Irregular Polygons - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about shapes with different sides and angles through visual examples and practice activities
What are Irregular Polygons?
An irregular polygon is a shape that has sides of different lengths and angles of different measurements. Unlike regular polygons where all sides and angles are equal, irregular polygons come in many different forms and are all around us in everyday life.
The word "polygon" comes from Greek words meaning "many angles." All polygons are closed shapes with straight sides, but irregular polygons don't follow the strict rules that regular polygons do.
You can find irregular polygons in many places: the shape of your classroom, the layout of a park, or even the pattern on a soccer ball. Understanding irregular polygons helps us describe and understand the world around us.
Key Concept
Irregular polygons have sides of different lengths and angles of different measurements. This makes them different from regular polygons where all sides and angles are equal.
Properties of Irregular Polygons
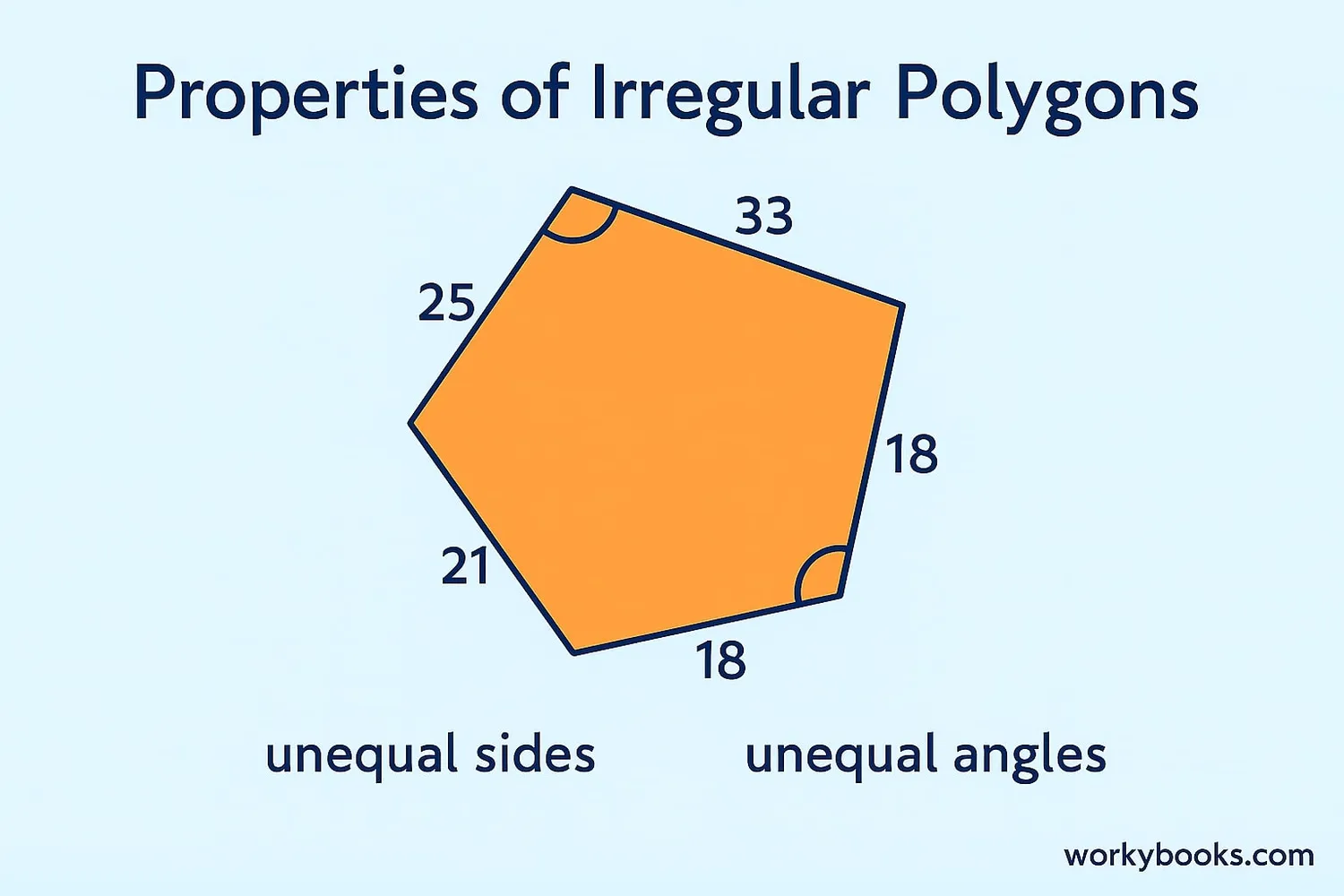
Irregular polygons have special properties that make them different from regular polygons:
