Less Than - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn to compare numbers using the less than symbol with simple explanations and practice activities
What is Less Than?
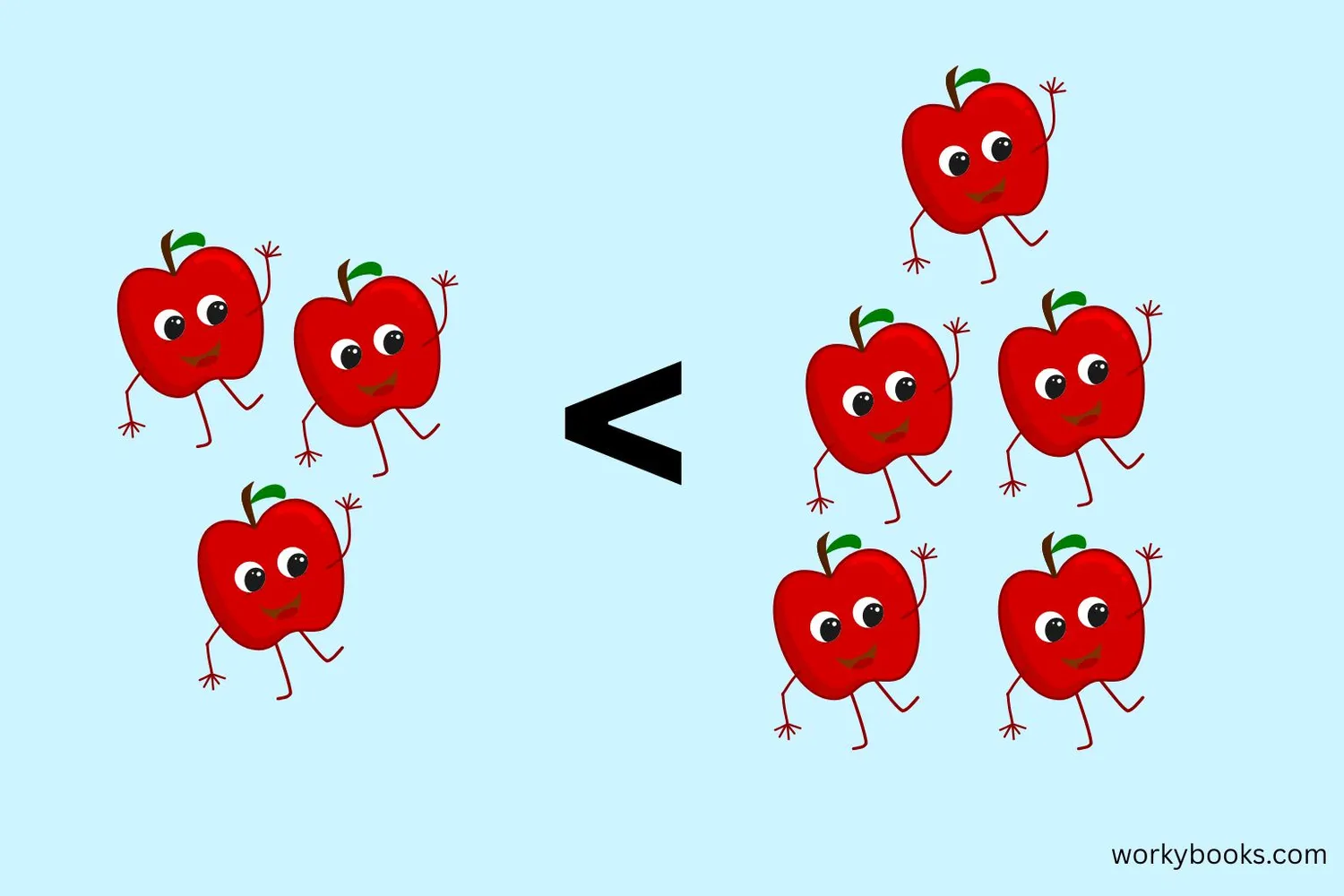
"Less than" is a math concept we use to compare two numbers or amounts. When we say one number is less than another, it means it's smaller or has a lower value.
We use the symbol < to show that one number is less than another. For example, 3 < 5 means "three is less than five."
Think of it like a hungry alligator - the alligator always wants to eat the bigger number! The open mouth points to the bigger number, while the pointy end points to the smaller number.
Key Concept
"Less than" is used to compare two numbers when the first number is smaller than the second number.
