Equivalent Decimals - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn how decimals can represent the same value with different place values
What are Equivalent Decimals?

Equivalent decimals are decimals that have the same value even though they might look different. Just like fractions can be equivalent (like 1/2 and 2/4), decimals can be equivalent too!
Think of decimals as a way to show parts of a whole. The place value of each digit matters. When we add zeros to the right of a decimal number, the value doesn't change. For example:
0.5 = 0.50 = 0.500
All of these represent the same amount: five tenths. The extra zeros at the end don't change the value, just like how adding zeros to the end of a whole number (like 5, 50, 500) would change the value.
Key Concept
Adding zeros to the right of a decimal number doesn't change its value. This is what makes decimals equivalent.
How to Find Equivalent Decimals
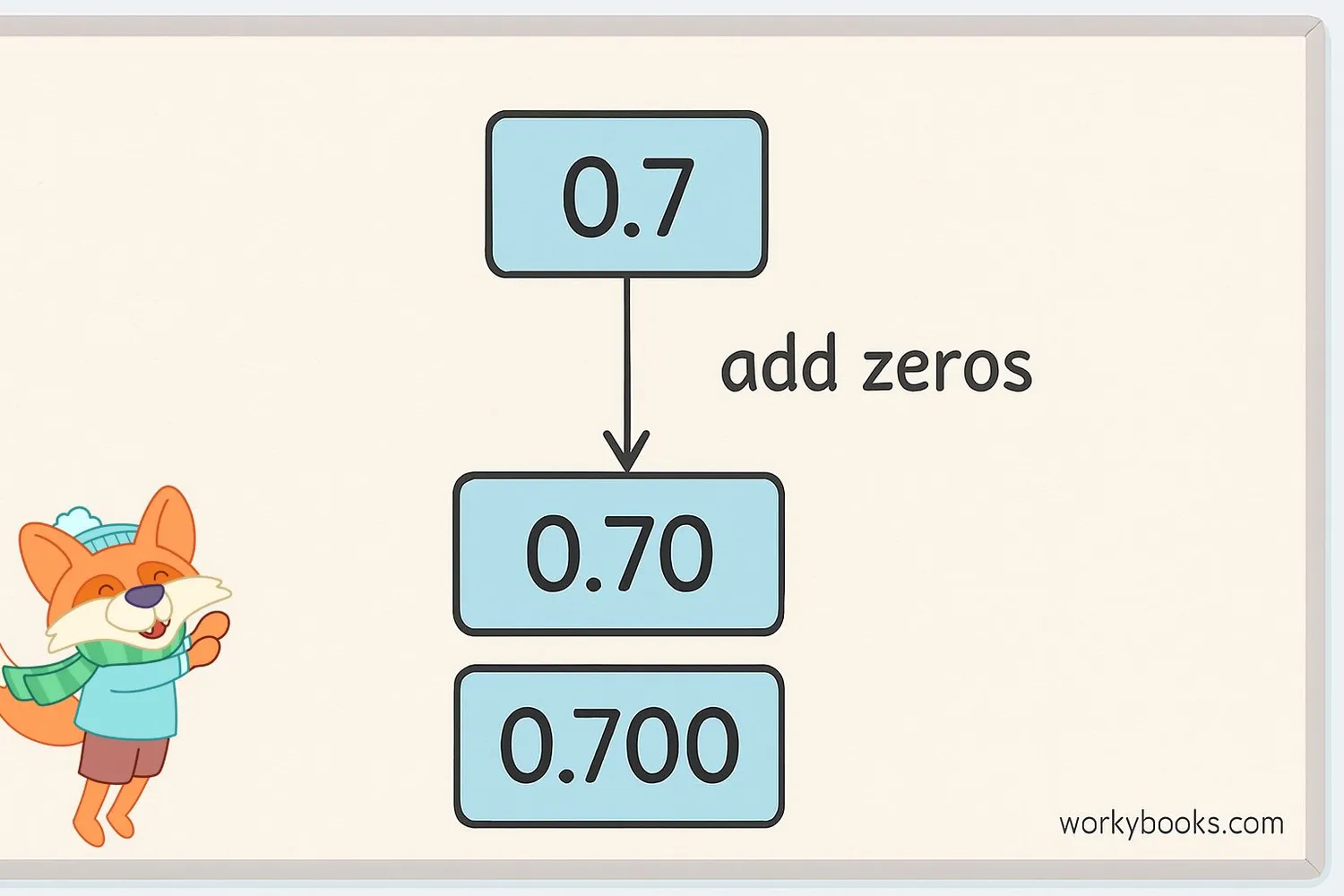
Finding equivalent decimals is simple once you understand the rule:
Conversion Rule
You can add zeros to the right of a decimal number without changing its value.
Example: Find decimals equivalent to 0.4
Step 1: Start with the decimal → 0.4
Step 2: Add zeros to the right → 0.40, 0.400, 0.4000
Step 3: All of these represent the same value: four tenths
You can also remove extra zeros at the end to simplify decimals. For example:
0.60 is the same as 0.6
0.2500 is the same as 0.25
Remember
Zeros at the end of a decimal number don't change its value, but zeros at the beginning do! For example, 0.5 and 0.05 are different values.
