Adding and Subtracting Decimals - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Master decimal operations with step-by-step methods, examples, and practice activities
Understanding Decimals
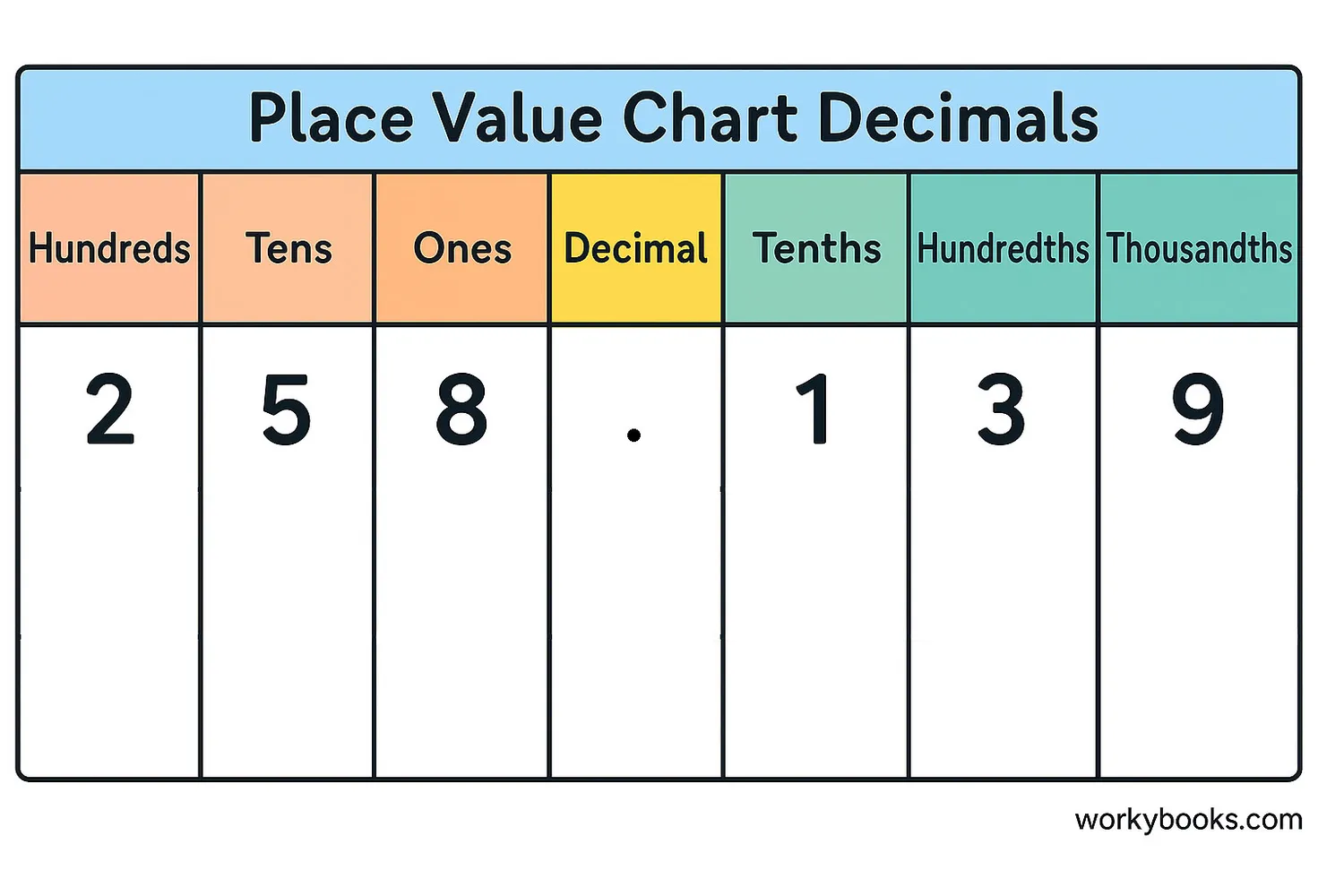
Decimals are numbers that include a whole number part and a fractional part separated by a decimal point. The decimal point is the dot (.) that separates the whole number from the fractional part. For example, in the number 15.75:
15 is the whole number part
75 is the fractional part (representing 75 hundredths)
Decimals help us represent numbers that are not whole, such as measurements, money amounts, and quantities that are between whole numbers. Understanding place value is crucial for working with decimals:
| Tens | Ones | Decimal Point | Tenths | Hundredths | Thousandths |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | . | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | . | 2 | 5 | ||
| 7 | . | 0 | 8 | 3 |
Key Concept
The decimal point separates the whole number part from the fractional part. Each place to the right of the decimal point is ten times smaller than the place to its left.
Adding Decimals

Adding decimals is similar to adding whole numbers, but with one important rule: always align the decimal points. This ensures that you're adding digits in the same place value positions. Here are the steps:
Example: Add 3.25 + 1.4
Step 1: Write vertically with decimal points aligned:
3.25
+ 1.40 (added a zero to make both have two decimal places)
------
Step 2: Add the numbers:
3.25
+ 1.40
------
4.65
The sum is 4.65
Remember
Adding zeros to the right of the last decimal digit doesn't change the value of the number, but it helps with alignment.
Subtracting Decimals

Subtracting decimals follows the same principles as adding decimals. The key is to align the decimal points and add zeros when needed to make the numbers have the same number of decimal places. Here's how:
Example: Subtract 5.3 - 2.75
Step 1: Write vertically with decimal points aligned (add zero to 5.3):
5.30
- 2.75
------
Step 2: Subtract the numbers (regroup where needed):
5.30
- 2.75
------
2.55
The difference is 2.55
Tip
If the number you're subtracting has more decimal places, add zeros to the number with fewer decimal places before subtracting.
