Vulnerability - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how people, places, and systems can be affected by challenges
What is Vulnerability?

Vulnerability is like having weak spots that make it easier for something bad to happen. It's when people, places, or systems might be harmed by challenges like natural disasters, economic problems, or social issues.
Imagine you're playing soccer. If you have a hurt ankle, that ankle is vulnerable - it's more likely to get injured again. Similarly, a house built on a hillside might be vulnerable to landslides, or a community without a hospital might be vulnerable during a health crisis.
Key Fact!
Vulnerability isn't just about physical things - people can be emotionally vulnerable too, like when they're feeling sad or lonely.
Vulnerability Assessment
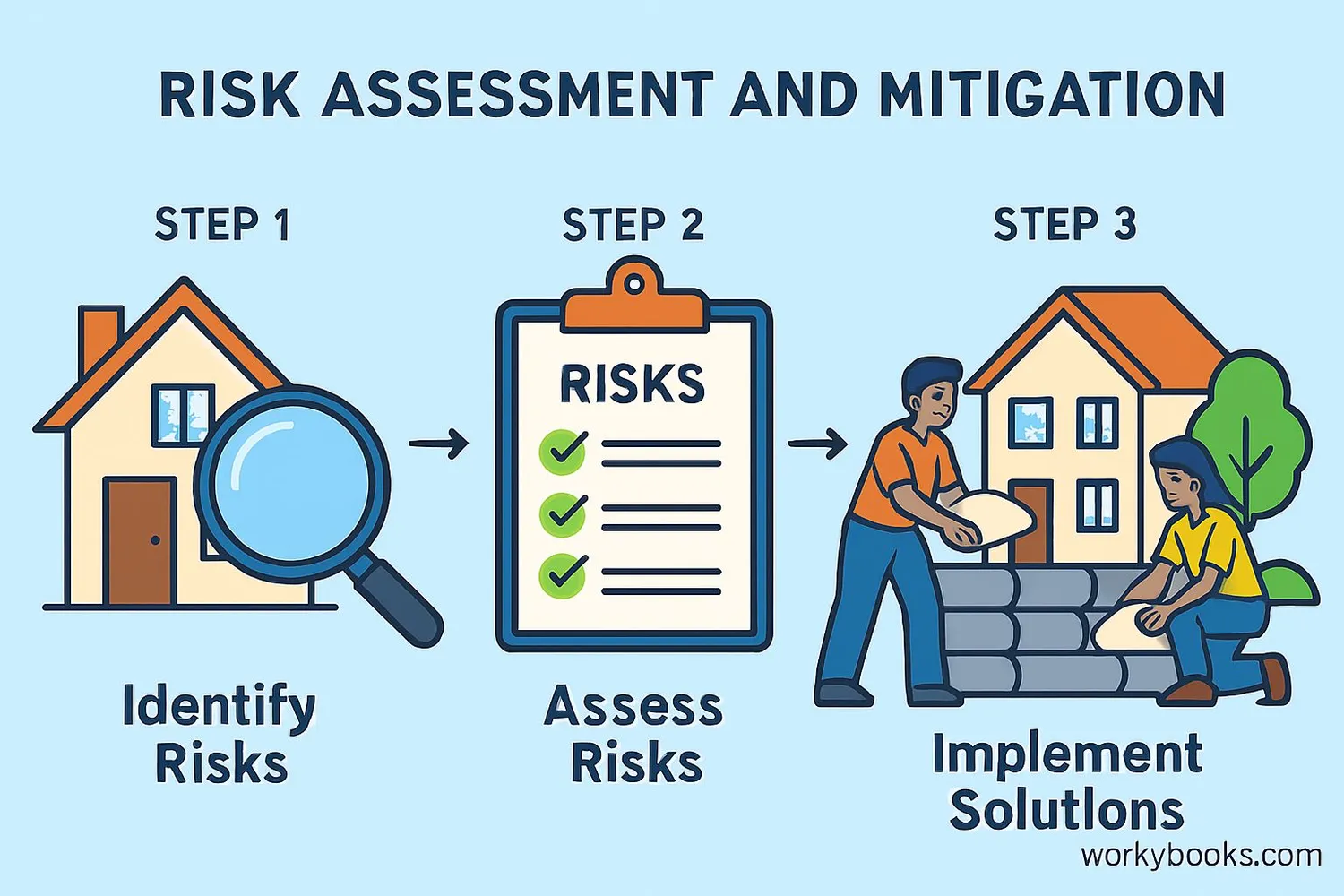
Vulnerability assessment is like being a detective for safety! It's the process of carefully examining:
• What dangers might happen (like floods or earthquakes)
• How much harm they could cause
• Who or what might be most affected
• What we can do to reduce the risks
Identify
Find potential dangers and who might be affected
Analyze
Study how serious the risks are
Prioritize
Determine which risks need attention first
Plan
Create strategies to reduce vulnerability
Real World Example
Before building a new school, engineers assess vulnerability to earthquakes by studying the land, building materials, and emergency plans.
Types of Vulnerability

