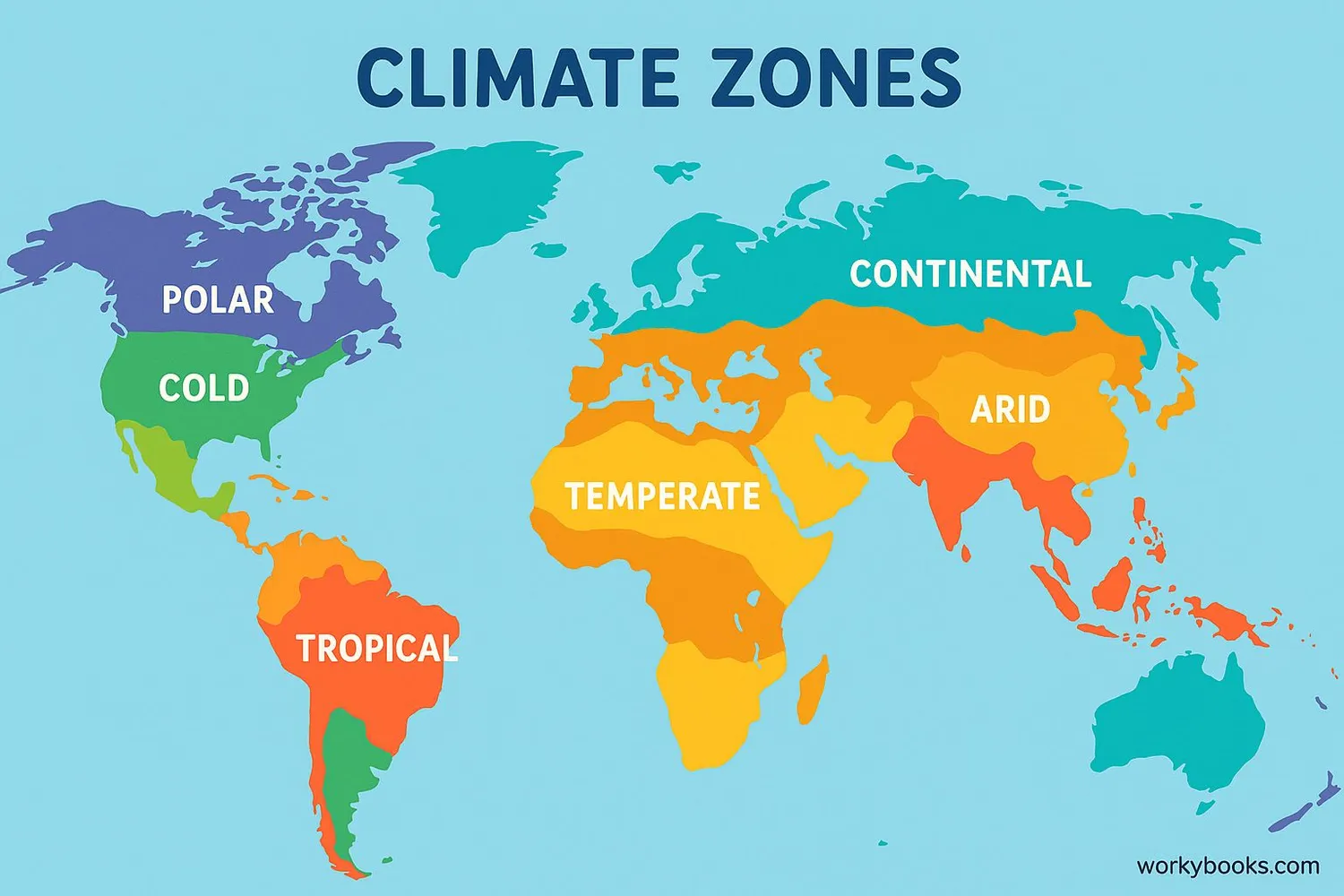
Climate Zones
Earth has different climate zones because the sun heats our planet unevenly. Scientists classify these into five main types:
Tropical
Hot and humid year-round, near the equator
Dry
Very little rain, like deserts
Temperate
Four distinct seasons, moderate temperatures
Continental
Warm summers, very cold winters
Polar
Cold year-round, near the poles
The Köppen climate classification is the most widely used system for classifying these climate zones. Developed by Wladimir Köppen in 1884, it uses letters to represent different climate types based on temperature and precipitation patterns. For example, "Af" stands for tropical rainforest climate, while "BSk" represents a cold semi-arid climate.
