Math Symbols - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about common mathematical symbols with simple explanations, examples, and practice activities
What Are Math Symbols?
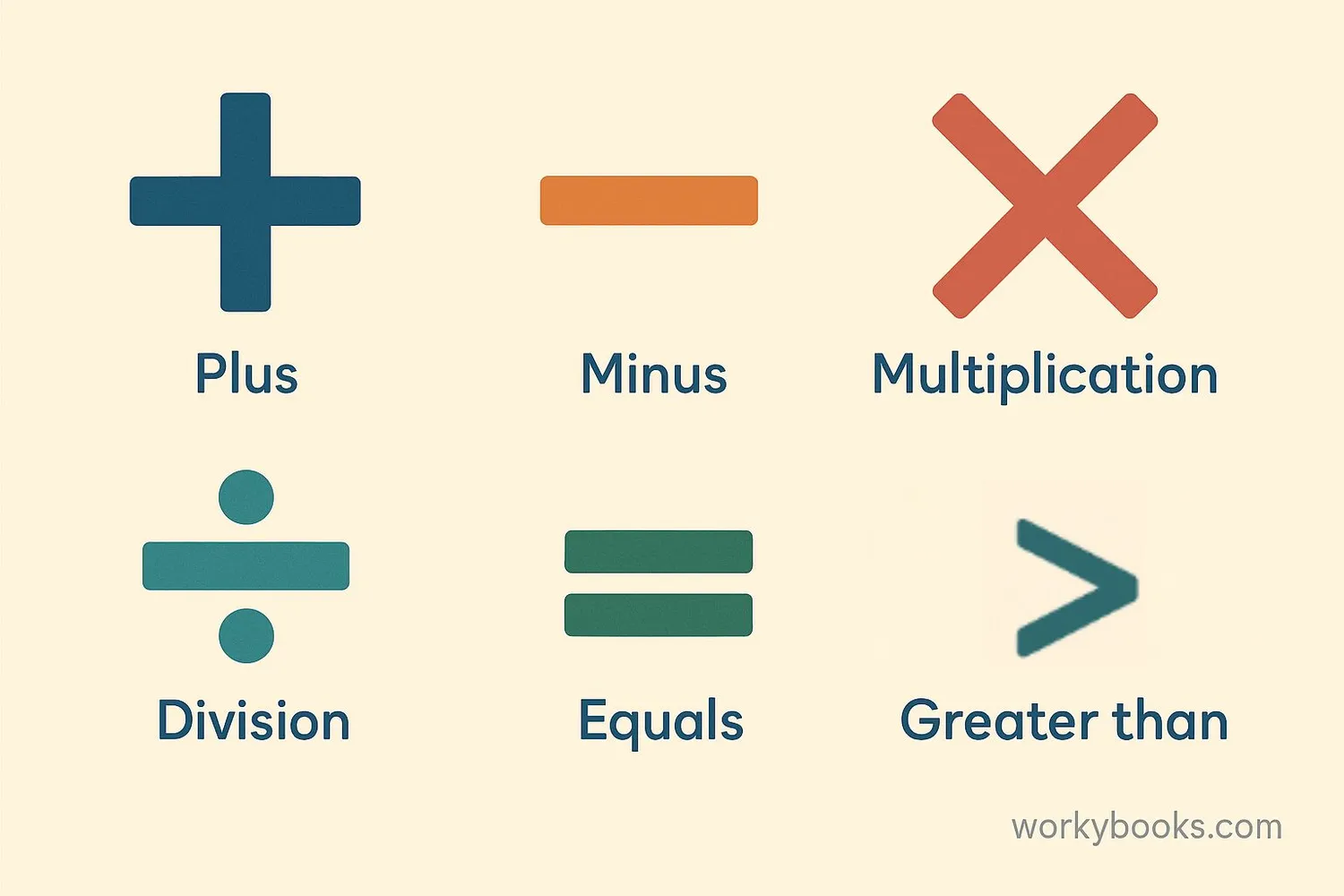
Math symbols are special signs and abbreviations that help us write mathematical ideas in a shorter way. Just like letters form words in a language, math symbols help us write mathematical sentences called expressions and equations.
Symbols make math easier to read and understand. They help us communicate mathematical ideas clearly without writing long sentences. Learning these symbols is like learning a new language that helps us solve problems.
Math symbols are used all around the world, so mathematicians from different countries can understand each other's work. This universal language of mathematics helps scientists, engineers, and people in many professions share ideas.
