Area of Trapezium - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn to calculate the area of trapezoids with step-by-step guides, visual examples, and practice activities
What is a Trapezium?
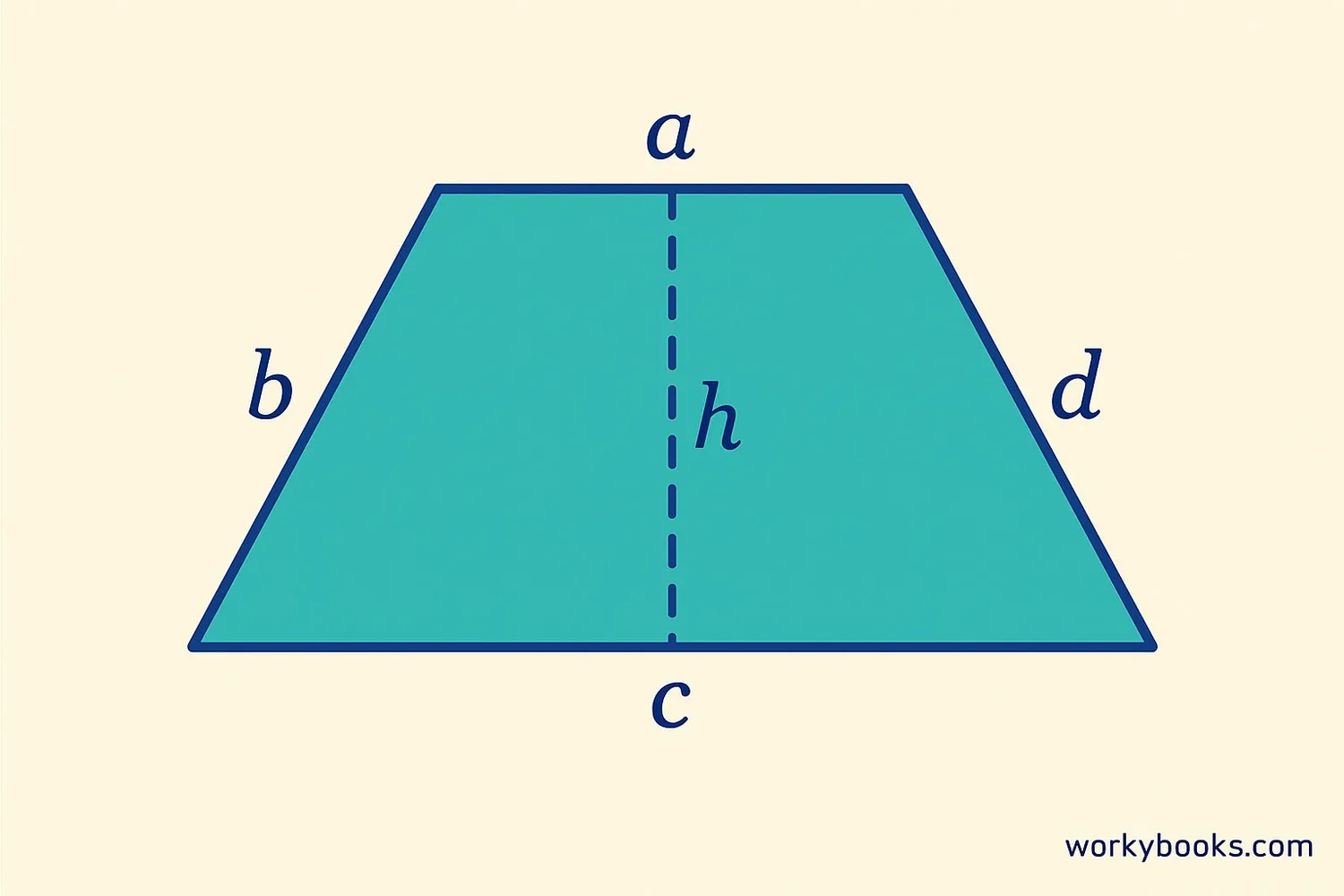
A trapezium (also called a trapezoid in some countries) is a special quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides. The parallel sides are called the bases of the trapezium, while the non-parallel sides are called the legs.
Important properties of a trapezium:
- It has four sides and four angles
- One pair of opposite sides is parallel
- The sum of all interior angles is always 360 degrees
- It can have zero or two right angles
Trapeziums are all around us! You can find them in bridges, tabletops, and even in the shape of some handbags.
Key Concept
The defining feature of a trapezium is that it has exactly one pair of parallel sides. These parallel sides are the bases.