Factors Affecting Climate
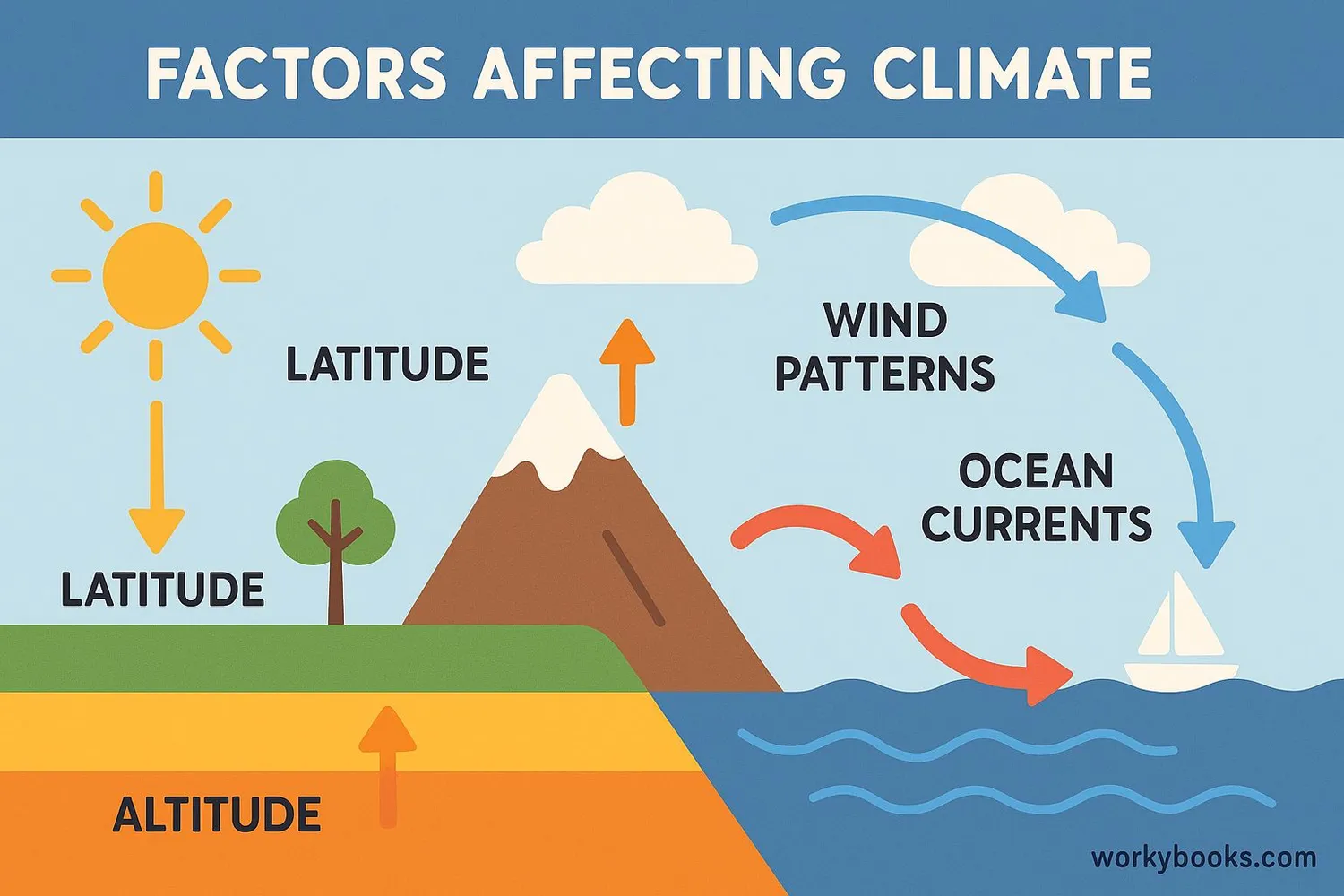
Many factors work together to create different climates around the world:
Latitude
Distance from the equator - closer means warmer
Altitude
Higher elevations are colder than lower ones
Ocean Currents
Warm or cold water flows affect nearby land
Wind Patterns
Global winds move air and moisture around
Landforms
Mountains can block or create rainfall patterns
For example, the Gulf Stream is a warm ocean current that flows from the Gulf of Mexico across the Atlantic Ocean. It makes Western Europe much warmer than other places at the same latitude. That's why London, England has milder winters than Newfoundland, Canada even though they're at similar latitudes!