1. Unequal side lengths: The sides of an irregular polygon are not all the same length.
2. Unequal angles: The interior angles (the angles inside the shape) are not all equal.
3. Varied symmetry: Irregular polygons may have no lines of symmetry or only a few, unlike regular polygons which have multiple lines of symmetry.
4. Complex appearance: Because of the unequal sides and angles, irregular polygons often have a more "natural" or less perfect appearance than regular polygons.
Despite these differences, irregular polygons still follow some important rules of geometry. For example, the sum of the interior angles of any polygon (regular or irregular) follows a specific pattern based on the number of sides.
Remember
Even though irregular polygons have unequal sides and angles, they still follow the rule that the sum of interior angles = (n-2) × 180°, where n is the number of sides.
Types of Irregular Polygons
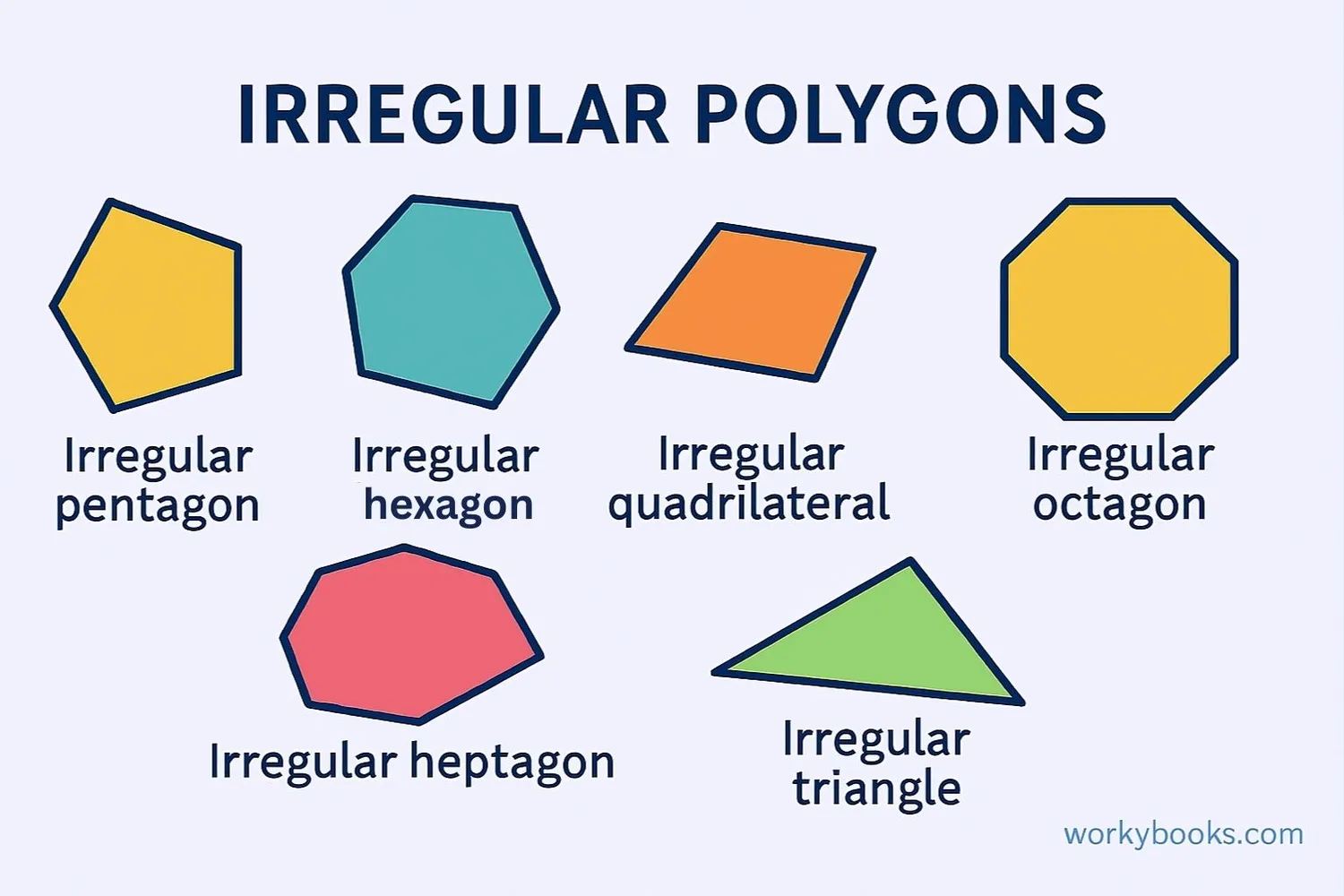
Irregular polygons are named based on how many sides they have, just like regular polygons. Here are some common types:
Irregular Triangles: Also called scalene triangles, these have three sides of different lengths and three different angles.