The Less Than Symbol
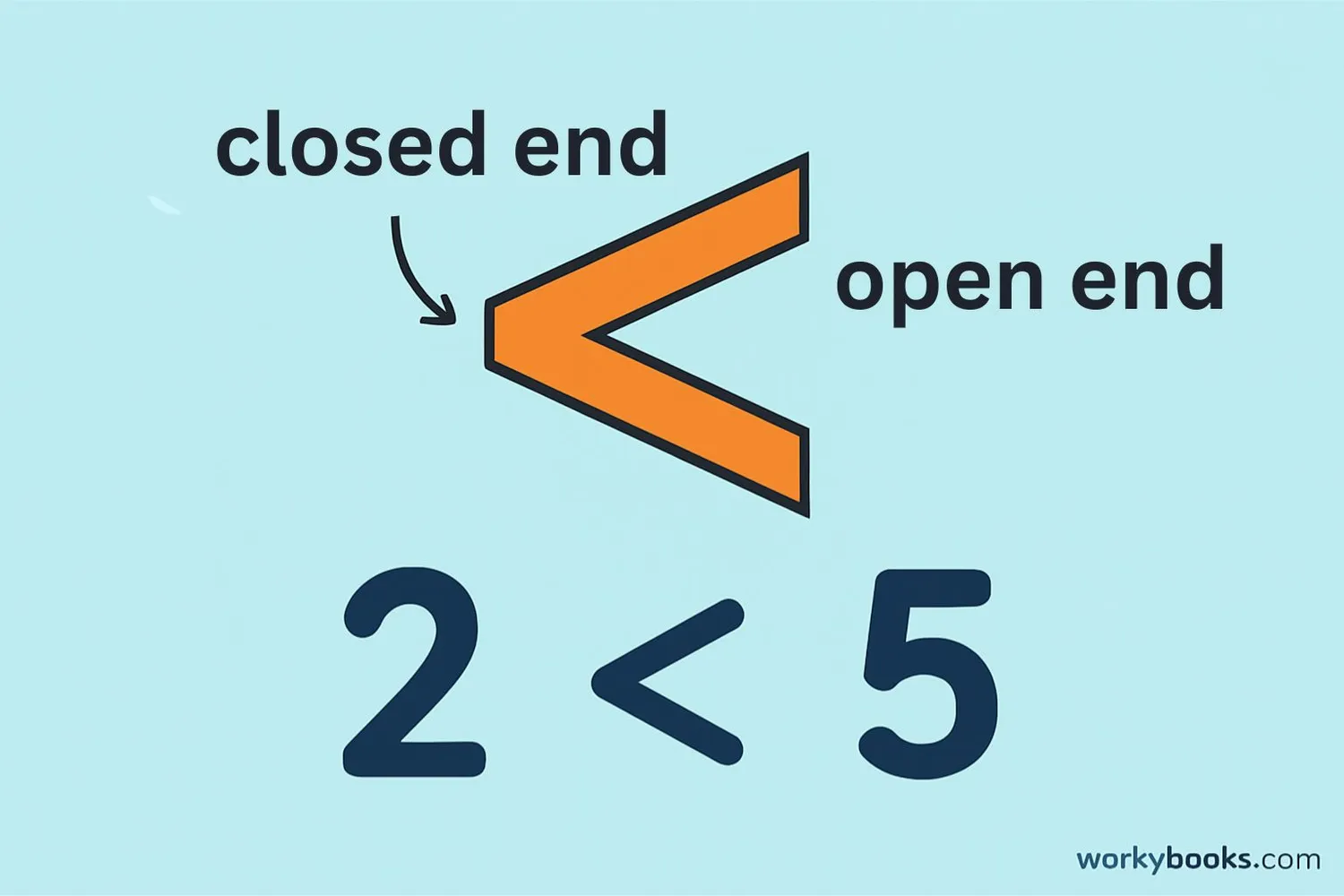
The less than symbol < looks like a sideways V. It has two important parts:
- The pointed end points to the smaller number
- The open end faces the larger number
We can also use a number line to understand less than. On a number line, numbers get bigger as we move to the right. So any number to the left is less than numbers to the right.
Remember
The less than symbol always points to the smaller number and opens toward the bigger number.
