Descending Order in Math - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn to arrange numbers from largest to smallest with clear explanations and practice activities
What is Descending Order?
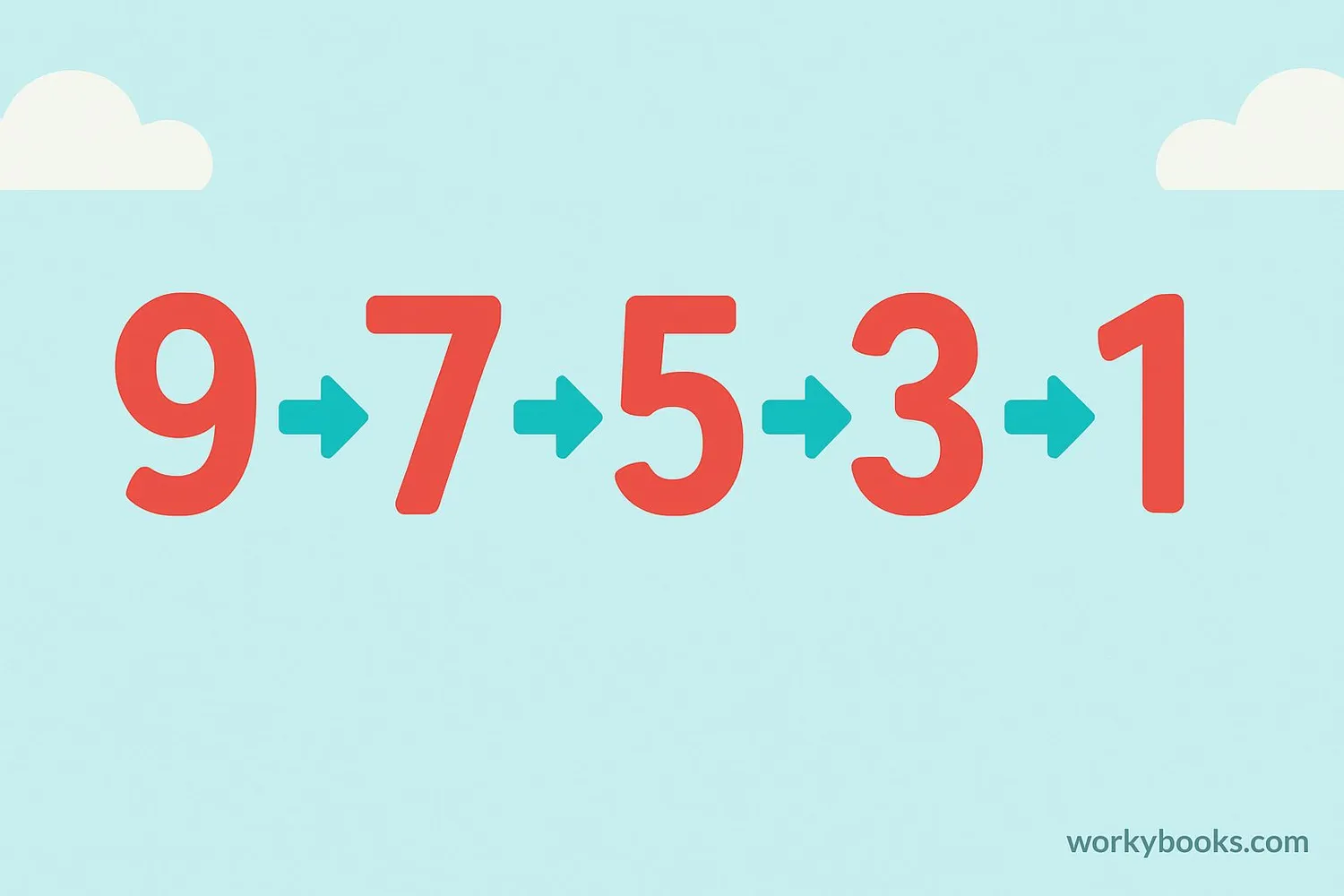
Descending order means arranging numbers from the largest to the smallest. It's like going down stairs - each step is smaller than the one before it.
When we arrange numbers in descending order, we start with the biggest number and end with the smallest. This helps us compare numbers easily and find the highest values quickly.
For example: 10, 8, 6, 4, 2 is in descending order because each number is smaller than the one before it.
Key Concept
Descending order = Largest to smallest. The first number is the biggest, and each following number is smaller.
How to Arrange Numbers in Descending Order

Follow these simple steps to arrange numbers in descending order:
Step 1: Look at all the numbers you need to arrange
Step 2: Find the largest number in the group
Step 3: Write that number first in your new list
Step 4: From the remaining numbers, find the next largest
Step 5: Continue until all numbers are in order
Let's practice with an example:
Arrange these numbers in descending order: 4, 9, 2, 7, 5
Step 1: The largest number is 9 → write it first
Step 2: Next largest is 7 → write it after 9
Step 3: Then comes 5 → add it to the list
Step 4: Next is 4 → add it
Step 5: Finally, 2 → add it last
The descending order is: 9, 7, 5, 4, 2
Remember
When arranging numbers with different place values (like 45, 123, 7), compare digit by digit from left to right.
Example: Arranging 3-digit numbers
Real-World Examples

Descending order is used in many real-life situations. Here are some examples:
Example 1: Race results - Winners are listed from 1st place (fastest time) to last place
Example 2: Test scores - Students might be ranked from highest score to lowest
Example 3: Product prices - Stores often show the most expensive items first
Example 4: Building floors - The top floor has the highest number
Let's practice with some number examples:
Example A: Arrange these numbers in descending order: 12, 5, 8, 15, 3
Solution: 15, 12, 8, 5, 3
Example B: Put these numbers in descending order: 45, 67, 23, 89, 12
Solution: 89, 67, 45, 23, 12
Example C: Which set is in descending order?
a) 10, 20, 30, 40 b) 40, 30, 20, 10
Solution: b) 40, 30, 20, 10
Practice Tip
When working with decimals, compare the whole number parts first. If they're equal, compare the decimal parts.
Practice Quiz
Test your understanding with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about descending order:
Number Trivia
Discover interesting facts about numbers and ordering:
Ancient Number Systems
The concept of ordering numbers dates back to ancient civilizations. The Egyptians and Babylonians used number systems that allowed them to arrange quantities from largest to smallest for trade and construction.
Computer Sorting
Computers use special algorithms to sort data in descending order. The fastest sorting algorithms can arrange millions of numbers in seconds by comparing and rearranging them efficiently.
World Records
The Guinness Book of World Records often lists achievements in descending order - from the tallest buildings to the fastest runners. This helps people quickly see the most impressive records.
Infinite Numbers
In mathematics, you can have infinite descending sequences of numbers that keep getting smaller but never stop. For example: 1, 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, 1/5, ... keeps going forever towards zero.





