Commutative Property of Addition - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn how numbers can be added in any order without changing the result
What is Commutative Property?
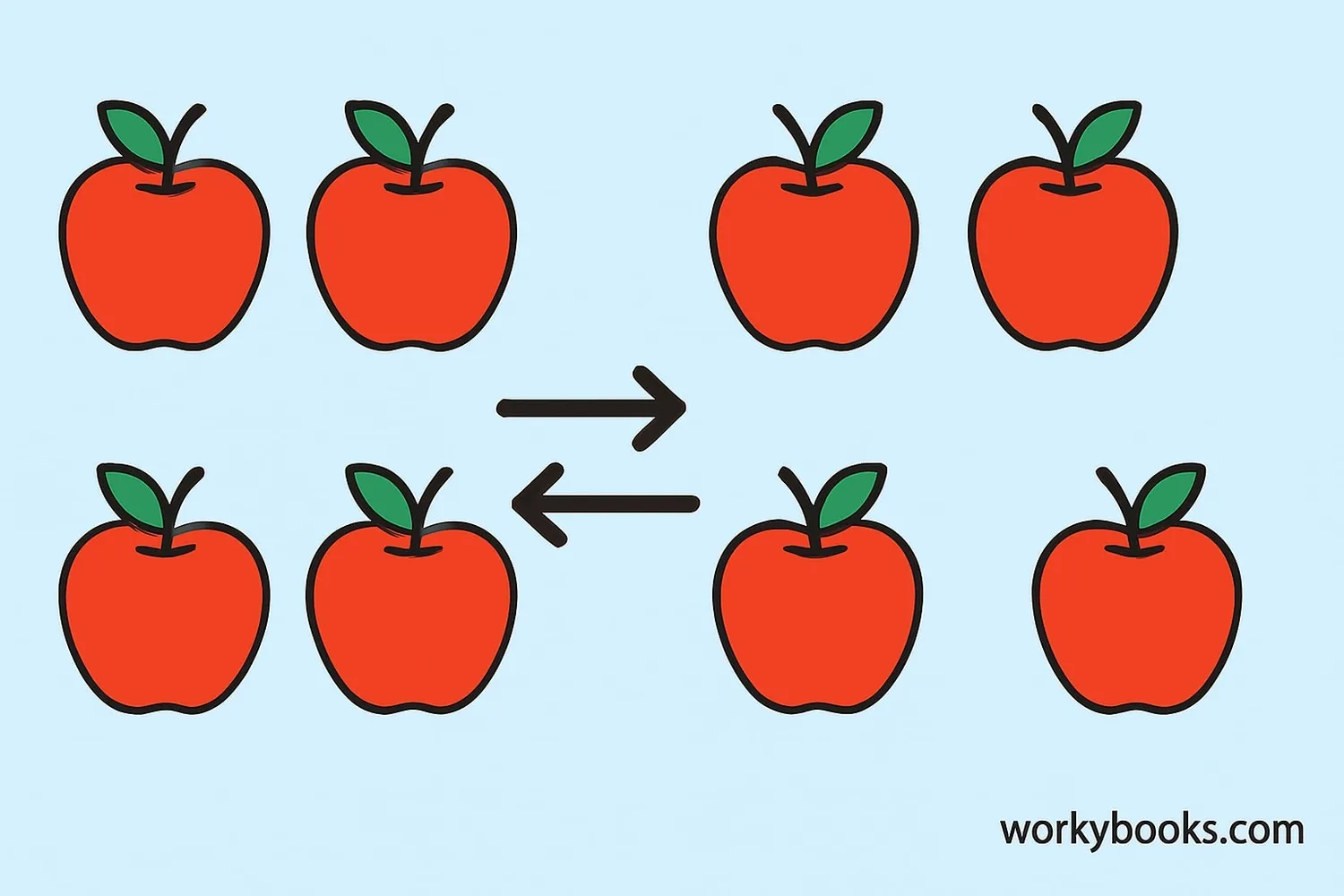
The commutative property is a fundamental rule in mathematics that tells us we can change the order of numbers when adding or multiplying without changing the result.
