Pulsar Stars - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the cosmic lighthouses of the universe!
What is a Pulsar?

A pulsar is a special kind of neutron star that acts like a cosmic lighthouse! Pulsars are the collapsed cores of massive stars that have exploded as supernovae. They spin incredibly fast and send out beams of radiation that we can detect from Earth as regular pulses of light or radio waves.
Think of a pulsar like a spinning lighthouse in space. Just as a lighthouse beam sweeps across the ocean, a pulsar's beam sweeps across space. When the beam points toward Earth, we see a pulse of light. Some pulsars spin hundreds of times per second!
Discovery Fact!
The first pulsar was discovered in 1967 by Jocelyn Bell Burnell and Antony Hewish. At first, they thought the regular pulses might be signals from aliens!
How Pulsars Form
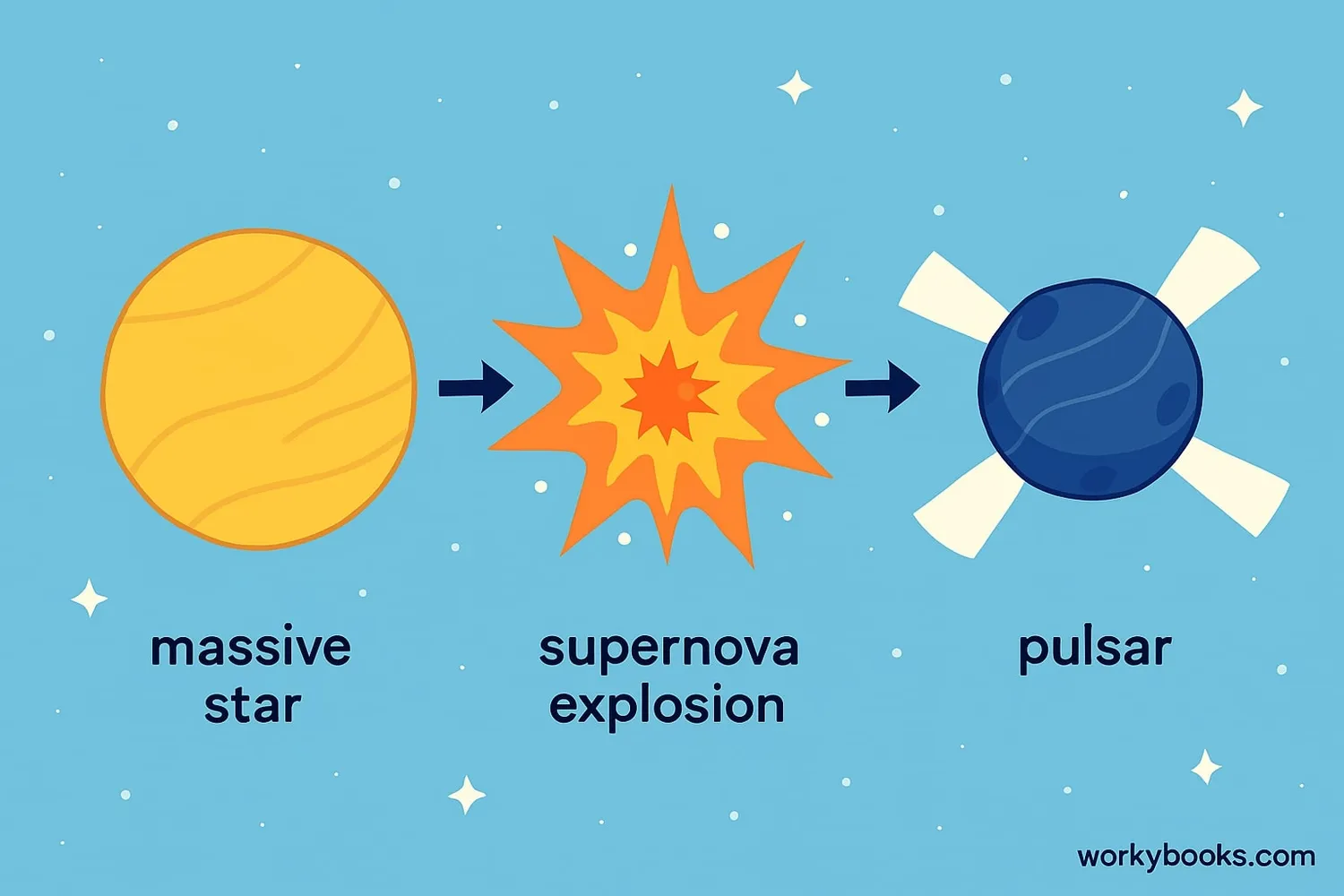
Pulsars form through an amazing cosmic process:
Massive Star
A star at least 8 times more massive than our Sun
Supernova
The star explodes in a supernova at the end of its life
Collapse
The core collapses under its own gravity
Neutron Star
The collapsed core becomes a super-dense neutron star
Pulsar Formation
If the neutron star spins rapidly and has a strong magnetic field, it becomes a pulsar
During the collapse, the star's core gets compressed into an incredibly dense object. Just one teaspoon of neutron star material would weigh as much as a mountain! The conservation of angular momentum causes the neutron star to spin very rapidly, sometimes hundreds of times per second.
