3 Dimensional Shapes - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about three-dimensional shapes with simple explanations, examples, and interactive activities
What are 3D Shapes?
Three-dimensional shapes (3D shapes) are objects that have length, width, and height. Unlike flat 2D shapes, 3D shapes take up space and can be held. They exist in our everyday world - from balls to boxes to ice cream cones!
The word "three-dimensional" means that these shapes have three measurements:
length (how long it is), width (how wide it is), and height (how tall it is).
Some important terms:
- Polyhedra: 3D shapes with flat faces (like cubes and pyramids)
- Non-polyhedra: 3D shapes with curved surfaces (like spheres and cones)
- Platonic solids: Special polyhedra with identical faces (tetrahedron, cube, octahedron, dodecahedron, icosahedron)
Key Concept
3D shapes are solid objects that have three dimensions: length, width, and height. They have volume and take up space.
Properties of 3D Shapes
All 3D shapes have special properties that help us describe and identify them:
Faces: These are the flat surfaces of a 3D shape. For example, a cube has 6 faces, all squares.
Edges: These are the lines where two faces meet. A cube has 12 edges.
Vertices: These are the corner points where edges meet (singular: vertex). A cube has 8 vertices.
Volume: The amount of space inside a 3D shape (measured in cubic units).
Surface Area: The total area of all the faces of a 3D shape (measured in square units).
Properties of Common 3D Shapes
| Shape | Faces | Edges | Vertices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cube | 6 | 12 | 8 |
| Cuboid (Rectangular Prism) | 6 | 12 | 8 |
| Sphere | 1 (curved) | 0 | 0 |
| Cone | 2 (1 flat, 1 curved) | 1 | 1 |
| Cylinder | 3 (2 flat, 1 curved) | 2 | 0 |
| Pyramid (Square base) | 5 | 8 | 5 |
| Tetrahedron | 4 | 6 | 4 |
Remember
Euler's Formula: For many polyhedra, Faces + Vertices - Edges = 2. Try it with a cube: 6 + 8 - 12 = 2!
Common 3D Shapes
All faces are squares
Perfectly round ball shape
Pointed top with circular base
Two circular bases with curved side
Triangular sides meeting at a point
Same cross-section along its length
Cube: A box-shaped object with six identical square faces. Examples: dice, sugar cubes.
Sphere: A perfectly round ball with no edges or corners. Examples: basketball, globe, marbles.
Cone: Has a circular base that narrows to a point (apex). Examples: ice cream cone, traffic cone.
Cylinder: Has two parallel circular bases connected by a curved surface. Examples: soda can, pencil.
Pyramid: Has a polygon base and triangular faces that meet at a point. Examples: Egyptian pyramids, tent.
Prism: Has two identical ends and flat sides. Examples: rectangular prism (tissue box), triangular prism (toblerone chocolate).
Real World Examples
Look around you! Books are rectangular prisms, balls are spheres, party hats are cones, and cans are cylinders.