Vulnerability comes in different forms. Understanding these helps us create better solutions:
Physical Vulnerability
Buildings, roads, and infrastructure that might be damaged
Social Vulnerability
Groups who might need extra help during emergencies
Economic Vulnerability
Financial challenges that make recovery difficult
Environmental Vulnerability
Natural systems that are easily damaged or depleted
Did You Know?
Children and elderly people often have higher social vulnerability because they might need special help during emergencies.
Vulnerability Management
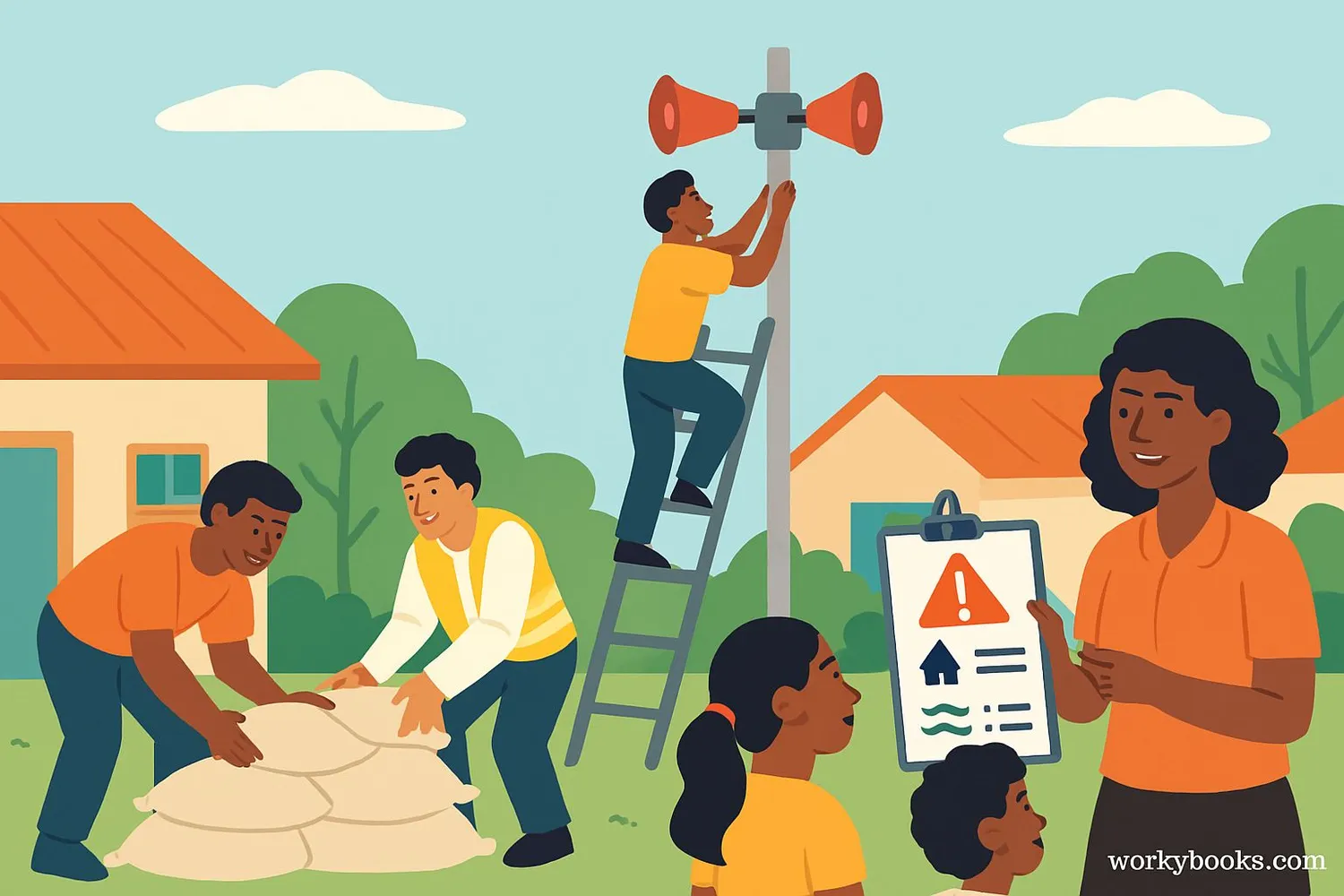