Incredible Density!
Pulsars are so dense that if you could bring a sugar-cube-sized piece to Earth, it would weigh about 100 million tons!
Types of Pulsars
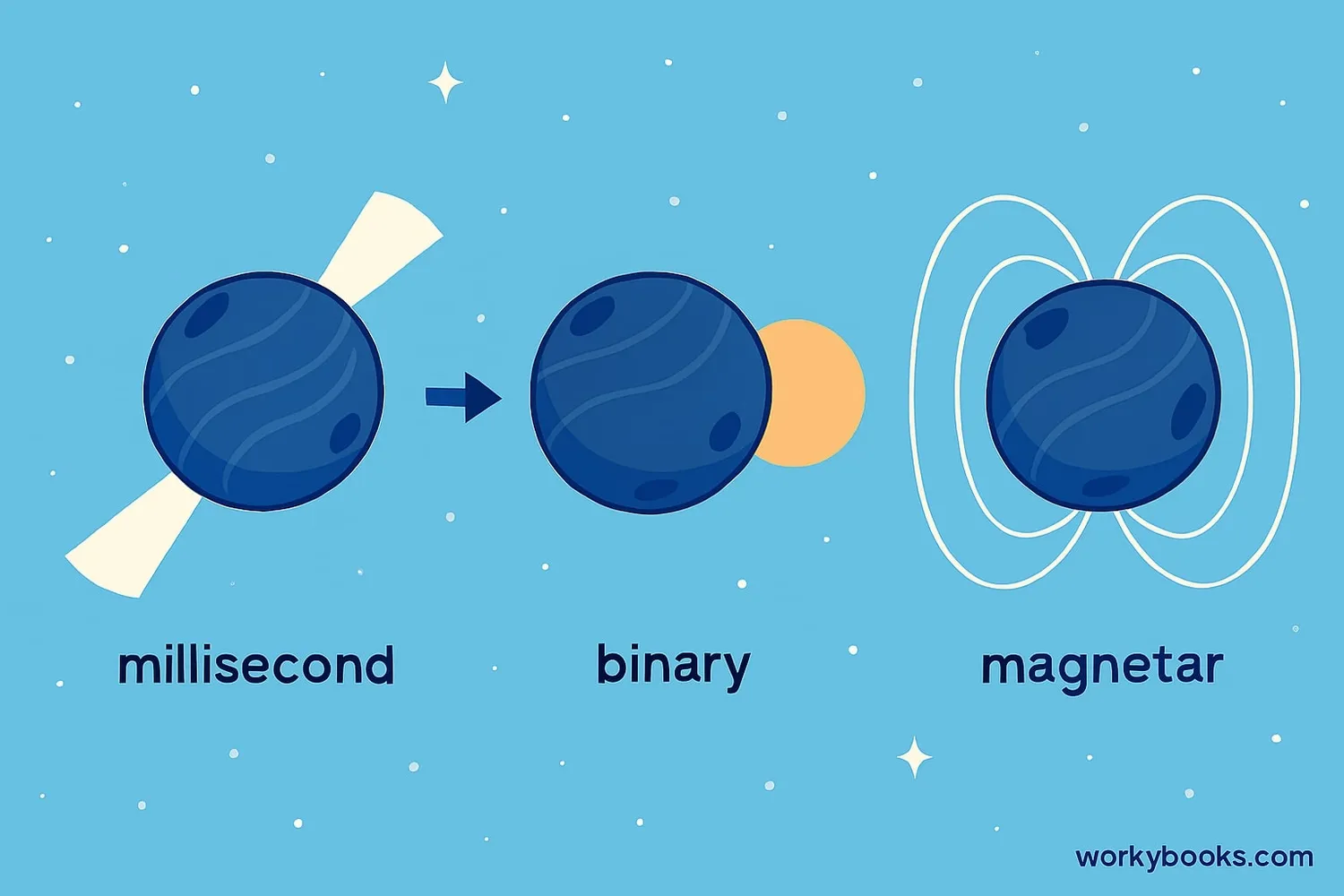
Not all pulsars are the same! Scientists have discovered several types:
Millisecond Pulsars
Spin hundreds of times per second! These are the fastest rotating pulsars.
Binary Pulsars
Orbit with another star, often pulling material from their companion.
Magnetars
Have the strongest magnetic fields in the universe - a trillion times stronger than Earth's!
X-ray Pulsars
Emit powerful X-rays instead of radio waves.
Gamma-ray Pulsars
Release the highest energy form of light - gamma rays.
Some famous pulsars include:
• The Crab Pulsar: Formed in a supernova observed in 1054 AD
• The Vela Pulsar: One of the brightest pulsars in the sky
• PSR J1748-2446ad: The fastest known pulsar, spinning 716 times per second!