Volume & Surface Area
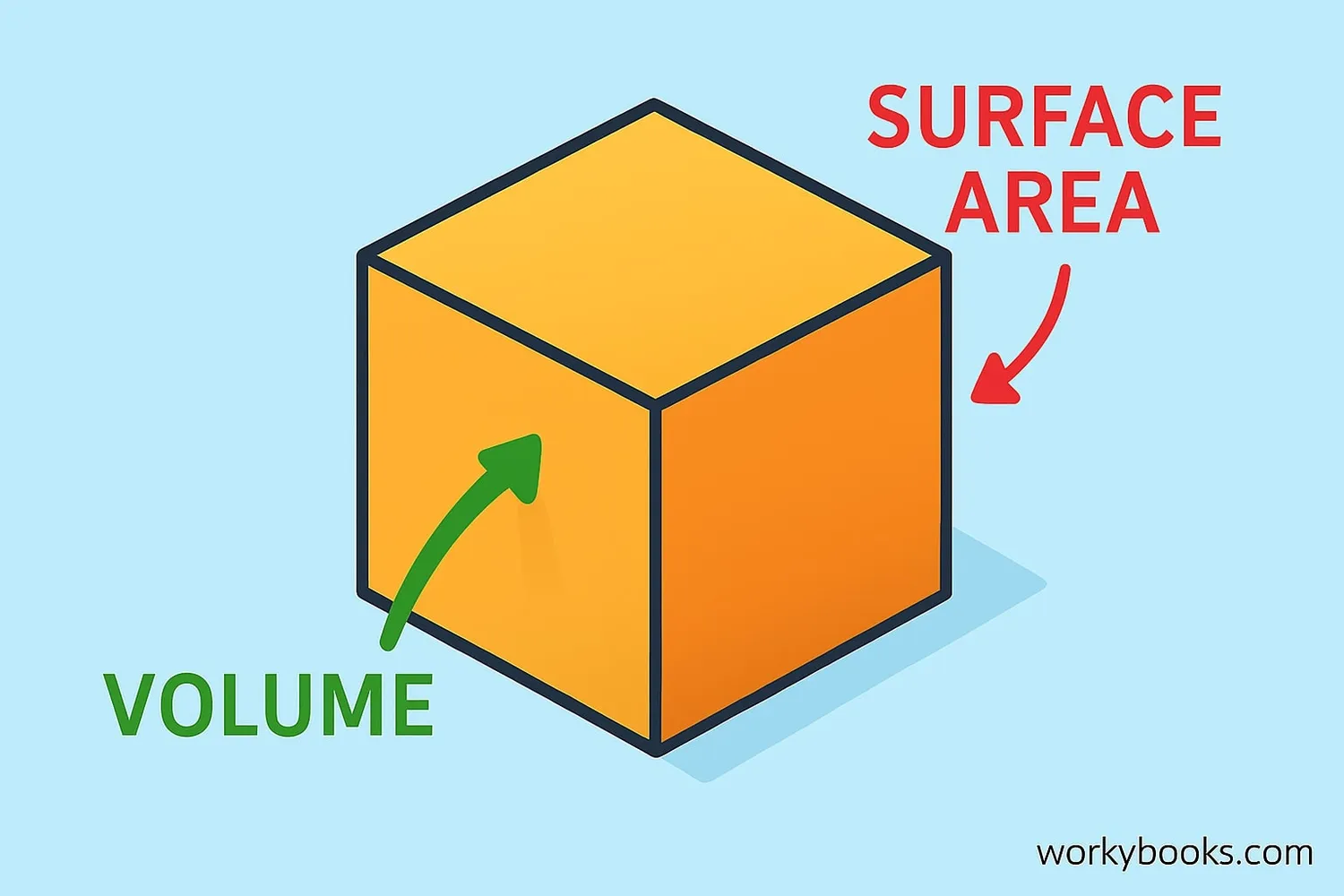
Volume tells us how much space is inside a 3D shape. We measure it in cubic units (like cm³ or m³).
Surface Area tells us how much material would be needed to cover the outside of a shape. We measure it in square units (like cm² or m²).
Volume Formulas
Surface Area Formulas
Practice Tip
Volume answers the question "How much can fit inside?" Surface area answers "How much paint would cover it?"