For addition, this means that a + b = b + a. No matter which number comes first, the sum will always be the same.
This property only works for addition and multiplication. It does not work for subtraction or division. Understanding this property helps us solve math problems more efficiently and recognize patterns in numbers.
Key Concept
The commutative property allows us to rearrange numbers when adding or multiplying without changing the final result.
Commutative Property of Addition
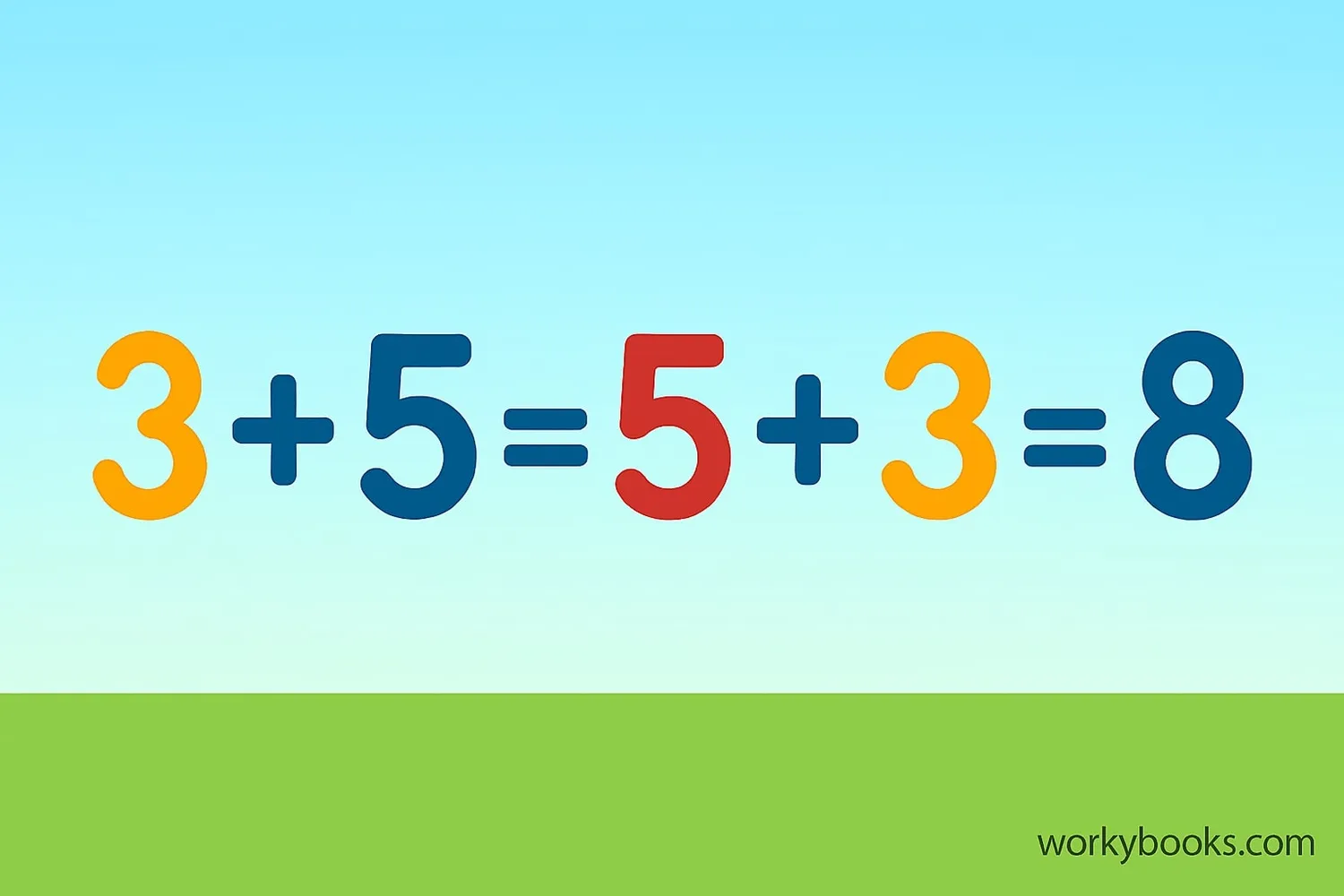
The commutative property of addition states that when adding numbers, the order doesn't matter. The sum remains the same regardless of how we arrange the numbers.