Comparing Numbers
When we compare numbers, we look at which one is smaller or larger. Here's how to compare two numbers:
Step 1: Count the digits - numbers with more digits are larger
Step 2: If numbers have the same digits, compare from left to right
Step 3: The first digit that's different tells us which number is smaller
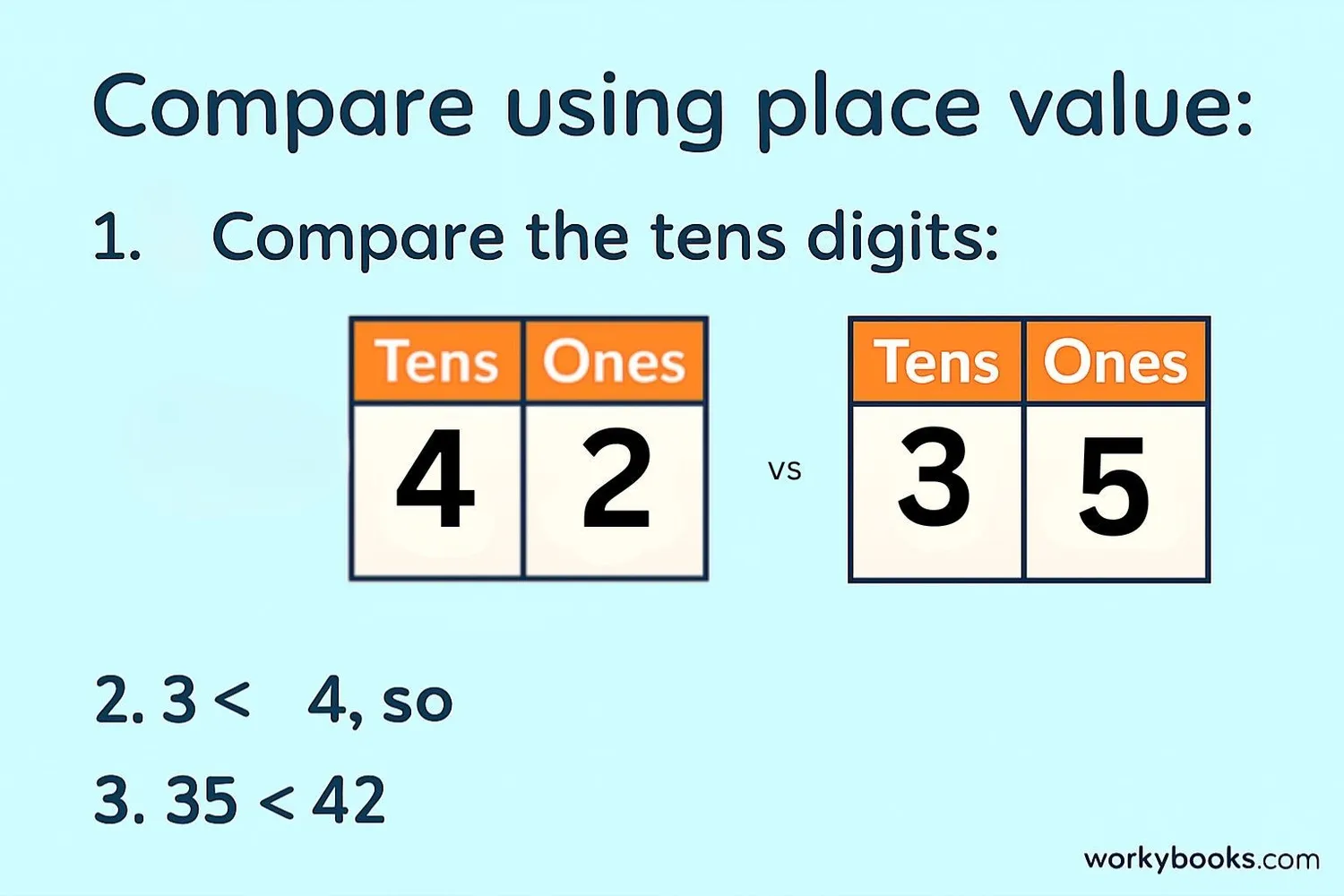
Let's compare 35 and 42:
Both have two digits, so we look at the tens place.
3 tens vs 4 tens - 3 is less than 4
So 35 < 42
Here's a chart comparing different numbers:
| First Number | Comparison | Second Number | Is Less Than? |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | < | 9 | Yes |
| 15 | < | 12 | No |
| 25 | < | 30 | Yes |
| 100 | < | 99 | No |
| 64 | < | 72 | Yes |
Comparison Tip
When comparing numbers with different digits, the number with more digits is always larger. For example, 100 > 99 because 100 has three digits while 99 has only two.
