2 Dimensional Shapes - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about flat shapes with easy explanations, properties, examples, and interactive activities
What are 2D Shapes?
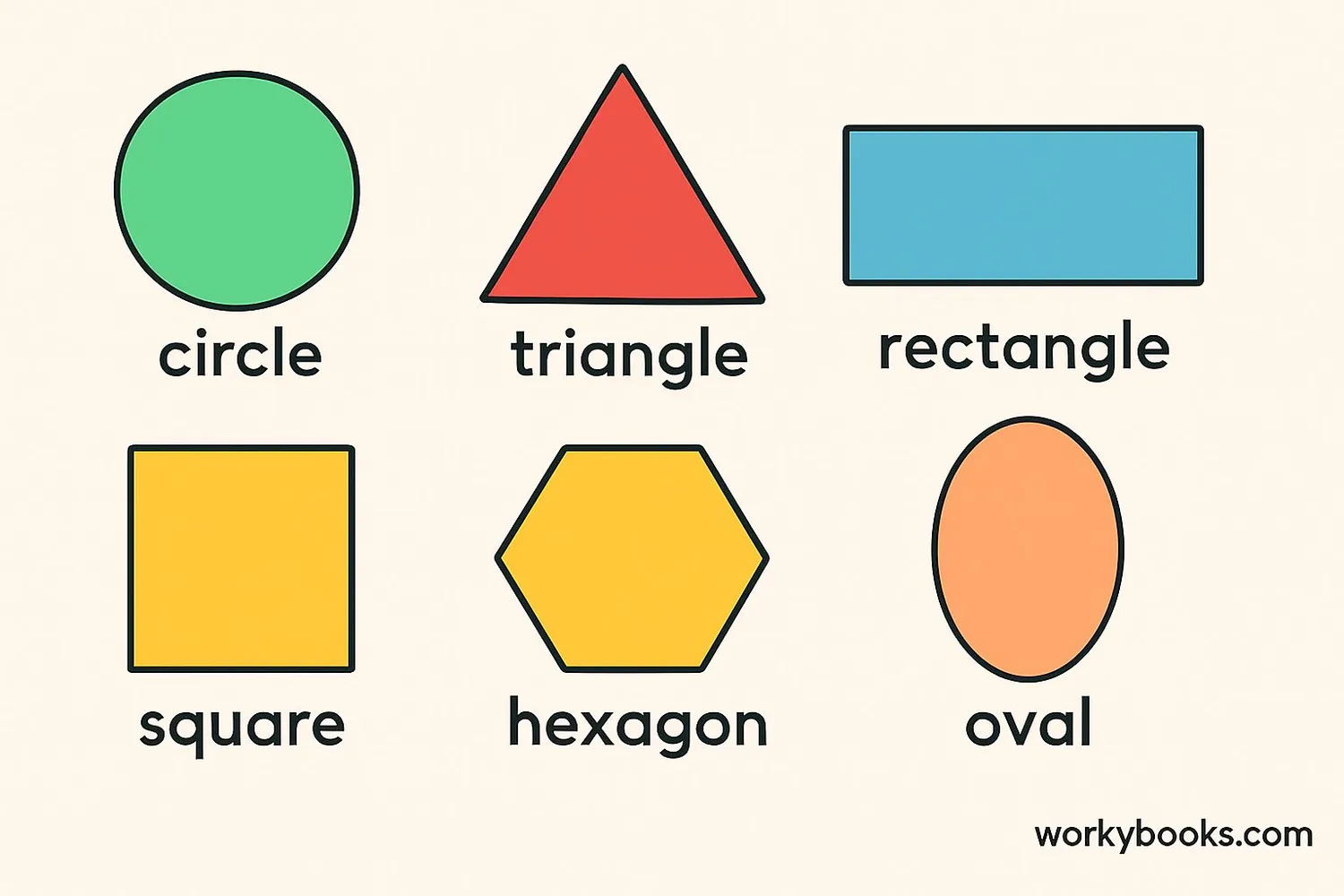
2-dimensional shapes, also called 2D shapes, are flat figures that have length and width but no depth. These shapes lie completely on a flat surface, like a piece of paper. The "2D" stands for two dimensions - length and width.
Unlike 3D shapes that have thickness (like a ball or a box), 2D shapes are completely flat. You can draw them on paper, but you can't hold them in your hand because they have no thickness. Common examples include circles, squares, triangles, and rectangles.
Understanding 2D shapes is an important foundation for geometry. These shapes are everywhere in our world - in signs, patterns, buildings, and nature.
Key Concept
2D shapes have only two dimensions: length and width. They are completely flat with no thickness.