Why Pulsars Matter
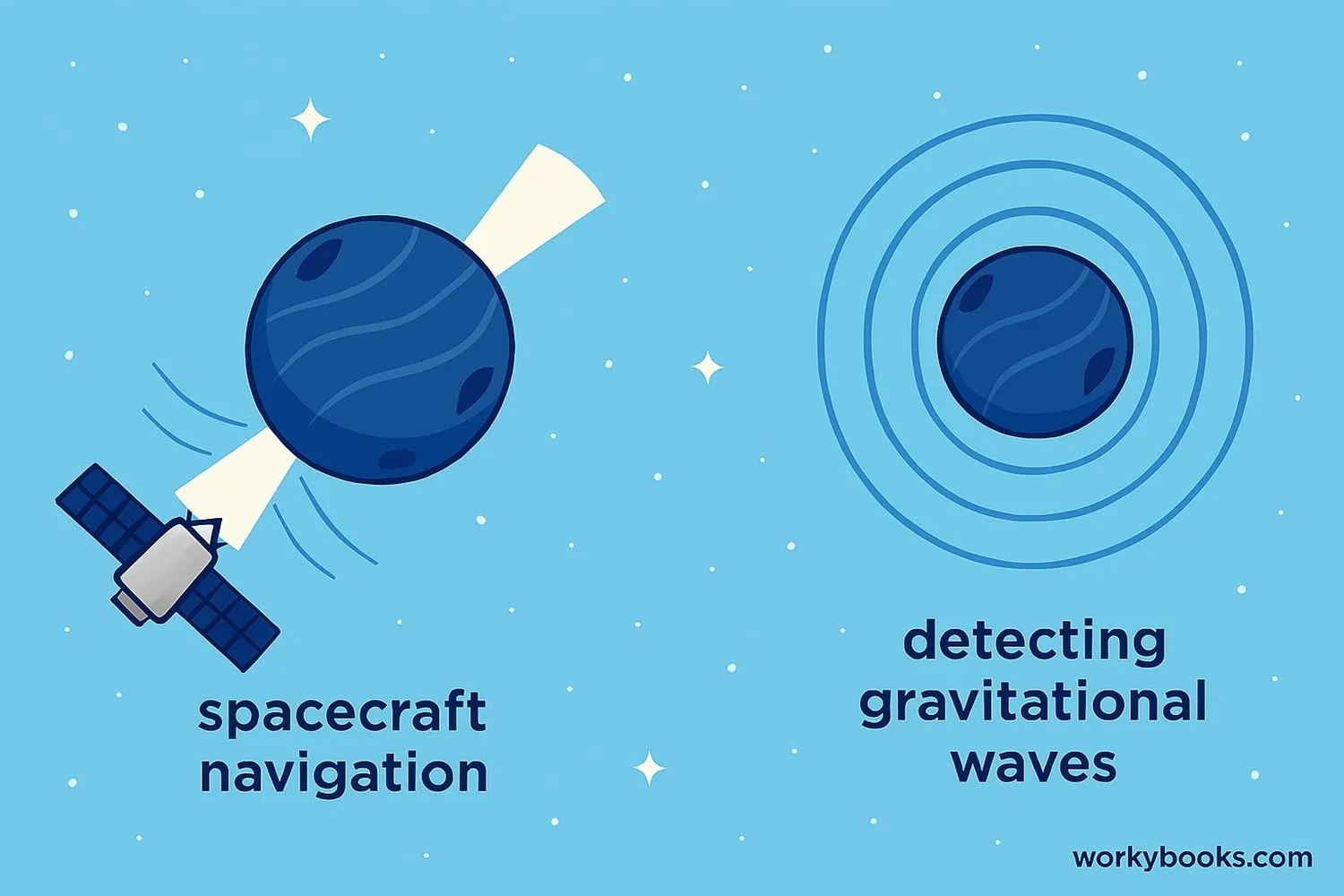
Pulsars aren't just fascinating cosmic objects - they're incredibly useful for science too! Here's why astronomers study them:
Space Navigation
Pulsars act like cosmic GPS! Their regular pulses help spacecraft navigate in deep space.
Testing Gravity
Binary pulsars help scientists test Einstein's theory of relativity with extreme gravity.
Gravitational Waves
Pulsar timing arrays help detect gravitational waves from supermassive black holes.
Pulsars also help us understand:
• The behavior of matter under extreme conditions
• How stars evolve and die
• The structure of our galaxy
• The nature of magnetic fields in space
By studying pulsars, we're learning about the most extreme environments in the universe!
Pulsar Quiz
Test your pulsar knowledge with this space quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about pulsars:
Pulsar Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about pulsars!
Precision Clocks
Pulsars are the most accurate clocks in the universe! Some are so precise that they only lose one second every 10 million years.
Golden Record
The Voyager spacecraft carry a map to Earth using pulsars as reference points, in case aliens find them!
Magnetic Power
Magnetars have magnetic fields so strong they could erase your credit card from half the Moon's distance away!
Ancient Light
The light from some pulsars has been traveling through space for thousands of years before reaching Earth.





