Magnitude - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about the size of things - from numbers to vectors - with simple explanations and activities
What is Magnitude?
Magnitude is a special math word that means size or amount. It tells us how big, small, long, heavy, or strong something is.
Think about it like this: when you measure how tall you are, the number you get is your height's magnitude. When you weigh yourself, that number is your weight's magnitude. Magnitude is all about the size of things!
Magnitude is always a positive number because it represents size. Even if something is moving backward, we still measure how far it moves with a positive magnitude.
Key Concept
Magnitude is the "size" of something - always positive and never negative.
Different Types of Magnitude
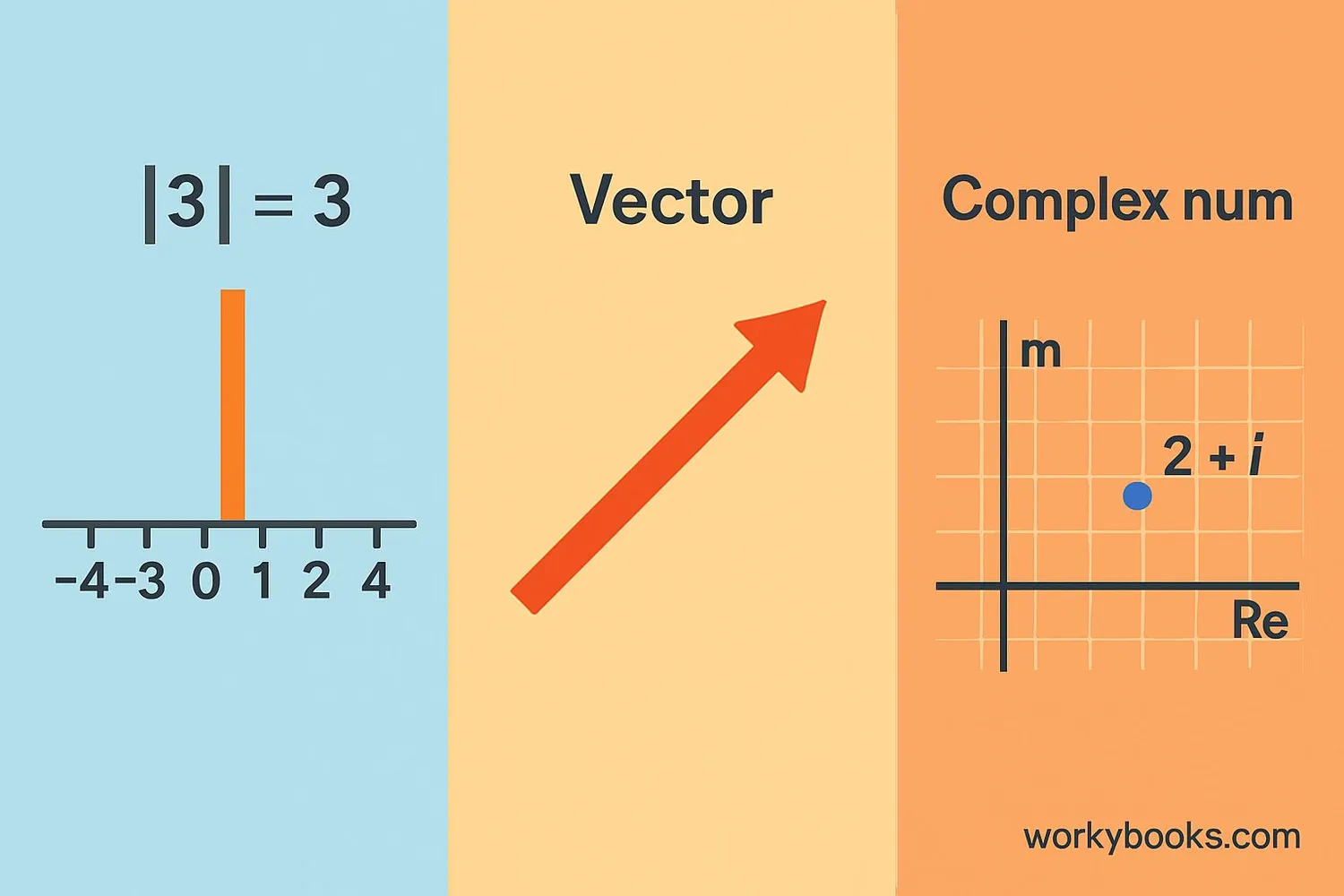
Magnitude can describe different things in math and science:
Absolute Value (Modulus): The magnitude of a number. It tells us how far a number is from zero on a number line. For example, | -5 | = 5 and | 5 | = 5. Both have the same magnitude!
Vectors: Arrows that have both size (magnitude) and direction. The magnitude of a vector is its length. If a vector represents movement, its magnitude tells us how far something moved.
Scalars: Quantities that have magnitude but no direction. Your height, weight, and temperature are all scalars.
Complex Numbers: Numbers with a real part and an imaginary part. Their magnitude is the distance from zero on a special grid.
Remember
Magnitude is always positive and tells us about size, while direction tells us where something is pointing.