Examples of Equivalent Decimals
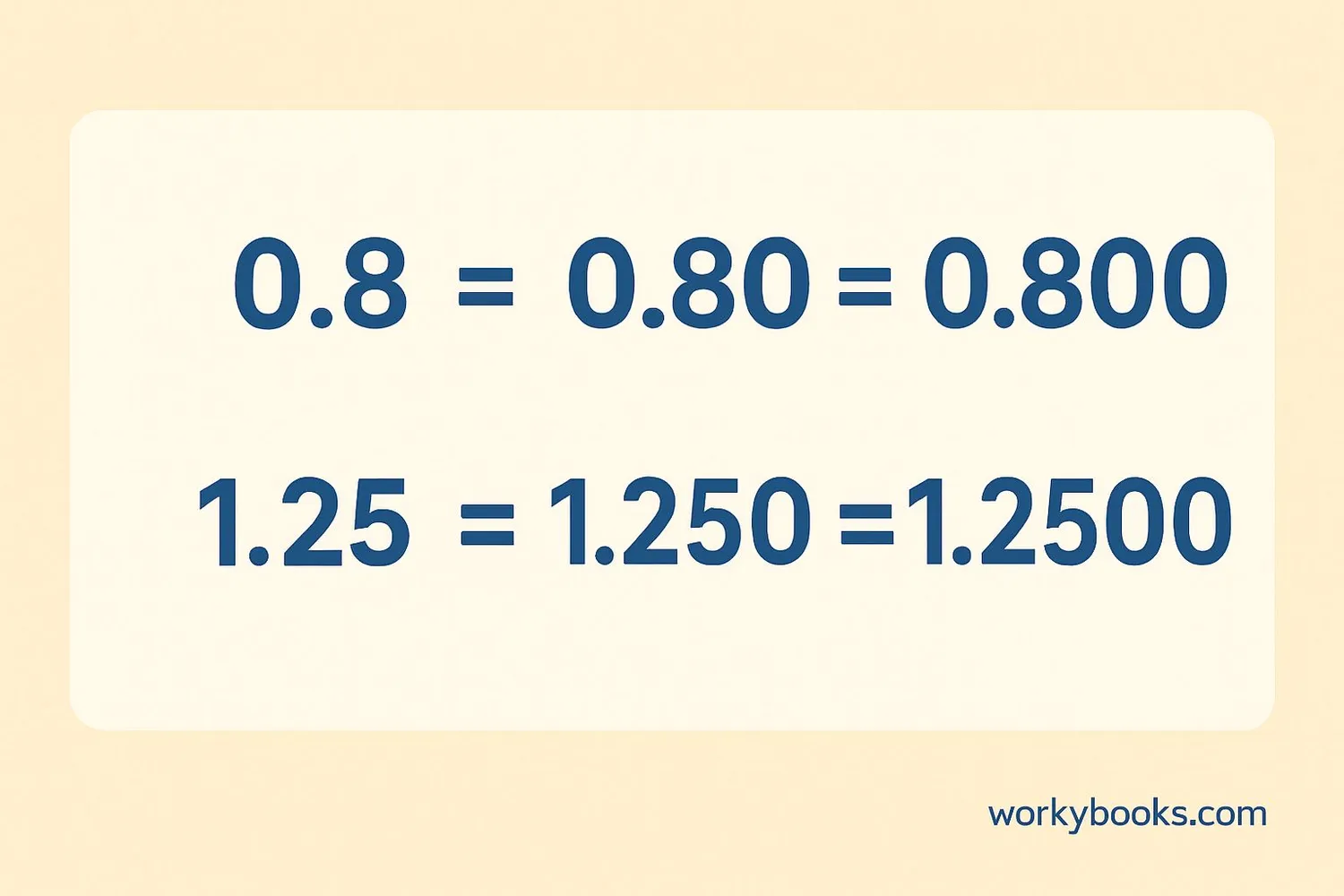
Let's look at some common examples of equivalent decimals:
Notice how in each case, we've added zeros to the right of the decimal without changing the value.
Why is this useful?
1. It helps us when comparing decimals (0.5 vs 0.50)
2. It makes adding and subtracting decimals easier
3. It helps us understand place value better
Practice Tip
To compare decimals, make them equivalent by adding zeros so they have the same number of decimal places.
Equivalent Decimals Quiz
Test your knowledge with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about equivalent decimals:
Decimal Trivia
Discover interesting facts about decimals and numbers:
Origin of Decimals
The decimal system was developed by Persian mathematician Al-Khwarizmi in the 9th century. The decimal point was introduced by Scottish mathematician John Napier in the early 17th century.
Decimal in Nature
Many patterns in nature follow decimal relationships. For example, the arrangement of leaves on a stem often follows patterns that can be described using decimals like 0.618 (the golden ratio).
Decimals in Space
NASA uses decimals with up to 15 decimal places when calculating spacecraft trajectories. A tiny error in decimals could cause a spacecraft to miss its target by thousands of miles!
Longest Decimal
The number Pi (π) has been calculated to over 62 trillion decimal places! But for most calculations, we only need 3.14 or 3.14159. The decimal expansion of Pi never ends and never repeats.