Commutative Property Formula
Numbers can be added in any order without changing the sum
Example 1
4 + 7 = 11
7 + 4 = 11
Same result!
Example 2
15 + 23 = 38
23 + 15 = 38
Same result!
Example 3
125 + 75 = 200
75 + 125 = 200
Same result!
Remember
This property works with any numbers - whole numbers, decimals, fractions, and even negative numbers!
Commutative Property of Multiplication
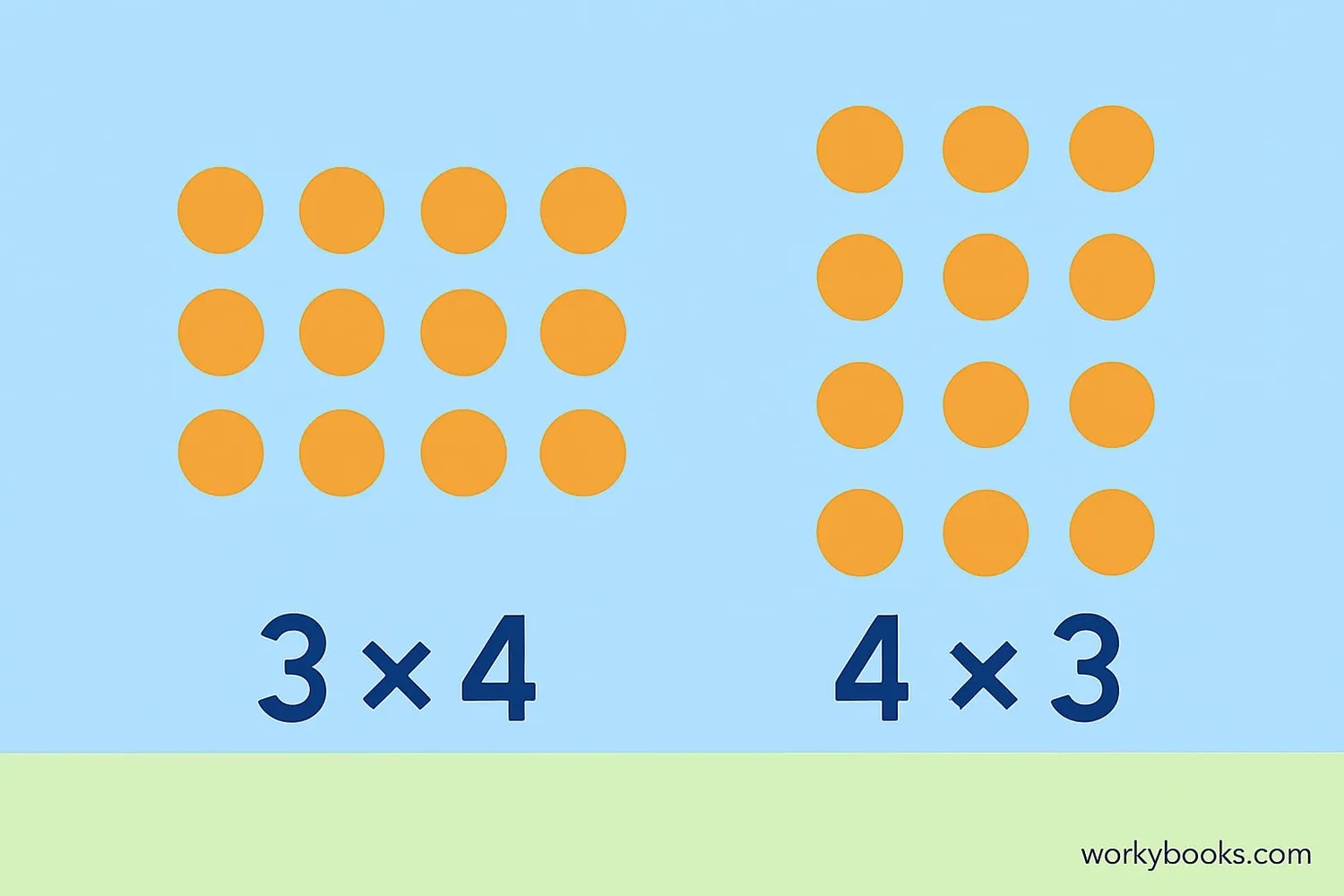
Just like addition, multiplication also follows the commutative property. This means that when multiplying numbers, the order doesn't affect the product.