How to Find Magnitude
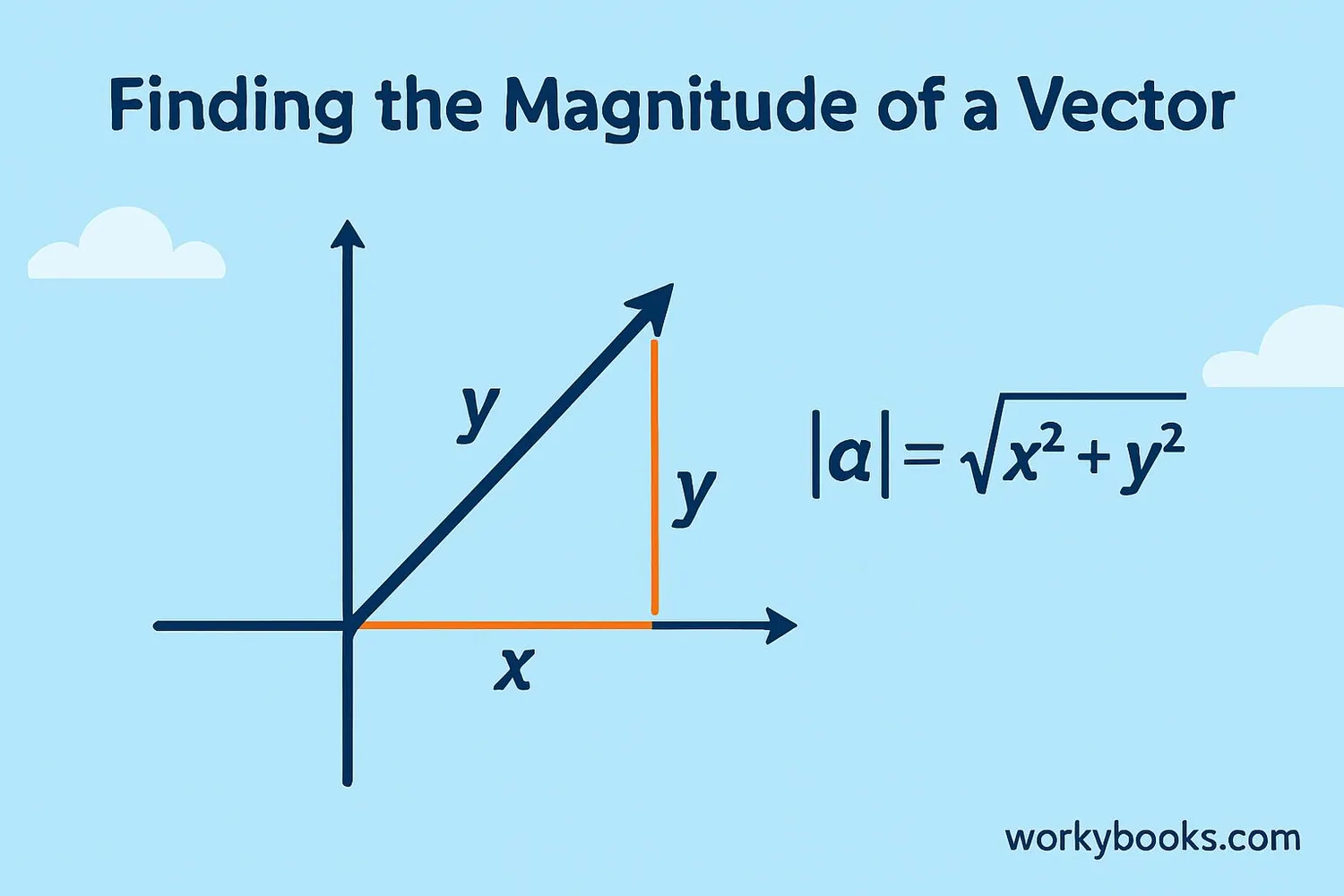
Here's how to find magnitude in different situations:
Absolute Value Magnitude
For any number, remove the negative sign (if it has one) to find its magnitude.
Vector Magnitude (2D)
For a vector (x, y), square both parts, add them, then take the square root.
Complex Number Magnitude
Similar to vectors, but for complex numbers like 3 + 4i.
Remember
Magnitude is always a positive number that represents size or amount.
Magnitude Examples
Let's practice finding magnitude with some examples:
Example 1: Absolute Value Magnitude
What is the magnitude of -7?
Solution: | -7 | = 7 (distance from zero)
Example 2: Vector Magnitude
Find the magnitude of vector (3, 4)
Solution: √(3² + 4²) = √(9 + 16) = √25 = 5
Example 3: Distance Magnitude
Sarah walked 5 blocks east and 12 blocks north. How far is she from her starting point?
Solution: √(5² + 12²) = √(25 + 144) = √169 = 13 blocks
Example 4: Complex Number Magnitude
What is the magnitude of 3 + 4i?
Solution: √(3² + 4²) = √(9 + 16) = √25 = 5
Notice that in examples 2-4, we got the same magnitude of 5! That's because (3,4) and 3+4i both represent a point that's 3 units in one direction and 4 units in another.
Interesting Pattern
3-4-5 is a special right triangle! Many magnitude problems use this pattern.
Magnitude Practice Quiz
Test your understanding with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about magnitude:
Magnitude Trivia
Discover interesting facts about magnitude:
Ancient Measurements
The concept of magnitude dates back to ancient civilizations. Egyptians used cubits (length from elbow to fingertip) to measure magnitude when building pyramids!
Richter Scale
Earthquakes are measured by magnitude on the Richter Scale. Each whole number increase means the earthquake is 10 times stronger in magnitude!
Star Brightness
Astronomers measure star brightness using "apparent magnitude." The brightest stars have the smallest magnitude numbers - even negative values!
Largest Number
The largest named number is "googolplex" - that's 1 followed by a googol of zeros! A googol is 1 followed by 100 zeros. That's a magnitude too big to imagine!