Irregular Quadrilaterals: These four-sided shapes include rectangles (if not squares), trapezoids, and other four-sided shapes with unequal sides and angles.
Irregular Pentagons: Five-sided shapes where the sides and angles are not all equal.
Irregular Hexagons: Six-sided shapes with varying side lengths and angle measurements.
There are also irregular heptagons (7 sides), octagons (8 sides), and polygons with even more sides. The number of possible irregular polygons is practically endless because there are so many ways to combine different side lengths and angles.
Irregular Triangle
3 unequal sides
Irregular Quadrilateral
4 unequal sides
Irregular Pentagon
5 unequal sides
Irregular Hexagon
6 unequal sides
Regular vs Irregular Polygons
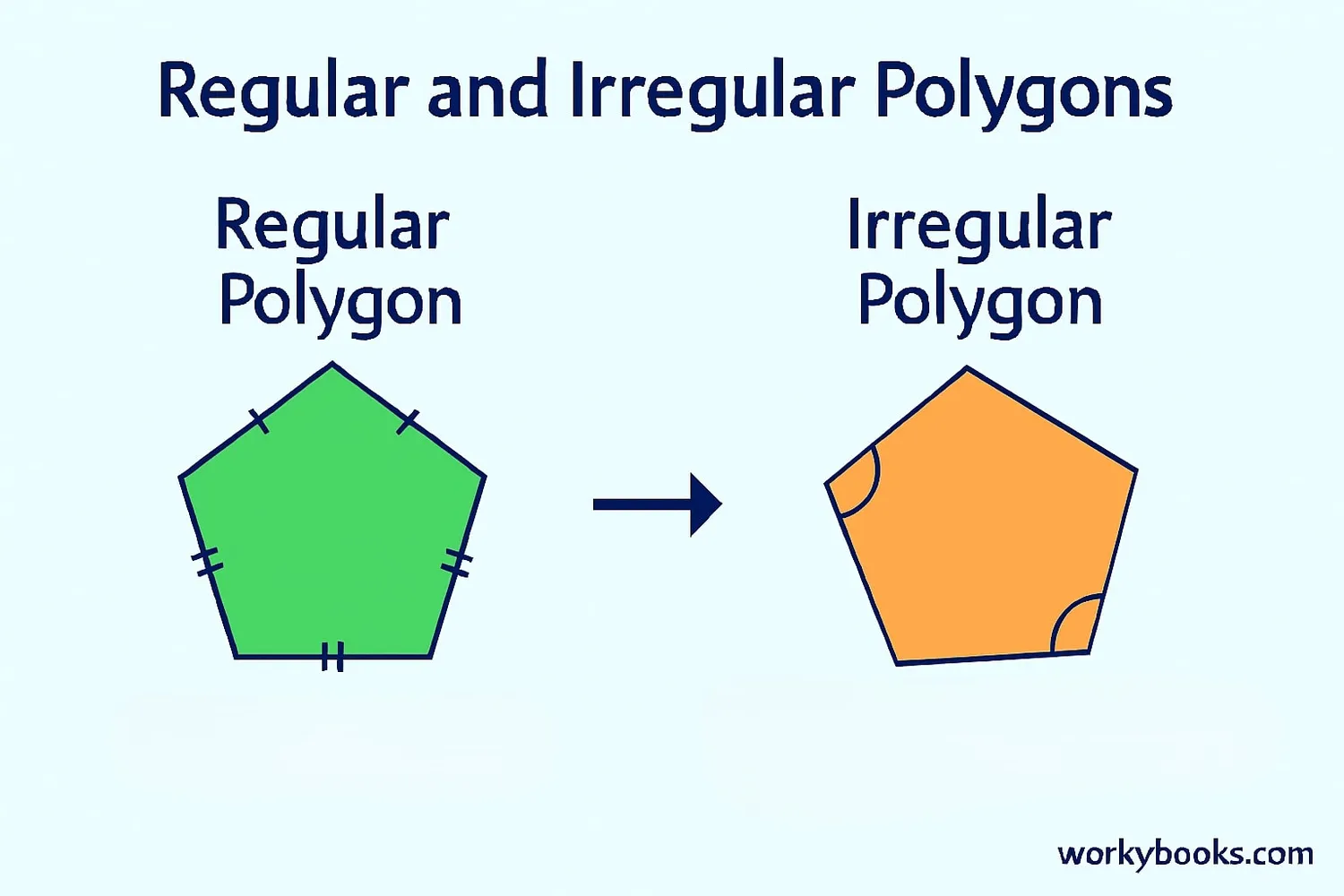
Understanding the difference between regular and irregular polygons is important in geometry. Here's how they compare:
| Feature | Regular Polygons | Irregular Polygons |
|---|---|---|
| Side lengths | All sides equal | Sides of different lengths |
| Interior angles | All angles equal | Angles of different measurements |
| Symmetry | High degree of symmetry | Little or no symmetry |
| Examples | Square, equilateral triangle | Rectangle, scalene triangle |
| Appearance | Uniform, predictable | Varied, unpredictable |
