Equal Sign - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about the equal sign symbol, its meaning in equations, and how to use it correctly
What is the Equal Sign?
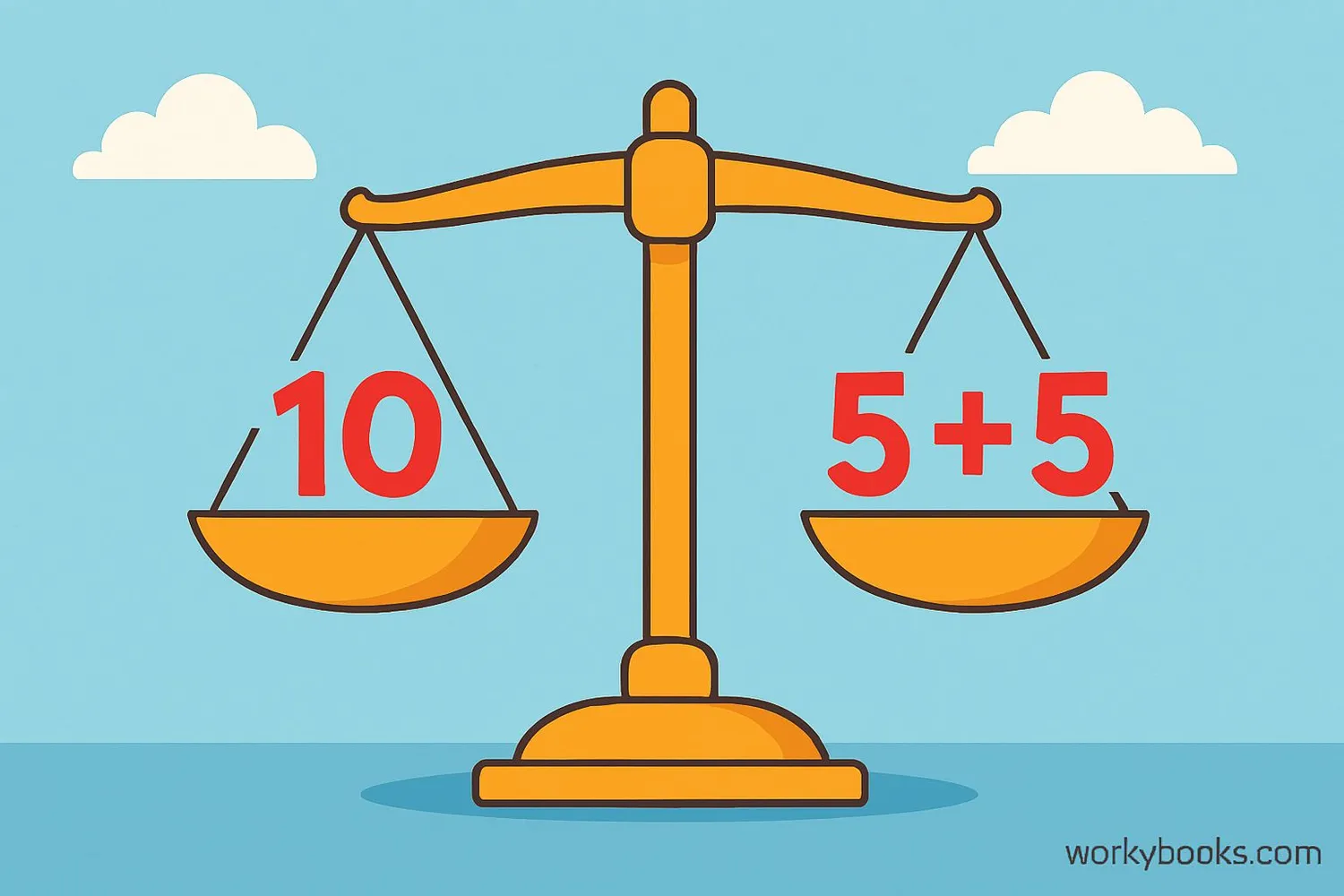
The equal sign (=) is a mathematical symbol used to show that two expressions have the same value. It tells us that what is on the left side of the sign has the exact same value as what is on the right side.
Think of the equal sign as a balance. When you see 3 + 2 = 5, it means that 3 + 2 balances perfectly with 5. They are equal in value.
The equal sign is one of the most important symbols in mathematics because it helps us show relationships between numbers and expressions. It's like a bridge connecting two ideas that have the same value.
Key Concept
The equal sign means "is the same as" or "has the same value as." It does not mean "the answer is coming."