Climate Change
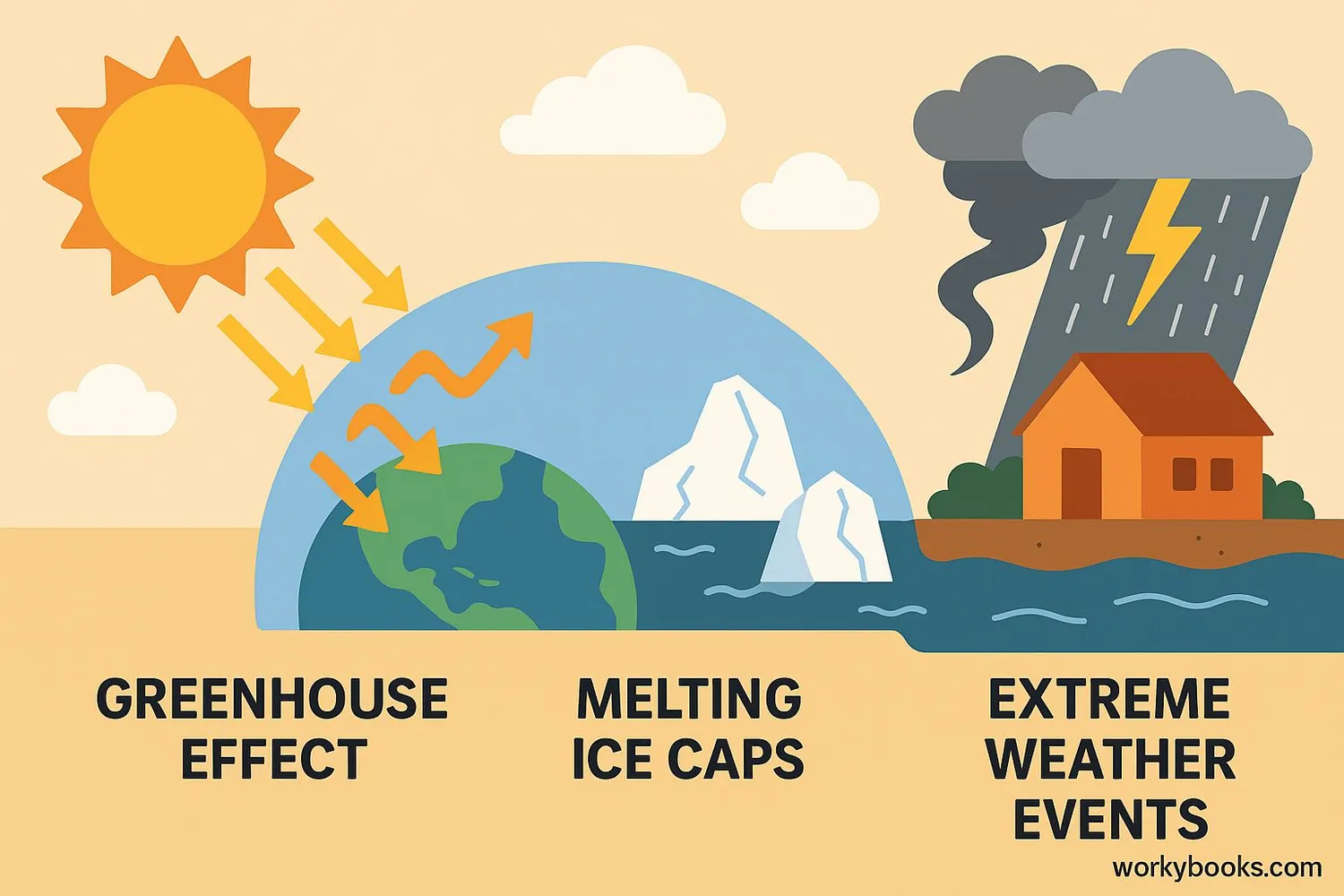
Climate change refers to significant changes in global temperatures and weather patterns over time. While climate has changed naturally throughout Earth's history, scientists are observing rapid changes happening now due to human activities.
The main cause is the increase in greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide (CO₂) in our atmosphere. These gases trap heat from the sun, causing Earth to warm up - this is called the greenhouse effect.
Effects of Climate Change
- Rising global temperatures
- Melting ice caps and glaciers
- Rising sea levels
- More extreme weather events
- Changes in plant and animal habitats
The good news is that people around the world are working on solutions! By using renewable energy, protecting forests, and developing new technologies, we can help slow climate change and protect our planet.
Climate Knowledge Quiz
Test what you've learned about climate with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you know.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about climate:
Amazing Climate Trivia
Discover some fascinating facts about Earth's climate:
Ancient Climate Records
Scientists can study Earth's climate history going back thousands of years by examining ice cores from glaciers. These ice layers contain bubbles of ancient air that reveal past temperatures and atmospheric conditions.
Extreme Climate Facts
The hottest temperature ever recorded on Earth was 134°F (56.7°C) in Death Valley, California in 1913. The coldest was -128.6°F (-89.2°C) at the Soviet Vostok Station in Antarctica in 1983.
Ocean Climate Control
Oceans cover 71% of Earth's surface and play a huge role in regulating climate. They absorb about 25% of the carbon dioxide we release into the atmosphere and have absorbed more than 90% of the excess heat from global warming.
Rainforest Climate Fact
Tropical rainforests like the Amazon create their own rainfall! The dense vegetation releases water vapor through transpiration, which forms clouds and produces rain. This cycle makes rainforests crucial to regional and global climate patterns.