Area Formula
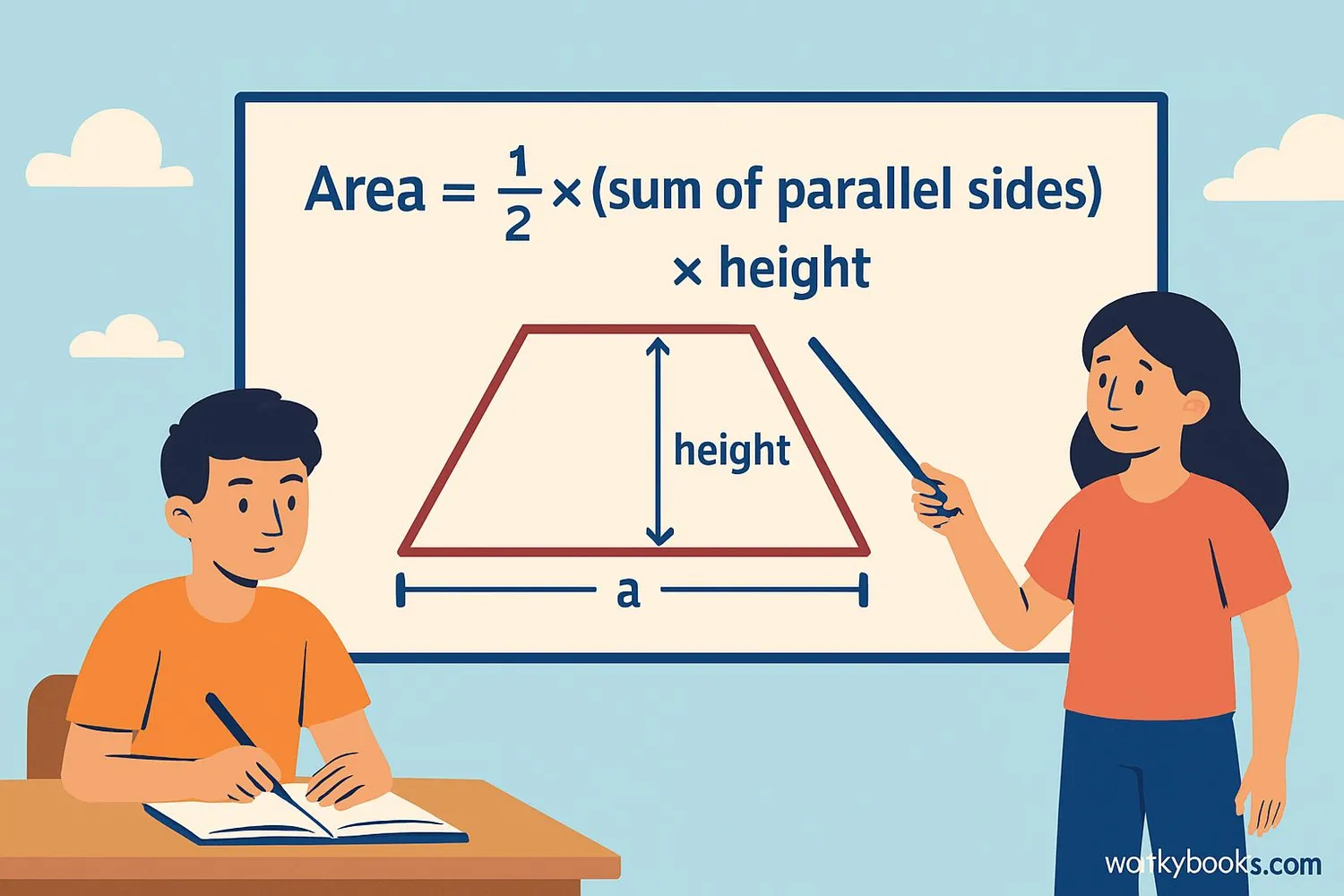
The area of a trapezium can be calculated using a simple formula:
Area Formula
Where:
a = length of first parallel side
c = length of second parallel side
h = perpendicular height between parallel sides
Remember
The height must be the perpendicular distance between the parallel sides, not the length of the slanted sides.
