Decimal to Binary - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn to convert between decimal and binary numbers with easy explanations and practice activities
What is Binary?
Binary is a number system that uses only two digits: 0 and 1. This is different from the decimal system we use every day which has ten digits (0-9).
Computers use binary because they work with electrical signals that can be either on (1) or off (0). Each binary digit is called a bit, and 8 bits make a byte.
Converting decimal (regular numbers) to binary helps us understand how computers store and process information. It's like learning a secret code that computers use!
Key Concept
Binary uses only two digits: 0 and 1. Each position in a binary number represents a power of 2, just like each position in a decimal number represents a power of 10.
How to Convert Decimal to Binary
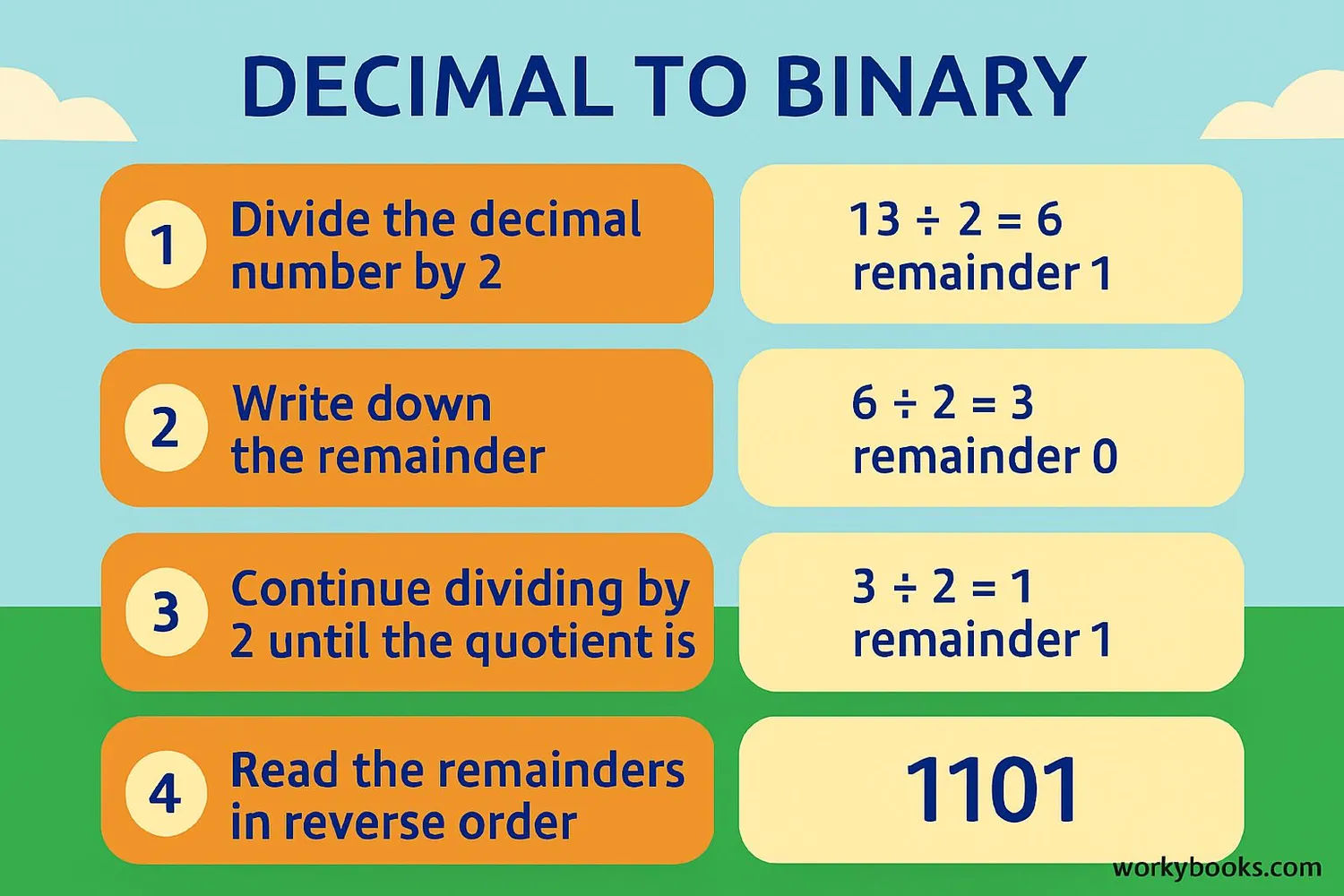
Here's how to convert decimal numbers to binary using the division-by-2 method:
Conversion Method
- Divide the decimal number by 2
- Write down the remainder (0 or 1)
- Divide the quotient by 2 again
- Repeat until the quotient is 0
- The binary number is the remainders read from bottom to top
Example: Convert 13 to binary
Step 1: 13 ÷ 2 = 6 with remainder 1
Step 2: 6 ÷ 2 = 3 with remainder 0
Step 3: 3 ÷ 2 = 1 with remainder 1
Step 4: 1 ÷ 2 = 0 with remainder 1
Now read the remainders from bottom to top: 1101
So 13 in decimal is 1101 in binary!