Properties of 2D Shapes
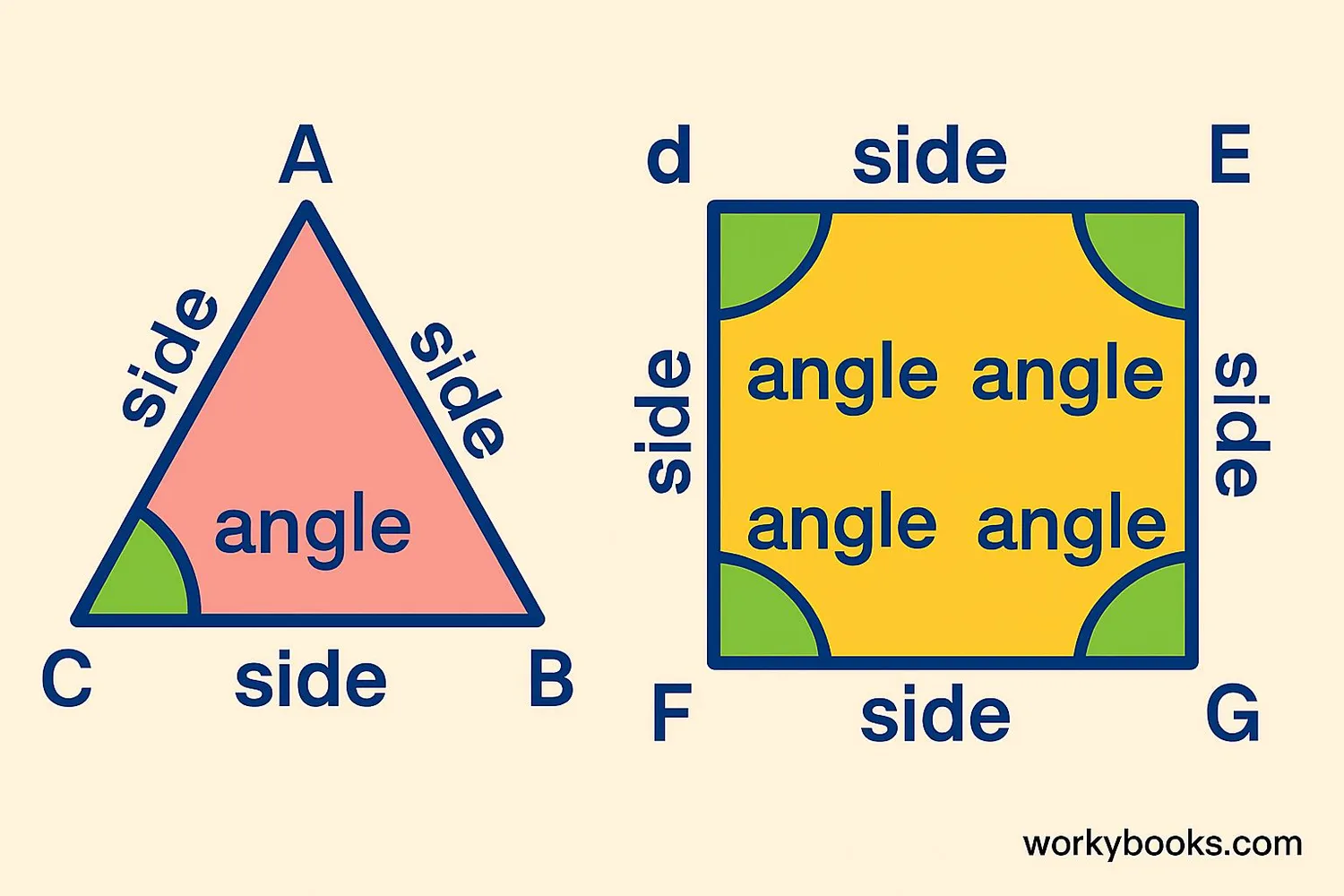
All 2D shapes have special characteristics called properties that help us identify and classify them:
Sides: These are the straight lines that make up the shape. For example, a triangle has 3 sides, a square has 4 sides, and a pentagon has 5 sides.
Vertices: These are the points where two sides meet (corners). The singular form is "vertex." A triangle has 3 vertices, a square has 4 vertices.
Angles: These are the spaces between two sides at each vertex. Angles are measured in degrees. Right angles (90 degrees) are common in squares and rectangles.
Symmetry: Many shapes have symmetry, meaning one half is a mirror image of the other half. A square has 4 lines of symmetry, while a rectangle has 2.
3 Vertices
3 Angles
4 Vertices
4 Right Angles
5 Vertices
5 Angles
6 Vertices
6 Angles
Remember
All polygons (shapes with straight sides) can be classified by the number of sides they have.