How to Calculate Area
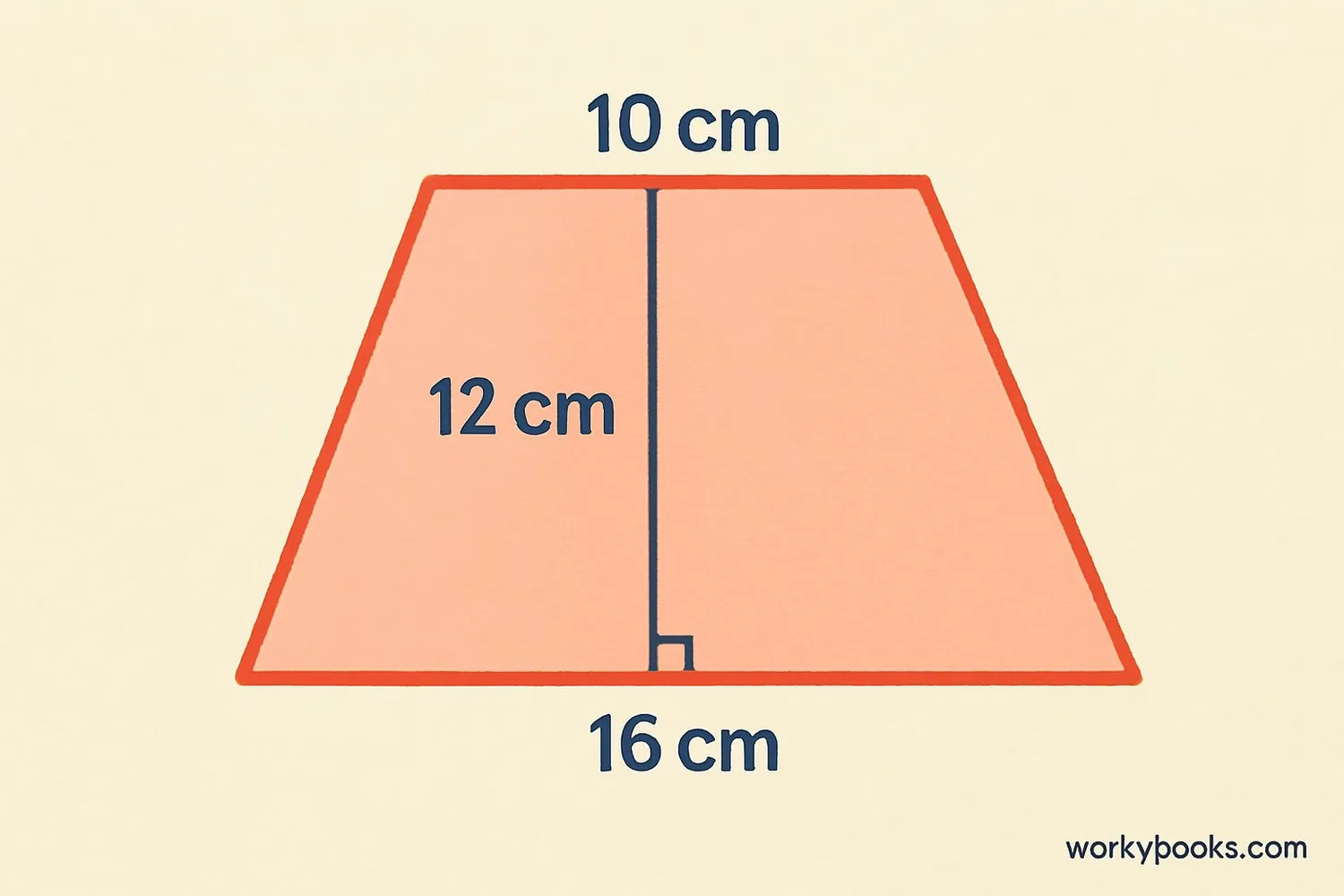
Follow these steps to calculate the area of a trapezium:
Example Calculation:
For a trapezium with parallel sides 10cm and 16cm, and height 12cm:
Step 1: a = 10cm, c = 16cm, h = 12cm
Step 2: a + c = 10 + 16 = 26cm
Step 3: (a + c) × h = 26 × 12 = 312
Step 4: Area = 312 ÷ 2 = 156 cm²
Calculation Tip
Always remember to divide by 2 at the end. A common mistake is to forget this step!
Real-World Examples
Let's practice with some real-world examples:
Example 1: A trapezoidal garden bed has parallel sides of 8m and 12m, with a height of 5m. What is its area?
Solution: Area = ½ × (8 + 12) × 5 = ½ × 20 × 5 = 50 m²
Example 2: A trapezium-shaped tile has parallel sides of 15cm and 20cm, and a height of 10cm. What is its area?
Solution: Area = ½ × (15 + 20) × 10 = ½ × 35 × 10 = 175 cm²
Example 3: A running track has a trapezium section with bases 100m and 80m, and height 50m. What area does this section cover?
Solution: Area = ½ × (100 + 80) × 50 = ½ × 180 × 50 = 4,500 m²
Example 4: A kite is shaped like a trapezium with parallel sides 40cm and 60cm, and height 70cm. What is its area?
Solution: Area = ½ × (40 + 60) × 70 = ½ × 100 × 70 = 3,500 cm²
Practice finding trapezium shapes around you - tabletops, buildings, or even pieces of pizza!
Real-World Tip
When measuring real objects, make sure you're measuring the perpendicular height, not the slanted side.
Practice Quiz
Test your understanding with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about trapeziums:
Math Trivia
Discover interesting facts about trapeziums:
Ancient Origins
The word "trapezium" comes from the Greek word "trapezion" meaning "a little table". Ancient Greek mathematicians studied trapezium properties over 2000 years ago.
Structural Strength
Trapezium shapes are commonly used in bridges and roof designs because they distribute weight efficiently. Many modern buildings use trapezium-shaped supports.
3D Shapes
When trapeziums are rotated in space, they form interesting 3D shapes called trapezoidal prisms. These are used in packaging and architecture.
In Nature
Trapezium shapes appear in nature too! Some crystals, leaves, and even the wings of certain butterflies form natural trapeziums.