Real-World Examples
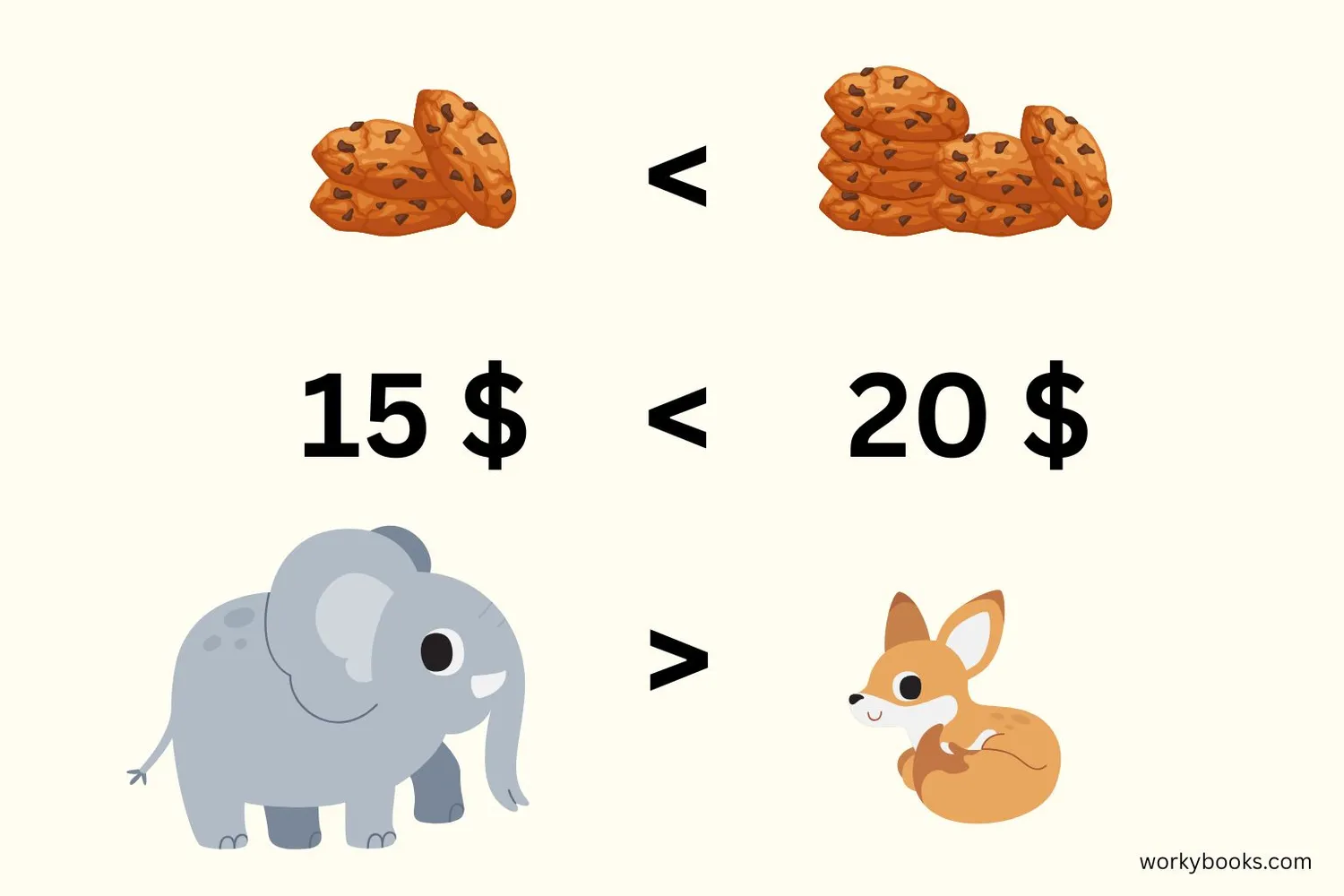
We use "less than" in many real-life situations. Here are some examples:
Example 1: Cookies
Sarah has 3 cookies. John has 5 cookies.
3 < 5, so Sarah has fewer cookies than John.
Example 2: Height
A tree is 12 feet tall. A building is 24 feet tall.
12 < 24, so the tree is shorter than the building.
Example 3: Money
A toy costs $5. A game costs $10.
5 < 10, so the toy is cheaper than the game.
Example 4: Temperature
Today's temperature is 68°F. Yesterday was 75°F.
68 < 75, so today is cooler than yesterday.
Example 5: Age
Lisa is 8 years old. Tom is 10 years old.
8 < 10, so Lisa is younger than Tom.
Practice Tip
Look for "less than" in your daily life - when comparing prices, ages, distances, or quantities. This will help you understand the concept better!
Practice Quiz
Test your understanding of "less than" with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about "less than":
Math Trivia
Discover interesting facts about math inequalities:
Historical Symbols
The symbols < and > were first used by British mathematician Thomas Harriot in the 1630s. Before that, mathematicians used words like "is less than" written out in full.
Comparing Very Large Numbers
Mathematicians use the same less than concept to compare huge numbers. For example, there are more possible chess games (10¹²⁰) than atoms in the observable universe (10⁸⁰), so 10⁸⁰ < 10¹²⁰.
Negative Numbers
With negative numbers, the "less than" concept still works! -10 < -5 because -10 is further to the left on the number line. This is because -10 is colder, lower, or smaller than -5.
Computer Comparisons
Computers use the less than concept millions of times every second. When you play a video game, the computer constantly compares numbers to decide what to display on screen and how objects interact.





