Commutative Property - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn how numbers can change order but keep the same value in addition and multiplication
What is the Commutative Property?
The commutative property is a special rule in math that says: When you add or multiply numbers, you can change their order and still get the same answer!
Think of it like swapping seats with a friend - even though you changed places, you're both still in the same classroom. The commutative property works for addition and multiplication, but not for subtraction or division.
For example, 4 + 6 is the same as 6 + 4. Both equal 10! And 3 × 5 is the same as 5 × 3. Both equal 15!
Key Concept
The commutative property means: Order doesn't matter when adding or multiplying!
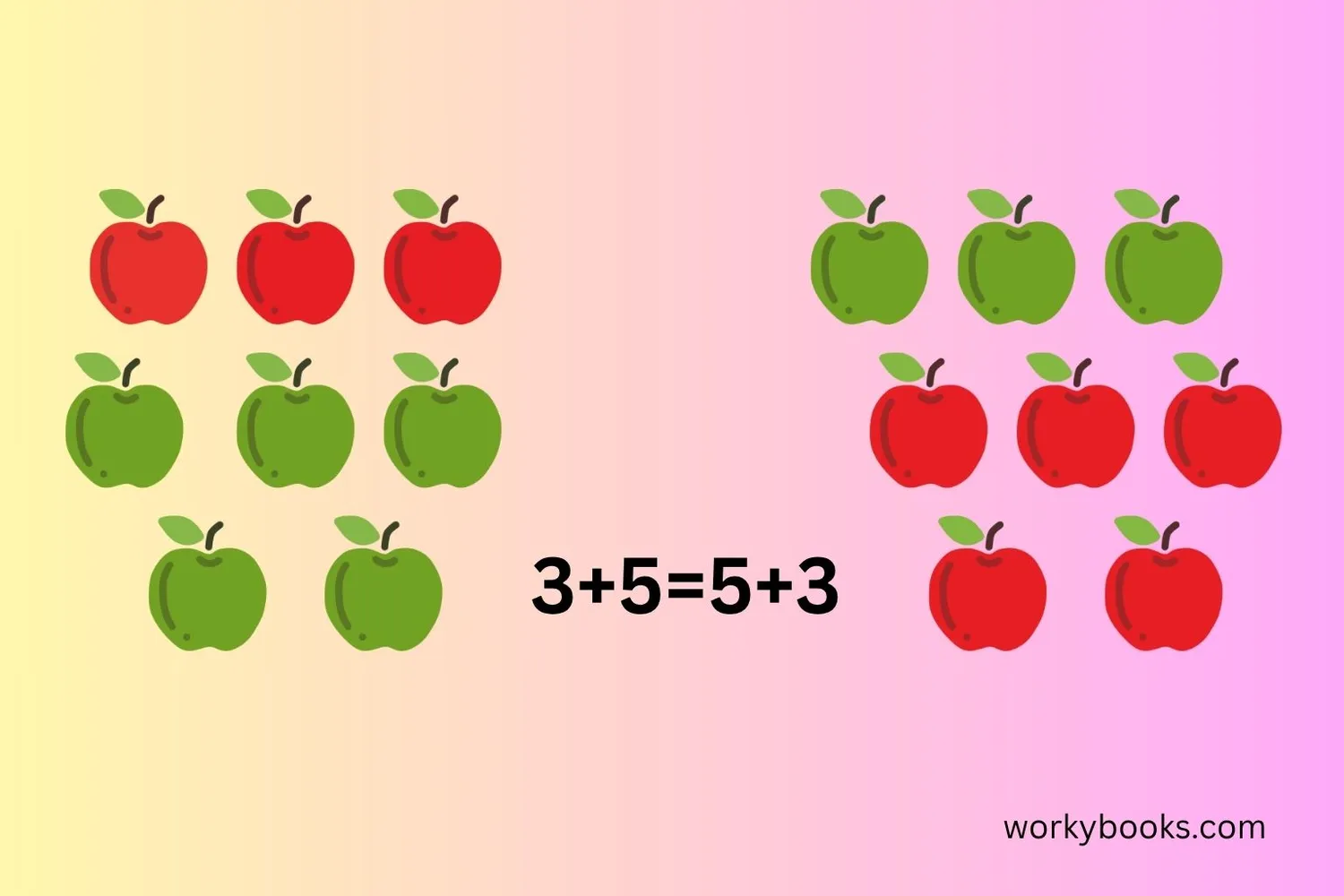
Commutative Property of Addition
The commutative property of addition tells us that when we add numbers, the order doesn't matter. You can add numbers in any sequence and still get the same total!
Commutative Property of Addition
No matter what numbers you use for a and b, the sum will always be the same!