Remember
Always write the remainders from bottom to top to get the correct binary number.
Decimal to Binary Conversion Charts
Conversion charts help us quickly find binary equivalents without calculating each time. Here are two useful charts:
Basic Decimal to Binary Conversion Chart
| Decimal | Binary |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 10 |
| 3 | 11 |
| 4 | 100 |
| 5 | 101 |
| 6 | 110 |
| 7 | 111 |
| 8 | 1000 |
| 9 | 1001 |
| 10 | 1010 |
Powers of 2 Reference Chart
| Power of 2 | Decimal Value | Binary Representation |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | 1 | 1 |
| 21 | 2 | 10 |
| 22 | 4 | 100 |
| 23 | 8 | 1000 |
| 24 | 16 | 10000 |
| 25 | 32 | 100000 |
| 26 | 64 | 1000000 |
| 27 | 128 | 10000000 |
Chart Tip
Notice how each new power of 2 adds another zero to the binary representation? This pattern helps with quick conversions!
Real-World Examples

Let's practice conversion with some real-world examples:
Example 1: A computer stores the number 5. What is its binary form?
Solution: 5 ÷ 2 = 2 R1, 2 ÷ 2 = 1 R0, 1 ÷ 2 = 0 R1 → 101
Example 2: Convert your age to binary. If you're 10 years old:
Solution: 10 ÷ 2 = 5 R0, 5 ÷ 2 = 2 R1, 2 ÷ 2 = 1 R0, 1 ÷ 2 = 0 R1 → 1010
Example 3: A pixel uses 8 bits (1 byte) to store color information. What's the largest decimal number that can be stored in 8 bits?
Solution: 28 - 1 = 255 (because binary 11111111 = 255)
Example 4: Convert binary 1101 back to decimal:
Solution: (1×8) + (1×4) + (0×2) + (1×1) = 8 + 4 + 0 + 1 = 13
Practice converting numbers you see around you - your house number, your favorite number, or the time!
Conversion Tip
To convert binary back to decimal, multiply each digit by its place value (powers of 2) and add them up.
Conversion Practice Quiz
Test your conversion skills with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about decimal to binary conversion:
Number System Trivia
Discover interesting facts about number systems:
Ancient Binary
The concept of binary numbers dates back to ancient India (2nd century BCE) where scholar Pingala described binary combinations in poetic meters. The modern binary system was developed by Gottfried Leibniz in 1679.
Computer Memory
Your computer's memory stores everything in binary - from numbers to letters to pictures. A single high-resolution photo might contain millions of binary numbers representing all its pixels!
Space Messages
The Arecibo message sent to space in 1974 used binary code to describe Earth's location, human DNA, and our solar system. It was 1,679 binary digits arranged in a grid.
Binary in Nature
Many things in nature follow binary patterns - like the branching of trees (left/right), the arrangement of leaves on stems, or the way some animal populations grow (each pair produces offspring).





