Geometric Shapes - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about 2D and 3D shapes with easy explanations and practice activities
What are Geometric Shapes?
Geometric shapes are figures that have a defined form and boundaries. They can be two-dimensional (flat) or three-dimensional (solid). The word "geometry" comes from the Greek words "geo" meaning "earth" and "metron" meaning "measurement."
We see geometric shapes everywhere in our daily lives. The screen you're looking at is probably a rectangle, your plate might be a circle, and many buildings are made up of various geometric shapes.
Understanding geometric shapes helps us:
- Recognize patterns in nature and human-made objects
- Solve problems involving space and measurement
- Create art and designs
- Build structures that are strong and stable
- Understand maps and navigate our world
Key Concept
Geometric shapes are defined forms with specific properties like sides, angles, and vertices. They help us describe and understand the world around us.
2D Shapes
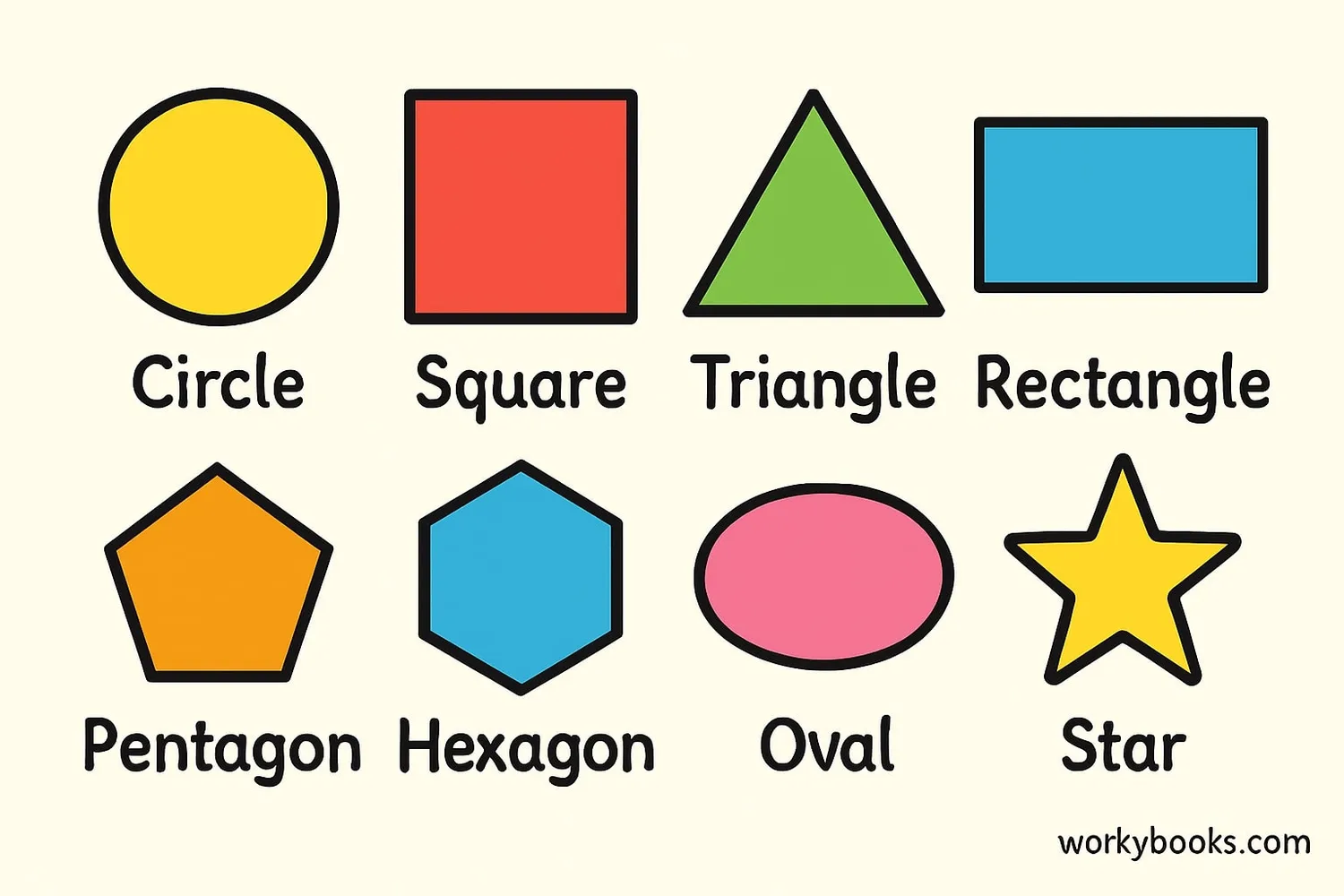
Two-dimensional (2D) shapes are flat figures that have length and width but no depth. They're also called plane shapes. Here are some common 2D shapes:
Properties of 2D Shapes
2D shapes have different properties that help us identify and classify them:
- Sides: The straight lines that form the shape
- Vertices: The points where two sides meet (corners)
- Angles: The space between two intersecting lines
- Symmetry: When one half of a shape mirrors the other half
Remember
2D shapes are flat and can be measured in terms of area and perimeter. They're the building blocks for understanding more complex geometric concepts.