Example 1
Example 2
Both equal 38! The numbers changed places, but the sum stayed the same.
Remember
This property only works for addition. For subtraction: 7 - 4 is not the same as 4 - 7!
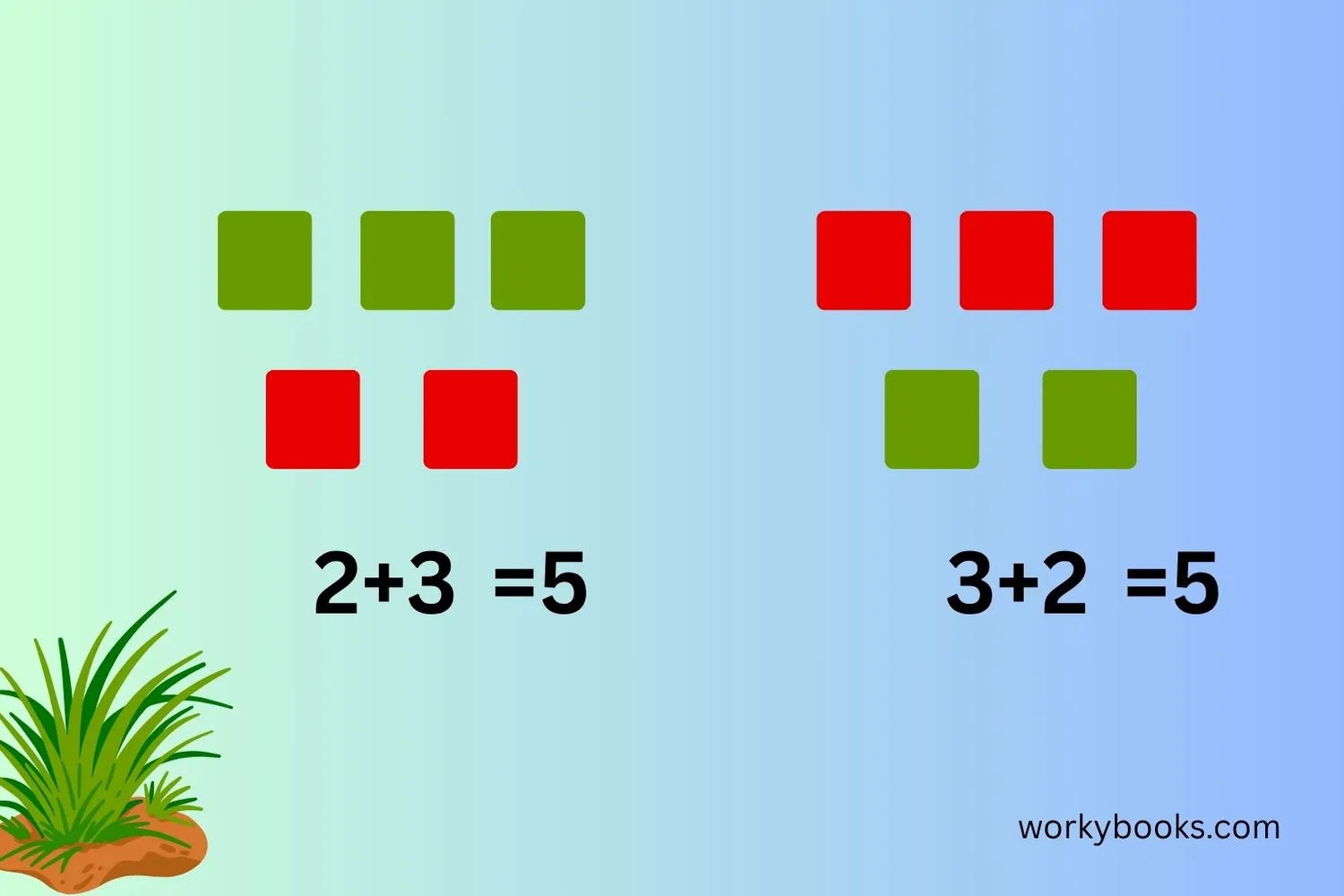
Commutative Property of Multiplication
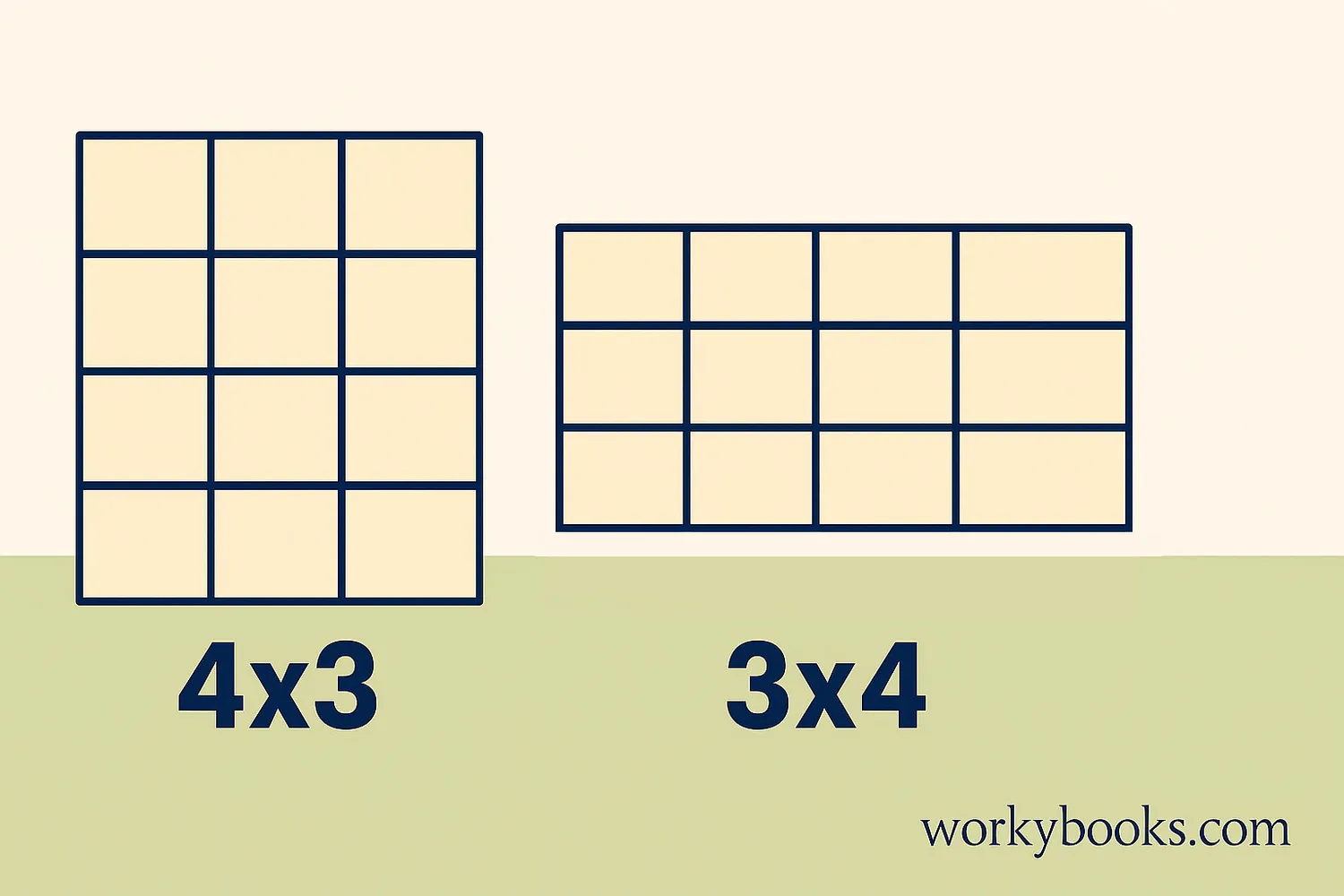
Just like with addition, the commutative property works for multiplication too! When you multiply numbers, changing the order doesn't change the product.
Commutative Property of Multiplication
No matter what numbers you use for a and b, the product will always be the same!
Example 1
Example 2
Both equal 48! Changing the order doesn't change the result.
Remember
This property only works for multiplication. For division: 12 ÷ 4 is not the same as 4 ÷ 12!