The Equal Sign Symbol
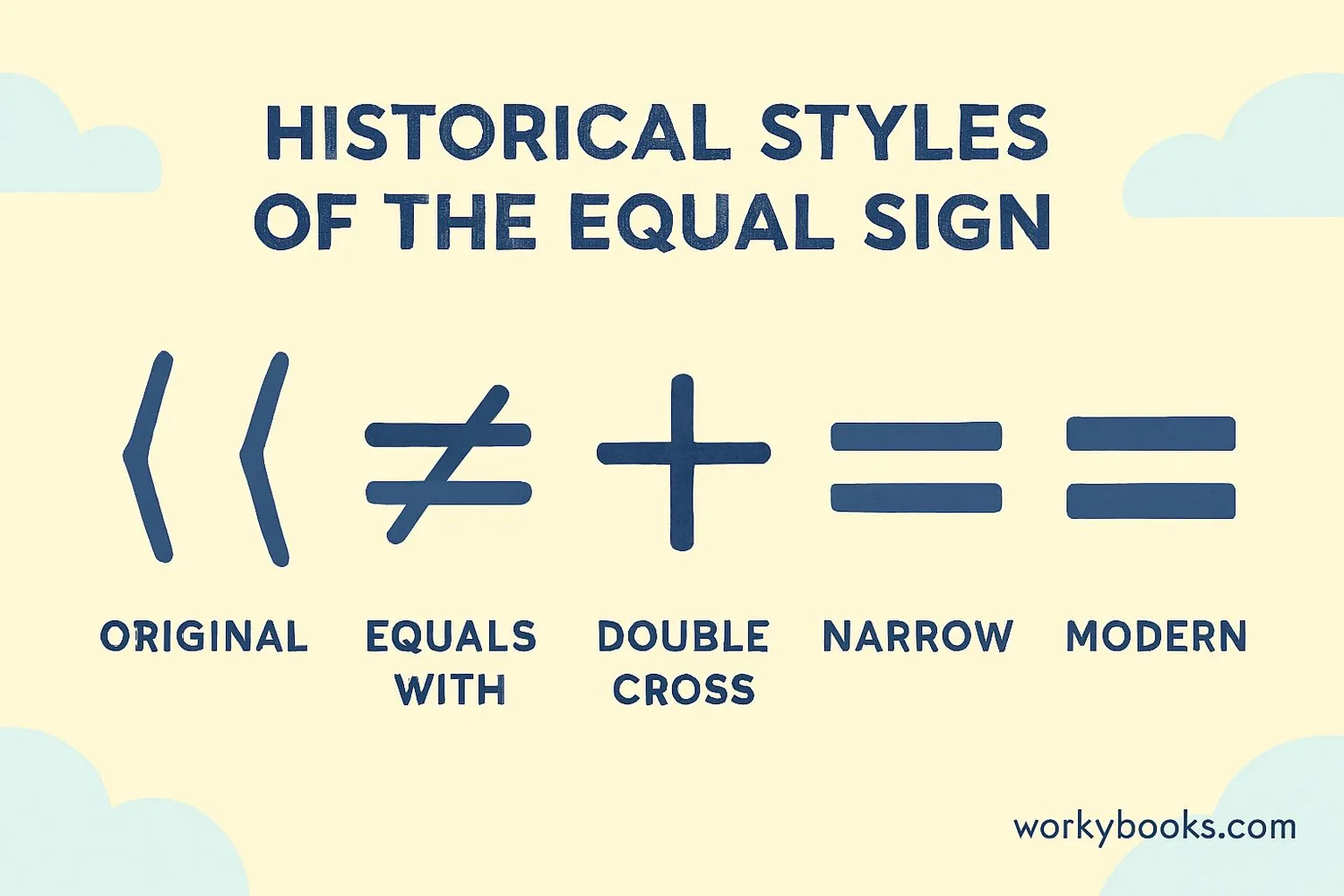
The equal sign is made up of two parallel horizontal lines of equal length: =. This simple but powerful symbol was invented over 400 years ago.
The two lines in the equal sign are always the same length and are parallel to each other. This design visually represents the idea of balance and equality between two things.
In handwriting and some fonts, the equal sign might look slightly different, but it always keeps its basic form of two parallel lines. In mathematics, consistency is important, so the equal sign always means the same thing no matter how it's written.
Remember
The equal sign always consists of two parallel horizontal lines of equal length. This design represents balance between two equal values.
The Equal Sign in Equations
In equations, the equal sign connects two expressions that have the same value. Here are some examples:
Simple Equations
All these expressions equal 8, showing different ways to represent the same value.
At the end: 2 + 3 = 5
In the middle: 4 + 1 = 3 + 2
At the beginning: 7 = 3 + 4
No matter where it appears, the equal sign always means that the values on both sides are the same.
Equation Tip
You can think of the equal sign as a balance point. Whatever is on the left must equal whatever is on the right.