3D Shapes
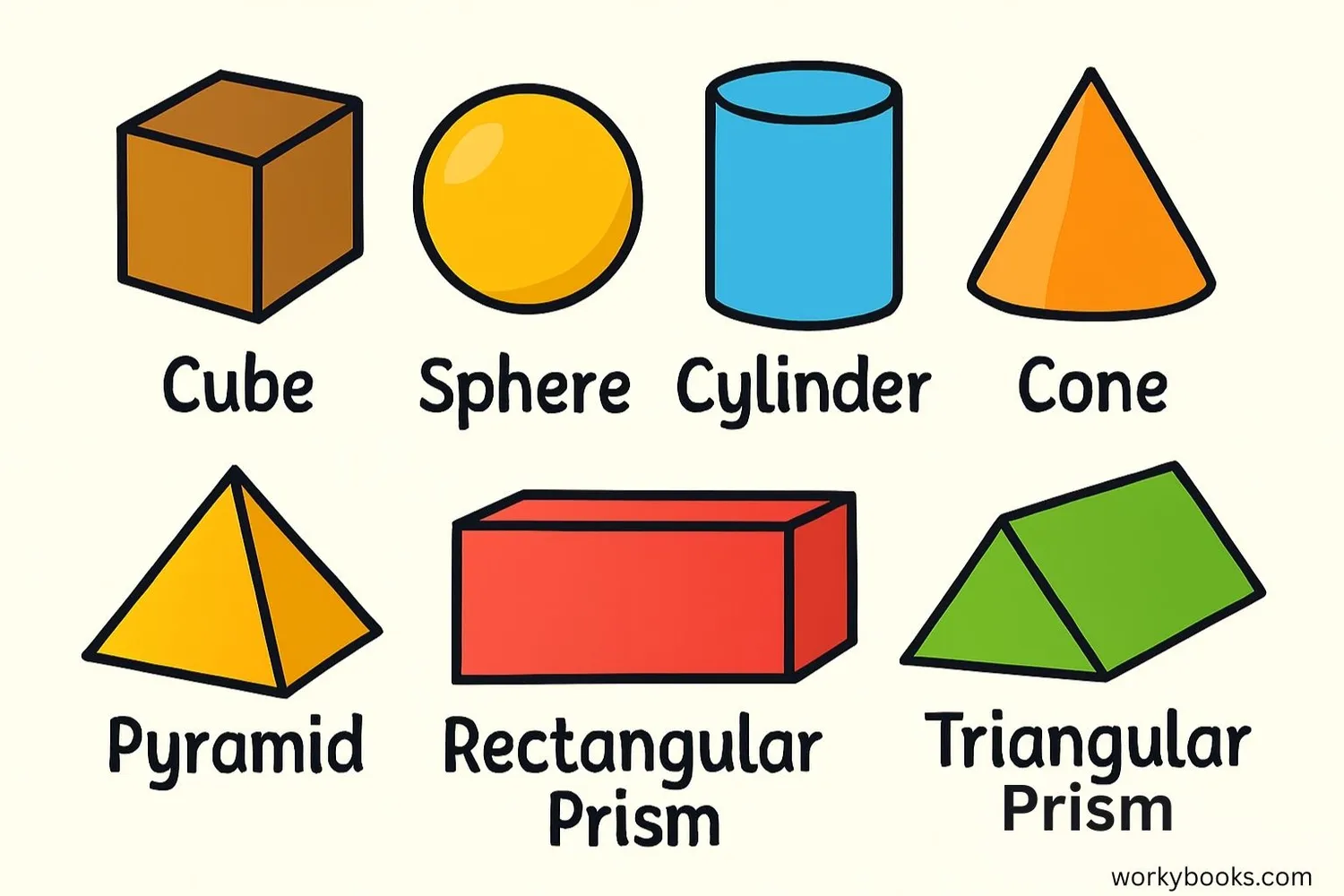
Three-dimensional (3D) shapes are solid figures that have length, width, and height (depth). Unlike 2D shapes, you can hold 3D shapes in your hand. Here are some common 3D shapes:
Properties of 3D Shapes
3D shapes have different properties that help us identify and work with them:
- Faces: The flat surfaces of a 3D shape
- Edges: The lines where two faces meet
- Vertices: The points where edges meet (corners)
- Volume: The amount of space inside a 3D shape
- Surface Area: The total area of all the faces
Real-World Connection
We see 3D shapes everywhere: balls (spheres), boxes (cubes or rectangular prisms), cans (cylinders), ice cream cones (cones), and Egyptian pyramids (pyramids).
Geometric Shapes Quiz
Test your knowledge about geometric shapes with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about geometric shapes:
Shape Trivia
Discover interesting facts about geometric shapes:
Honeycomb Geometry
Honeybees build their honeycombs with hexagonal cells. This shape allows them to store the most honey using the least amount of wax. Mathematicians have proven that hexagons are the most efficient shape for this purpose.
The Platonic Solids
There are only five 3D shapes where all faces are identical regular polygons, and the same number of faces meet at each vertex. These are called Platonic solids: tetrahedron, cube, octahedron, dodecahedron, and icosahedron.
Pyramid Power
The Great Pyramid of Giza in Egypt is one of the most famous geometric structures in the world. Its square base and triangular sides form a perfect pyramid shape. The ratio of its proportions follows the mathematical constant pi (π).
Molecular Shapes
At the molecular level, compounds form specific geometric shapes. For example, water molecules form a bent shape, carbon dioxide is linear, and methane forms a tetrahedron. These shapes determine many of the properties of substances.