Commutative Property Formula
Numbers can be multiplied in any order without changing the result
Example 1
5 × 6 = 30
6 × 5 = 30
Same product!
Example 2
8 × 12 = 96
12 × 8 = 96
Same product!
Example 3
25 × 4 = 100
4 × 25 = 100
Same product!
Remember
The commutative property for multiplication works for all numbers, just like with addition.
Non-Commutative Operations
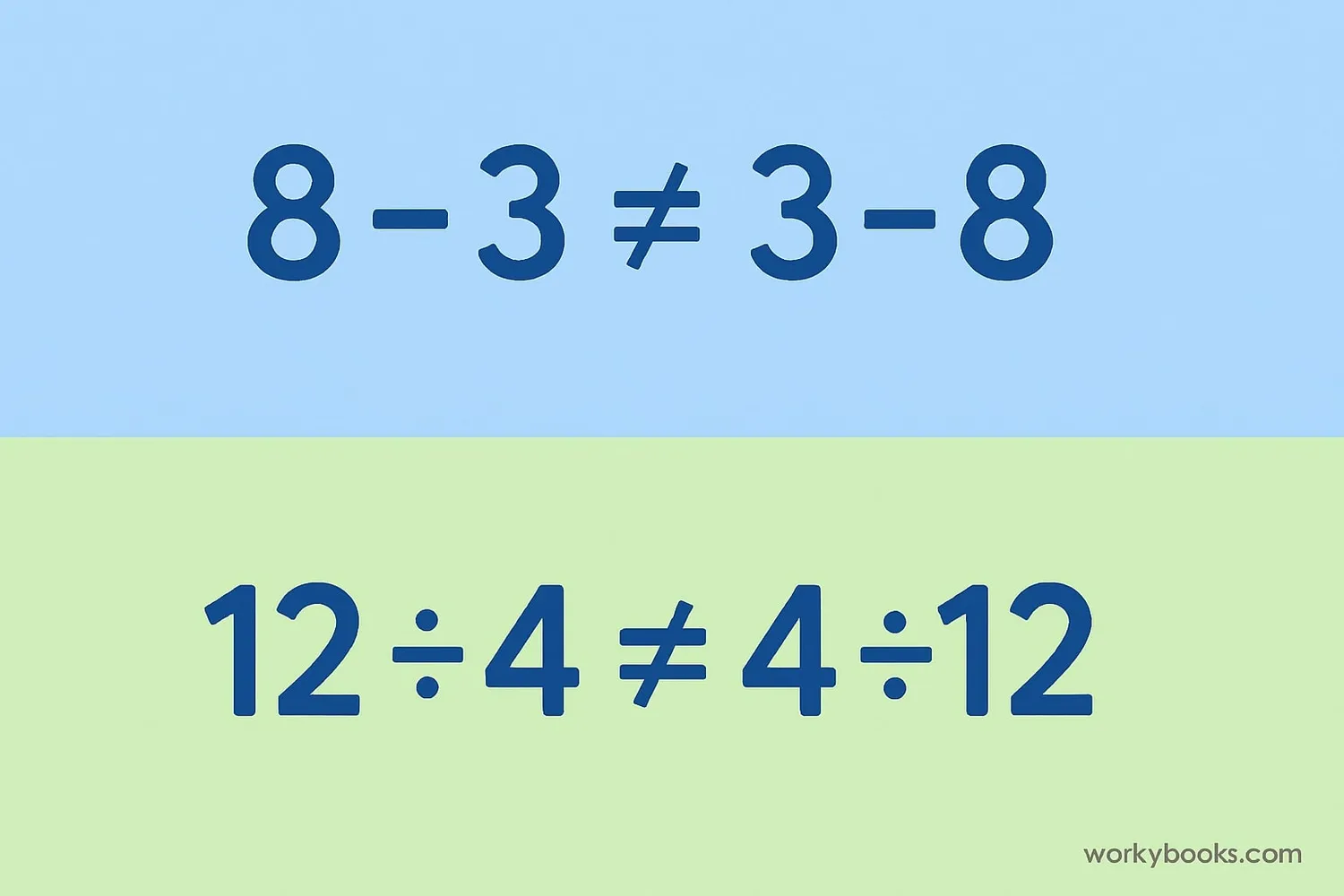
While addition and multiplication are commutative, subtraction and division are not. Changing the order of numbers in subtraction or division changes the result.
For subtraction: a - b ≠ b - a (unless a = b)
For division: a ÷ b ≠ b ÷ a (unless a = b or a = 0)
Here are some examples:
| Operation | Original | Reversed | Commutative? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Addition | 7 + 3 = 10 | 3 + 7 = 10 | Yes |
| Multiplication | 5 × 4 = 20 | 4 × 5 = 20 | Yes |
| Subtraction | 9 - 2 = 7 | 2 - 9 = -7 | No |
| Division | 12 ÷ 3 = 4 | 3 ÷ 12 = 0.25 | No |
Important Note