Comparing Math Properties
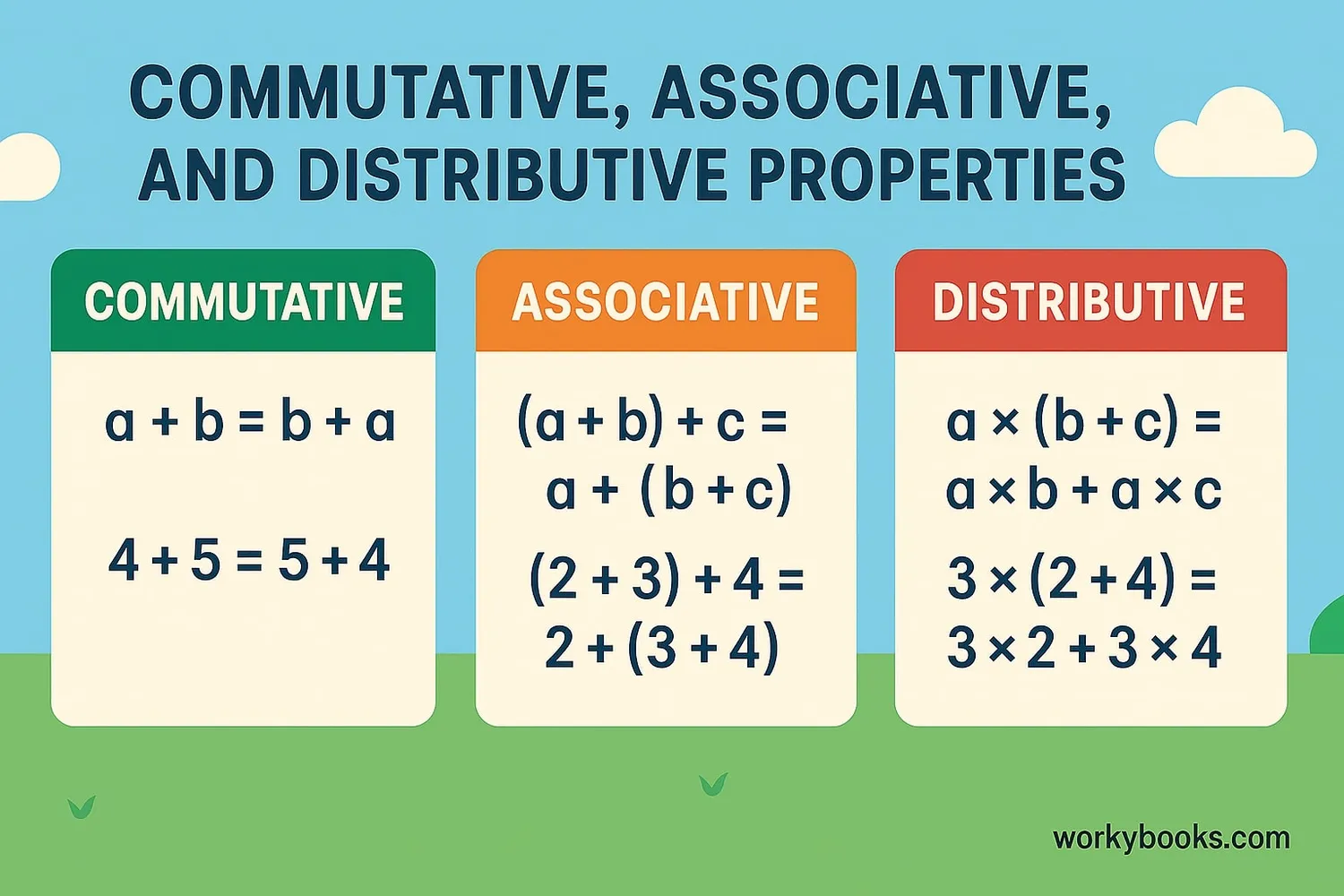
The commutative property is just one of several important math properties. Let's compare it to the associative and distributive properties:
| Property | Meaning | Works With | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commutative | Changing order of numbers | Addition, Multiplication | 8 + 5 = 5 + 8 |
| Associative | Changing grouping of numbers | Addition, Multiplication | (2 + 3) + 4 = 2 + (3 + 4) |
| Distributive | Multiplying over addition | Multiplication over Addition | 3 × (4 + 5) = (3×4) + (3×5) |
Key Difference
Commutative = Changing order of numbers
Associative = Changing grouping of numbers
Distributive = Combining multiplication and addition
Real-World Examples

The commutative property isn't just for math class - we use it in everyday life too! Here are some real-world examples:
Example 1: Money
When counting coins, order doesn't matter:
Both equal 35 cents! (15¢ from nickels + 20¢ from dimes)
Example 2: Seating Arrangements
When arranging chairs, the total number stays the same:
Both arrangements have 30 chairs!
Example 3: Baking Cookies
When making cookies, adding ingredients:
The order you add dry ingredients doesn't change the total amount!
Remember
Look for the commutative property when you see situations where order doesn't affect the outcome!
Commutative Property Quiz
Test your understanding with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about the commutative property:
Math Property Trivia
Discover interesting facts about math properties:
Ancient Discovery
The commutative property was recognized as early as ancient Egypt and Babylon. Egyptian mathematicians used it in their calculations for building pyramids!
Beyond Numbers
The commutative property applies to other mathematical concepts too! For example, rotating an object 90° left then 90° up gives the same result as 90° up then 90° left.
Not Always True
In advanced mathematics, some operations are not commutative. Matrix multiplication and quaternion multiplication are examples where order matters!
Daily Use
You use the commutative property every time you add numbers in a different order to make calculation easier. For example: 7 + 8 + 3 = (7 + 3) + 8 = 10 + 8 = 18.