3D Shape Nets

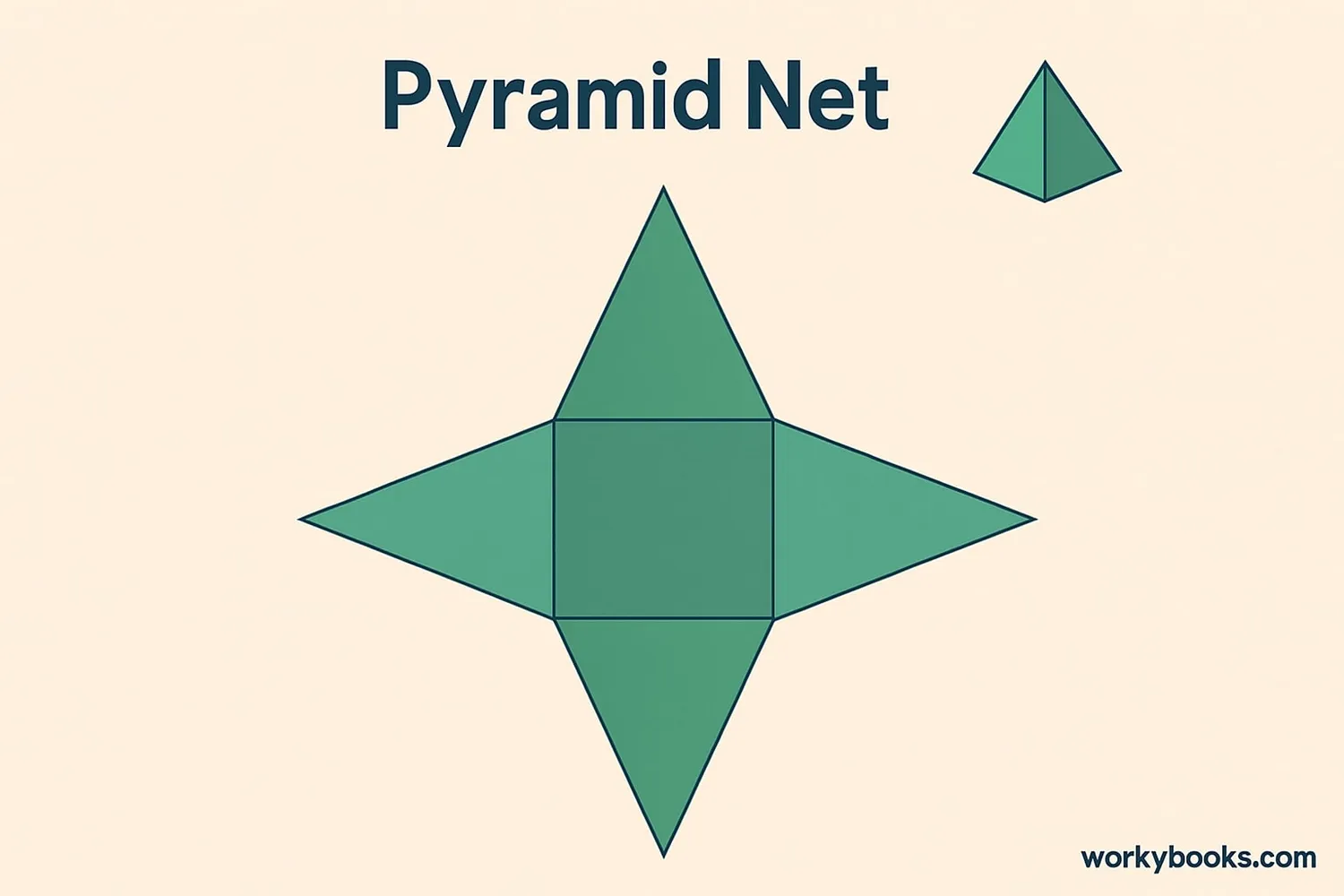
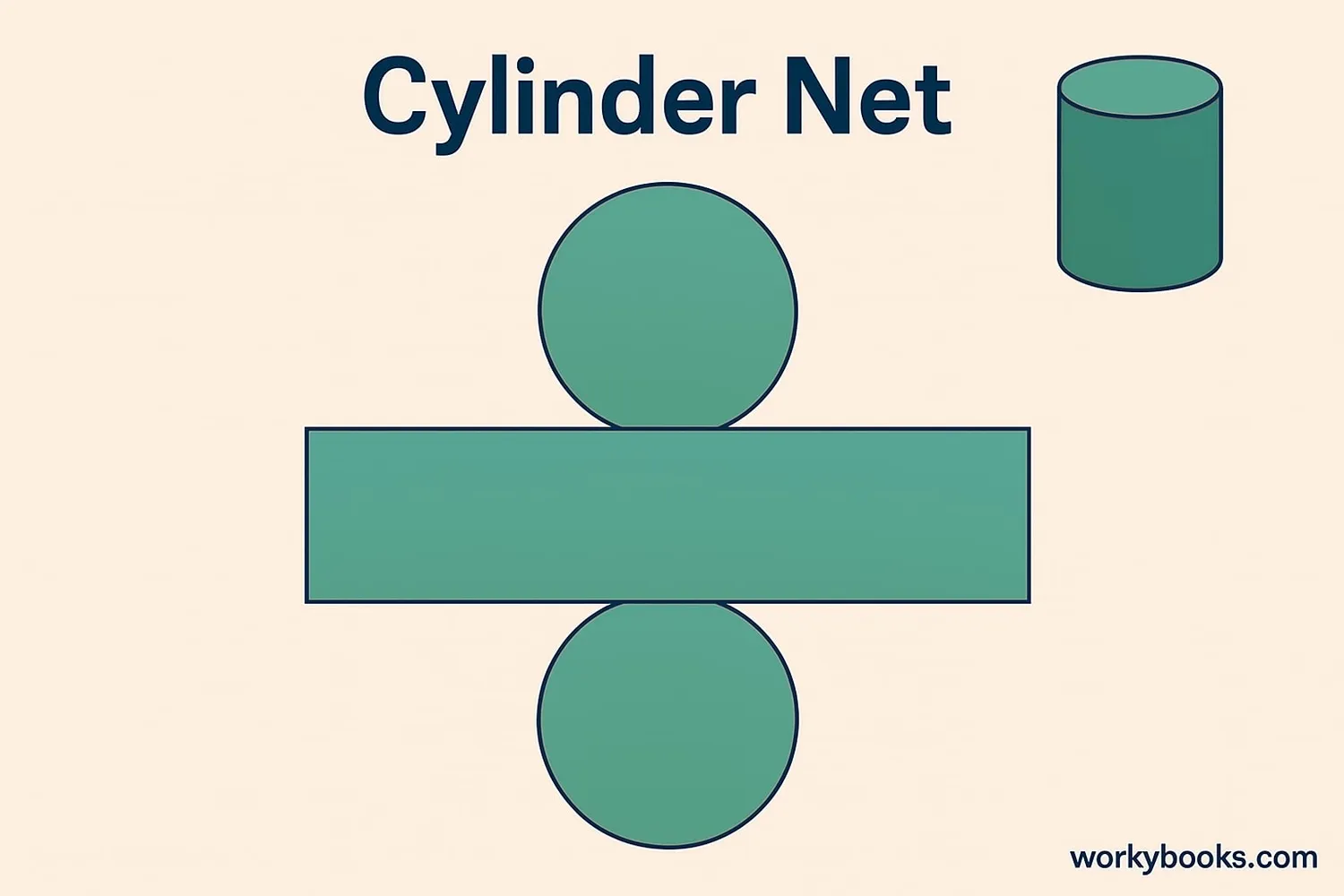
A net is a 2D pattern that can be folded to make a 3D shape. It's like a blueprint for creating the shape!
Nets help us understand how a 3D shape is put together. Each net shows all the faces of the shape arranged flat.
Examples:
- A cube net has 6 squares arranged in different patterns
- A pyramid net has a polygon base with triangles attached to each side
- A cylinder net has a rectangle and two circles
You can print nets, cut them out, fold along the edges, and tape them together to make 3D models!
Try This
Draw your own net for a rectangular prism. How many rectangles do you need? How would they connect?
3D Shapes Quiz
Test your knowledge of 3D shapes with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about 3D shapes:
Shape Trivia
Discover interesting facts about 3D shapes:
Nature's Shapes
Honeybees use hexagons to build their honeycombs because this shape uses the least amount of wax to hold the most honey. Hexagons fit together perfectly with no wasted space!
Atomic Shapes
In chemistry, the carbon atoms in a diamond form a tetrahedral shape. This strong 3D structure makes diamonds the hardest natural material on Earth!
Ancient Architecture
The Great Pyramid of Giza is the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. It was originally covered in smooth white limestone casing stones that formed a perfect pyramid shape.
Planetary Shapes
While planets appear spherical, they're actually slightly flattened at the poles due to rotation. This shape is called an oblate spheroid, making Earth about 43km wider at the equator than pole-to-pole.