Types of 2D Shapes
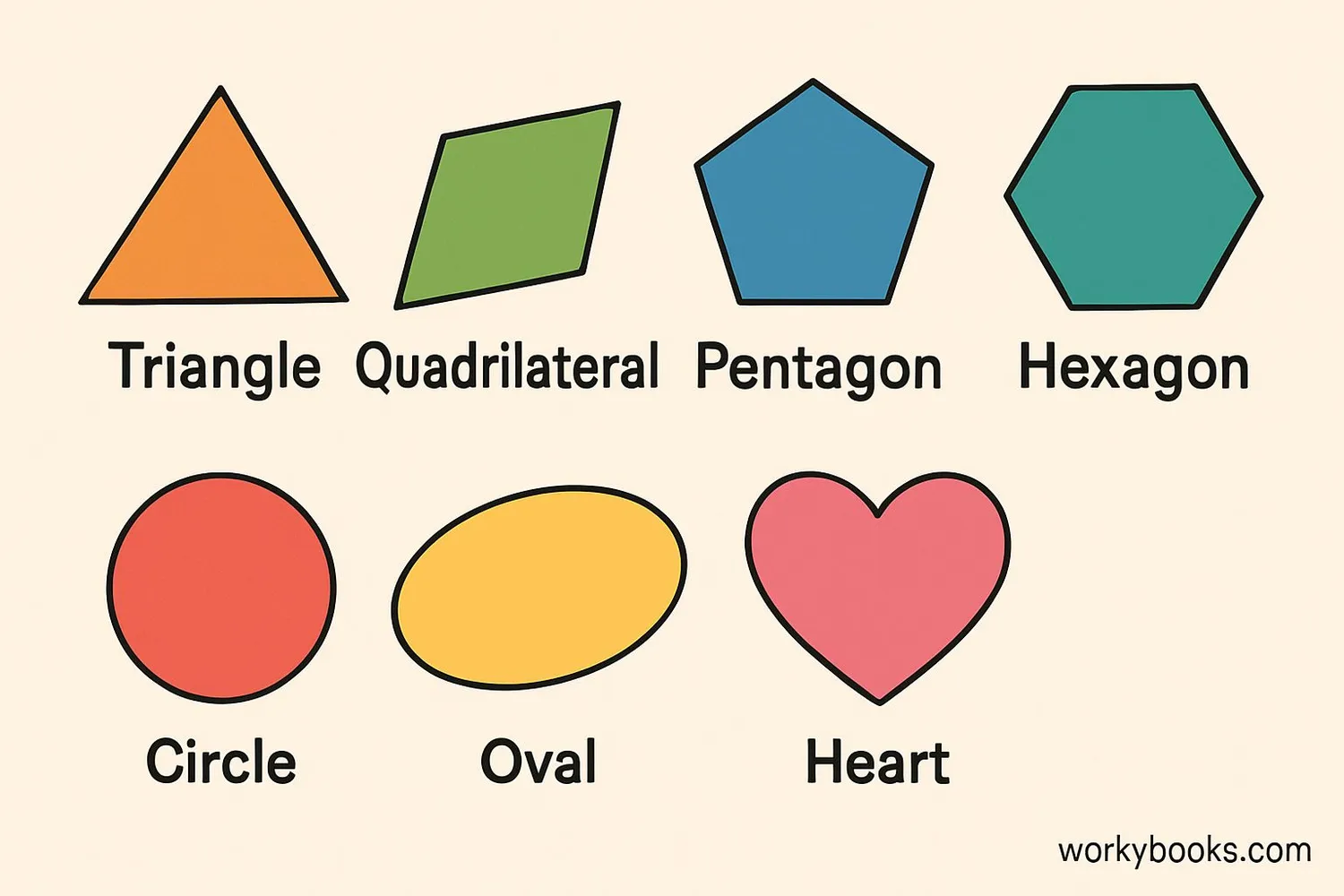
2D shapes can be classified into different categories based on their properties:
Polygons: Closed shapes with straight sides. These include:
- Triangle (3 sides)
- Quadrilateral (4 sides) - square, rectangle, rhombus, trapezoid
- Pentagon (5 sides)
- Hexagon (6 sides)
- Octagon (8 sides)
- Circle - perfectly round, no sides
- Oval - like a stretched circle
- Heart - curved shape with two rounded parts at top
No Vertices
Curved
Opposite Angles Equal
1 Pair Parallel Sides
No Straight Sides
Shape Tip
All quadrilaterals have four sides, but they can have different properties: squares have equal sides and angles, rectangles have equal angles, and rhombuses have equal sides.