Real-World Examples
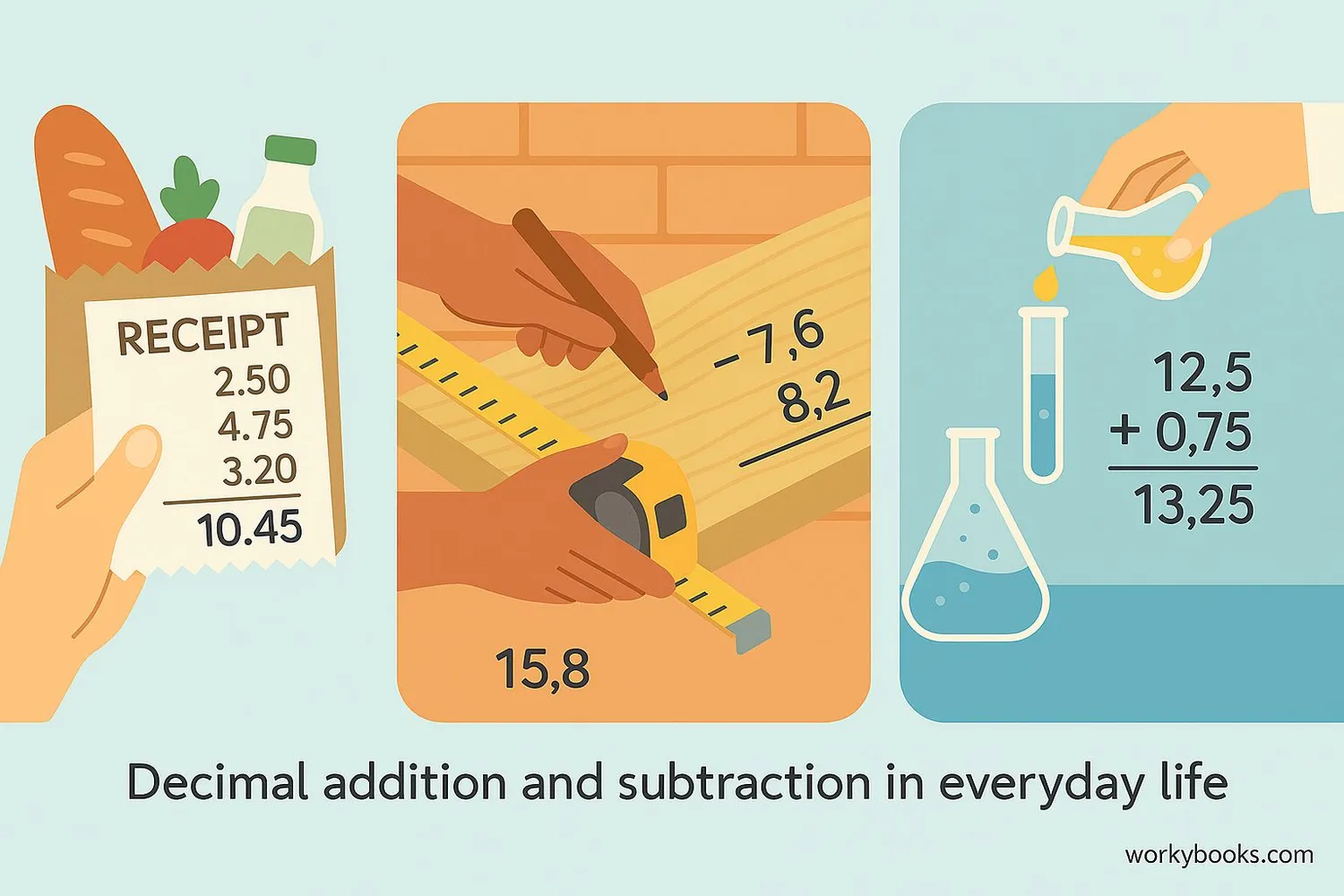
Let's explore some practical examples of adding and subtracting decimals in real-world situations:
Example 1: Money at the Store
Sarah bought a notebook for $3.75 and a pen for $1.25. How much did she spend?
Solution: $3.75 + $1.25 = $5.00
Example 2: Measuring Length
A carpenter cut a 2.5 meter board from a 3.75 meter plank. How much wood remains?
Solution: 3.75m - 2.5m = 1.25m
Example 3: Cooking Measurements
A recipe calls for 0.75 cups of sugar. If Maria already added 0.25 cups, how much more does she need?
Solution: 0.75 cups - 0.25 cups = 0.50 cups
Example 4: Temperature Change
The temperature was 23.5°C in the morning. By afternoon, it rose by 4.75°C. What was the afternoon temperature?
Solution: 23.5°C + 4.75°C = 28.25°C
Practice Tip
Look for decimals around you - in recipes, store prices, measurements, and weather reports. Practice adding and subtracting them!
Decimal Operations Quiz
Test your understanding of adding and subtracting decimals with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about adding and subtracting decimals:
Decimal Trivia
Discover interesting facts about decimals and their history:
Origin of Decimals
Decimal fractions were first developed by Chinese mathematicians in the 4th century BCE and later refined by Arab and Persian mathematicians. The decimal point was introduced by John Napier in the early 17th century.
Decimal Precision
The world record for calculating pi stands at 100 trillion decimal places! Calculating this took 157 days using a powerful computer in 2022.
Space Calculations
NASA uses decimal calculations with up to 15 decimal places for spacecraft navigation. A tiny error in decimal calculation could send a spacecraft millions of miles off course!
Decimal in Daily Life
About 90% of countries use decimal currency systems. The US decimalized its currency in 1792 with the Coinage Act, establishing dollars and cents.