Vulnerability management is about making people, places, and systems stronger and more resilient. It's like giving them armor against challenges! Here's how we do it:
Prevention
Stopping problems before they happen
Preparation
Getting ready for possible challenges
Response
Acting when challenges occur
Recovery
Rebuilding and learning after challenges
Good vulnerability management includes:
• Building stronger structures
• Creating emergency plans
• Teaching safety skills
• Setting up warning systems
• Making sure help is available when needed
Climate Change & Vulnerability

Climate change makes some vulnerabilities worse by creating new challenges and making existing ones more serious:
Sea-level rise: Coastal communities become more vulnerable to flooding
Extreme weather: More intense storms increase physical vulnerability
Drought: Farming communities face economic vulnerability
Heat waves: Elderly and sick people experience health vulnerability
Important Fact
Climate change doesn't affect everyone equally. People in poorer countries often face greater vulnerability even though they've contributed less to climate change.
Community Vulnerability

Communities can be vulnerable too! Community vulnerability is about how prepared a neighborhood or town is to handle challenges. Some communities are more vulnerable because of:
• Limited resources like hospitals or fire stations
• Many elderly or very young residents
• Language barriers that make warnings difficult
• Poverty that makes recovery harder
• Location in high-risk areas like floodplains
Building Resilience
Strong communities work together to reduce vulnerability
Education
Teaching everyone about risks and safety
Community Networks
Creating systems to help vulnerable members
Vulnerability Knowledge Quiz
Test what you've learned about vulnerability with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you understand.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about vulnerability:
Interesting Vulnerability Facts
Discover some fascinating facts about vulnerability:
Global Differences
People in low-income countries are often 7 times more likely to die from natural disasters than those in high-income countries, showing how economic vulnerability affects safety.
Historical Lesson
The 2005 Hurricane Katrina disaster taught important lessons about social vulnerability when elderly and low-income residents faced greater challenges during evacuation and recovery.
Animal Vulnerability
Polar bears are vulnerable to climate change because melting sea ice makes hunting harder. Their vulnerability shows how environmental changes affect living creatures.
Cyber Vulnerability
Computer systems can be vulnerable too! Hackers look for security weaknesses, which is why software updates often include "vulnerability patches" to fix these weak spots.