Transformations of 2D Shapes
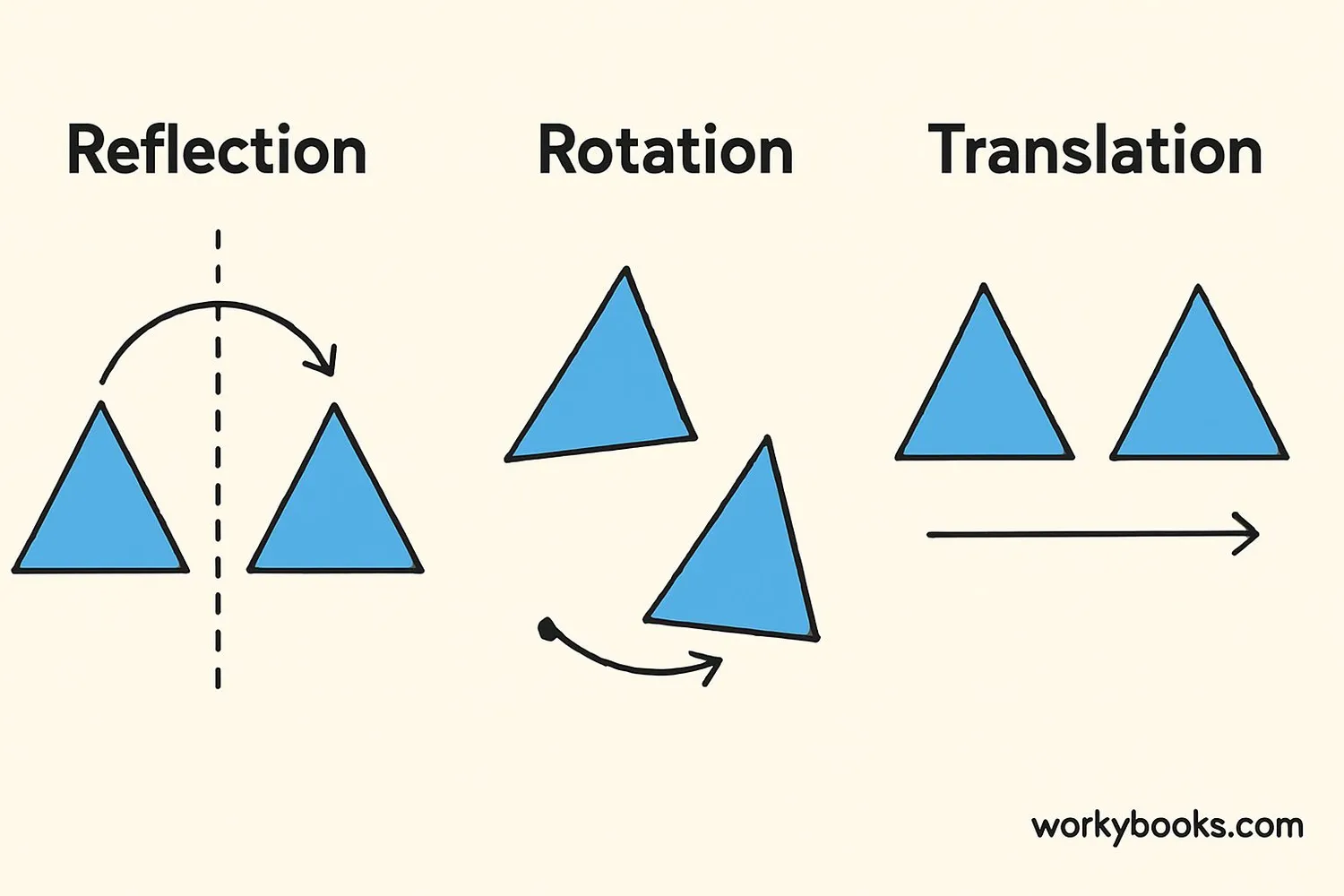
Transformations are ways to move or change a shape without altering its size or shape. There are three main types of transformations:
Flipping a shape over a line (like a mirror image)
Turning a shape around a fixed point
Sliding a shape without turning or flipping it
Transformation Tip
During any transformation, the shape maintains its size and shape - only its position or orientation changes.
2D Shapes Practice Quiz
Test your knowledge of 2D shapes with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about 2D shapes:
Shape Trivia
Discover interesting facts about shapes:
Ancient Geometry
The ancient Egyptians used geometry over 4,000 years ago to measure land after Nile River floods. They developed many concepts about shapes that we still use today.
Shapes in Nature
Hexagons are nature's most efficient shape! Bees use hexagons in their honeycombs because this shape uses the least amount of wax to hold the most honey.
Famous Shape Structures
The Great Pyramid of Giza is the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. It's a square pyramid, with a square base and four triangular sides.
Circle Measurements
The ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter is always π (pi), which is approximately 3.14. This mathematical constant has been studied for thousands of years.