It's important to note that some shapes can be confusing. For example, a rectangle has equal angles (all 90°) but can have different side lengths (if it's not a square). This makes it an irregular polygon because not all sides are equal.
Similarly, a rhombus has all sides equal but can have different angles, making it irregular if the angles aren't all equal.
Remember
A polygon is only regular if ALL sides are equal AND ALL angles are equal. If either condition isn't met, the polygon is irregular.
Real-World Examples
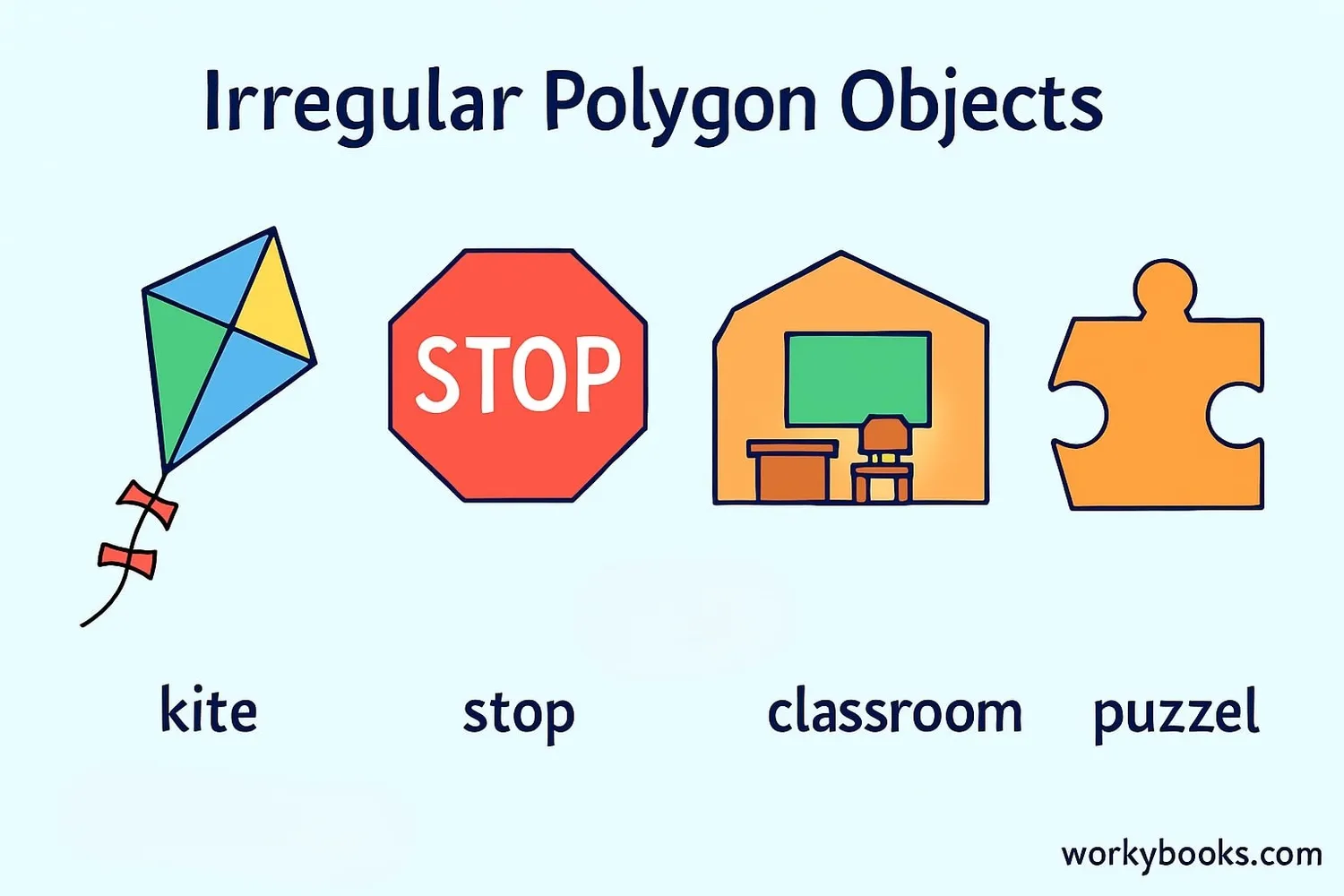
Irregular polygons are all around us! Here are some common examples:
1. Most rooms in buildings: While some rooms might be perfect squares, most have slightly different wall lengths, making them irregular quadrilaterals.
2. Kites: Many kites are irregular quadrilaterals with two pairs of adjacent sides that are equal, but all four sides aren't necessarily equal.
3. Pieces of a jigsaw puzzle: Each piece has a unique shape with different side lengths and angles, making them irregular polygons.
4. Countries on a map: The borders of most countries form irregular polygons with many sides of different lengths.
5. Leaves: While many leaves have symmetry, their exact shapes are irregular polygons with slightly different side measurements.
Can you find more examples of irregular polygons in your classroom or home? Look for shapes that have straight sides but aren't perfect squares, equilateral triangles, or other regular polygons.
Look Around
Take a moment to look around you. How many irregular polygons can you spot in your immediate environment?
Polygon Practice Quiz
Test your knowledge about irregular polygons with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about irregular polygons:
Geometry Trivia
Discover interesting facts about polygons and geometry:
Ancient Geometry
The ancient Greeks were the first to systematically study polygons around 300 BCE. Euclid's "Elements" contained extensive information about both regular and irregular polygons.
Polygon Names
Polygons are named using Greek prefixes indicating the number of sides: "tri" for 3, "quad" for 4, "penta" for 5, "hexa" for 6, "hepta" for 7, "octa" for 8, "nona" for 9, and "deca" for 10.
Nature's Polygons
While many people think of honeycombs as perfect regular hexagons, most actual honeycombs are made of irregular hexagons with slightly different shapes and sizes.
Building Design
Famous irregular polygon buildings include the Pentagon (which is actually a regular pentagon) and the CCTV Headquarters in Beijing, which is an irregular quadrilateral loop.