The Equal Sign with Three Lines
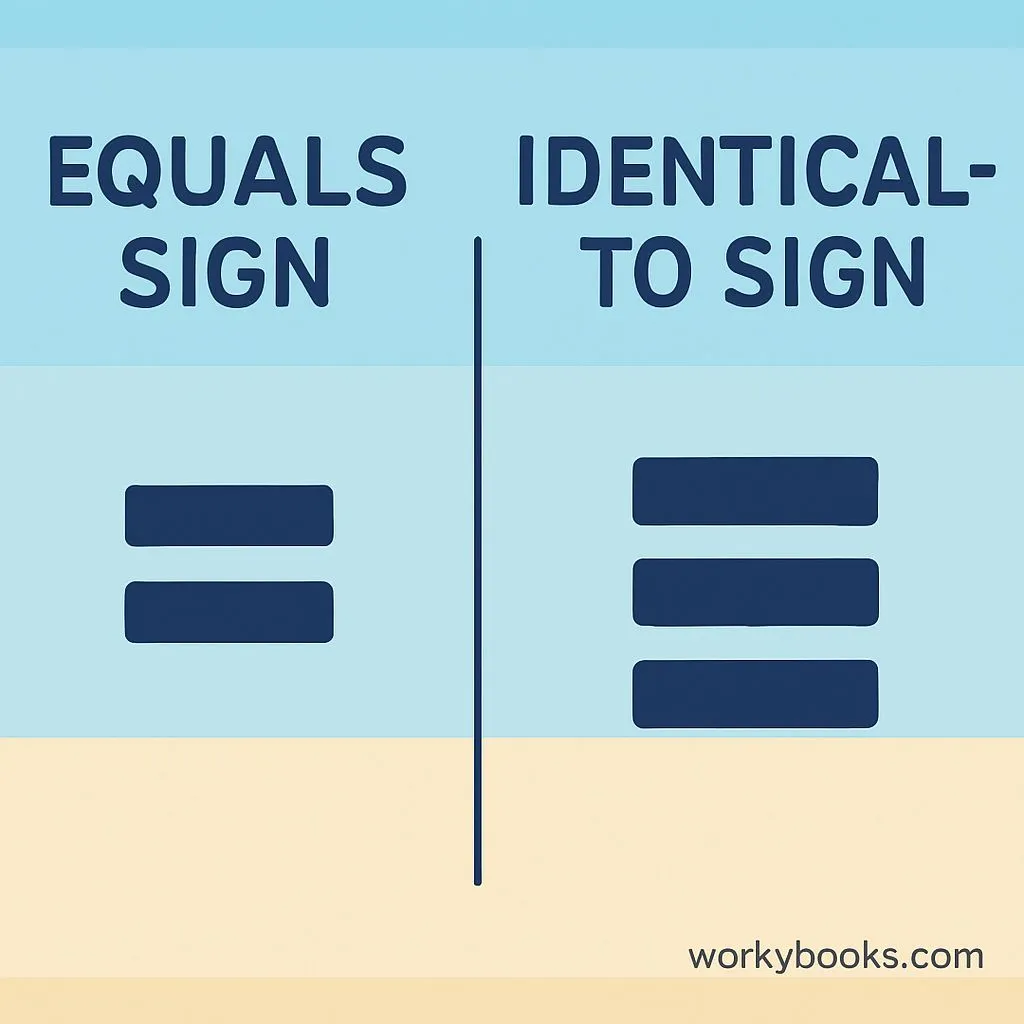
You might sometimes see a symbol that looks like three horizontal lines: ≡. This is not the same as the equal sign. It's called the "identical to" or "congruence" symbol.
While the equal sign (=) means that two expressions have the same value, the three-line symbol (≡) has special meanings:
1. Identical equality: The expressions are equal for all values of variables
2. Geometric congruence: Two shapes have exactly the same size and shape
3. Modular arithmetic: Numbers have the same remainder when divided by a certain number
For example, in algebra, we might write (x + 1)² ≡ x² + 2x + 1. This means the two expressions are identical—they're equal for every possible value of x.
Important Note
The three-line symbol (≡) has more specific meanings than the regular equal sign (=). It's used in advanced mathematics.
History of the Equal Sign

The equal sign was invented by the Welsh mathematician Robert Recorde in 1557. He introduced it in his book "The Whetstone of Witte."
Before Recorde invented the equal sign, mathematicians had to write out the word "equals" or use abbreviations. This made mathematical writing very long and complicated.
Recorde chose two parallel lines of the same length because he said "no two things can be more equal." His new symbol was slowly adopted by other mathematicians and eventually became standard throughout the world.
It took about 100 years for the equal sign to become widely used. Today, it's one of the most recognized mathematical symbols worldwide.
Historical Fact
Robert Recorde's equal sign was much longer than the one we use today. It was about five times longer than it was wide!
Equal Sign Quiz
Test your knowledge about the equal sign with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about the equal sign:
Math Symbol Trivia
Discover interesting facts about mathematical symbols:
Slow Adoption
It took over 100 years for the equal sign to become widely used after Robert Recorde invented it. Many mathematicians continued to write out the word "equals" for decades.
Symbol Variations
Some computer programming languages use double equals signs (==) to check for equality, and single equals signs (=) to assign values to variables.
Universal Symbol
The equal sign is one of the few mathematical symbols that is the same in nearly every language and country around the world, making it truly universal.
Longest Equation
The longest mathematical equation ever written contained over 200 billion equal signs! It was a proof that took hundreds of mathematicians years to complete.