Always remember that subtraction and division are not commutative. The order matters in these operations!
Other Mathematical Properties
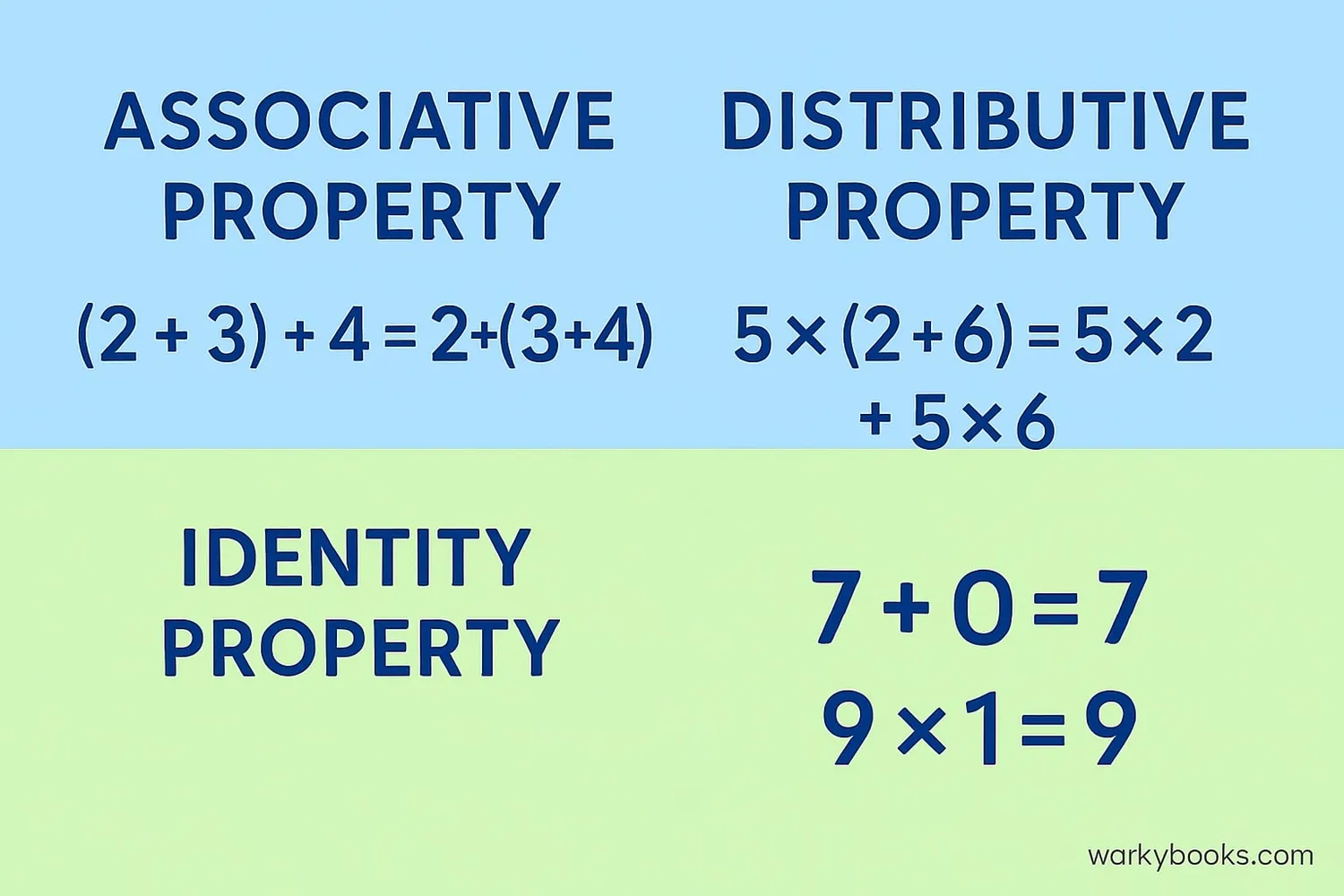
Besides the commutative property, there are other important properties in mathematics:
Associative Property
When adding or multiplying three or more numbers, the way we group them doesn't change the result.
Addition: (a + b) + c = a + (b + c)
Multiplication: (a × b) × c = a × (b × c)
Distributive Property
Multiplying a number by a sum is the same as multiplying by each addend and adding the products.
Formula: a × (b + c) = (a × b) + (a × c)
Example: 3 × (4 + 5) = 3×4 + 3×5 = 12 + 15 = 27
Identity Property
Addition: Adding zero to any number doesn't change its value (a + 0 = a)
Multiplication: Multiplying any number by one doesn't change its value (a × 1 = a)
Remember
Each property has specific rules that help us understand how numbers behave in different operations.
Commutative Property Quiz
Test your understanding with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about the commutative property:
Math Properties Trivia
Discover interesting facts about mathematical properties:
Historical Origins
The commutative property was first recognized by ancient Egyptian and Babylonian mathematicians around 1800 BCE, but it was formally named and studied by mathematicians in the 19th century.
Beyond Numbers
The commutative property applies to other mathematical concepts too! For example, in set theory, the union of sets is commutative: A ∪ B = B ∪ A.
Matrix Exception
Matrix multiplication is generally not commutative. For matrices A and B, A×B usually doesn't equal B×A. This is why the commutative property doesn't apply to all mathematical operations.
Real-Life Application
When putting on shoes and socks, the order matters (socks then shoes). This is a non-commutative operation in real life! But adding money to your piggy bank is commutative - the order doesn't matter.