Key Concept
Math symbols are a universal language that helps people communicate mathematical ideas clearly and efficiently.
Basic Arithmetic Symbols
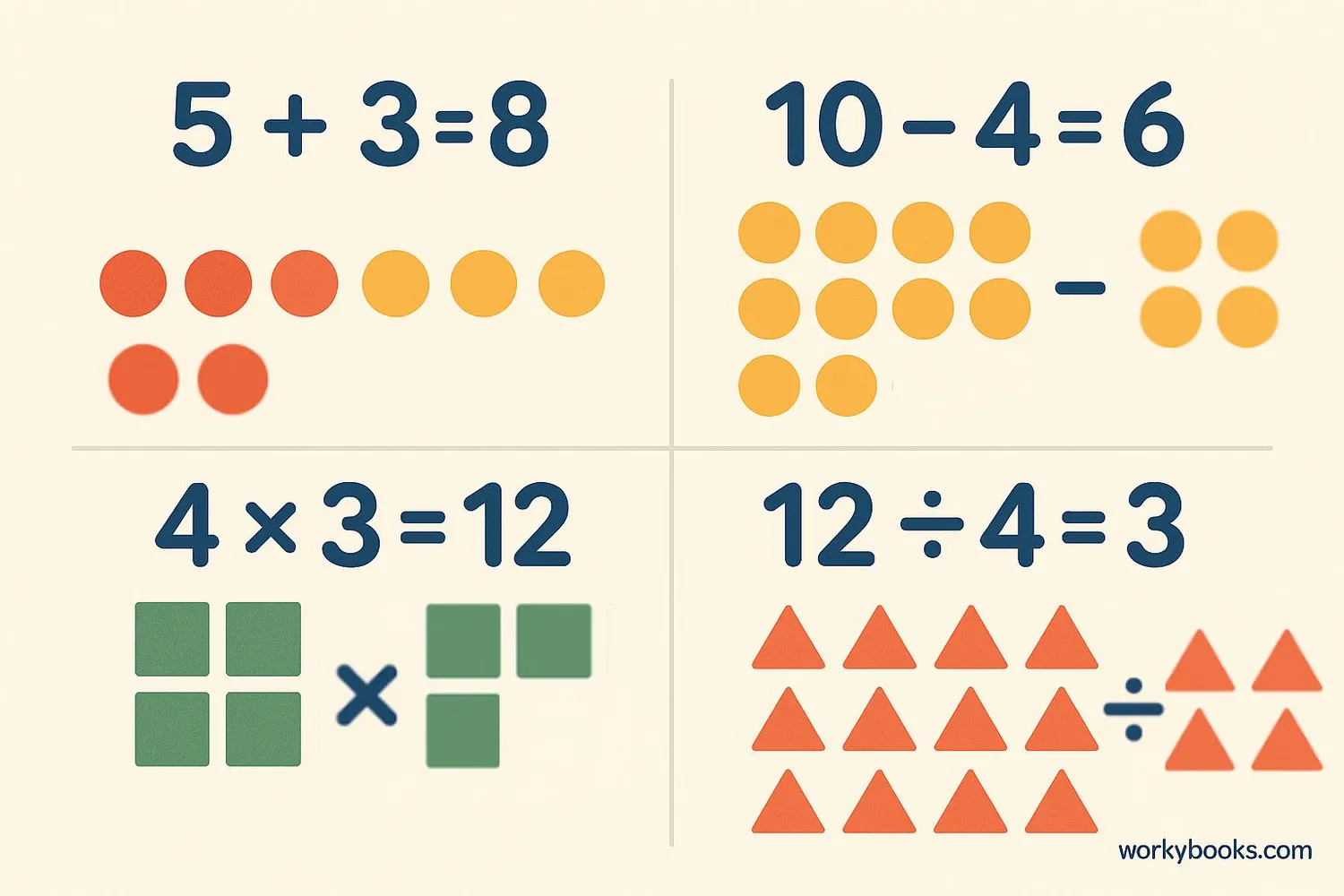
The four basic operations in math are addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Each has its own special symbol:
The plus sign shows that we are combining or adding numbers together.
The minus sign shows that we are taking away or subtracting one number from another.
The multiplication sign shows that we are adding equal groups together.
The division sign shows that we are sharing or dividing into equal parts.
Remember
Multiplication is a quicker way to add the same number multiple times. Division is the opposite of multiplication.
Comparison Symbols
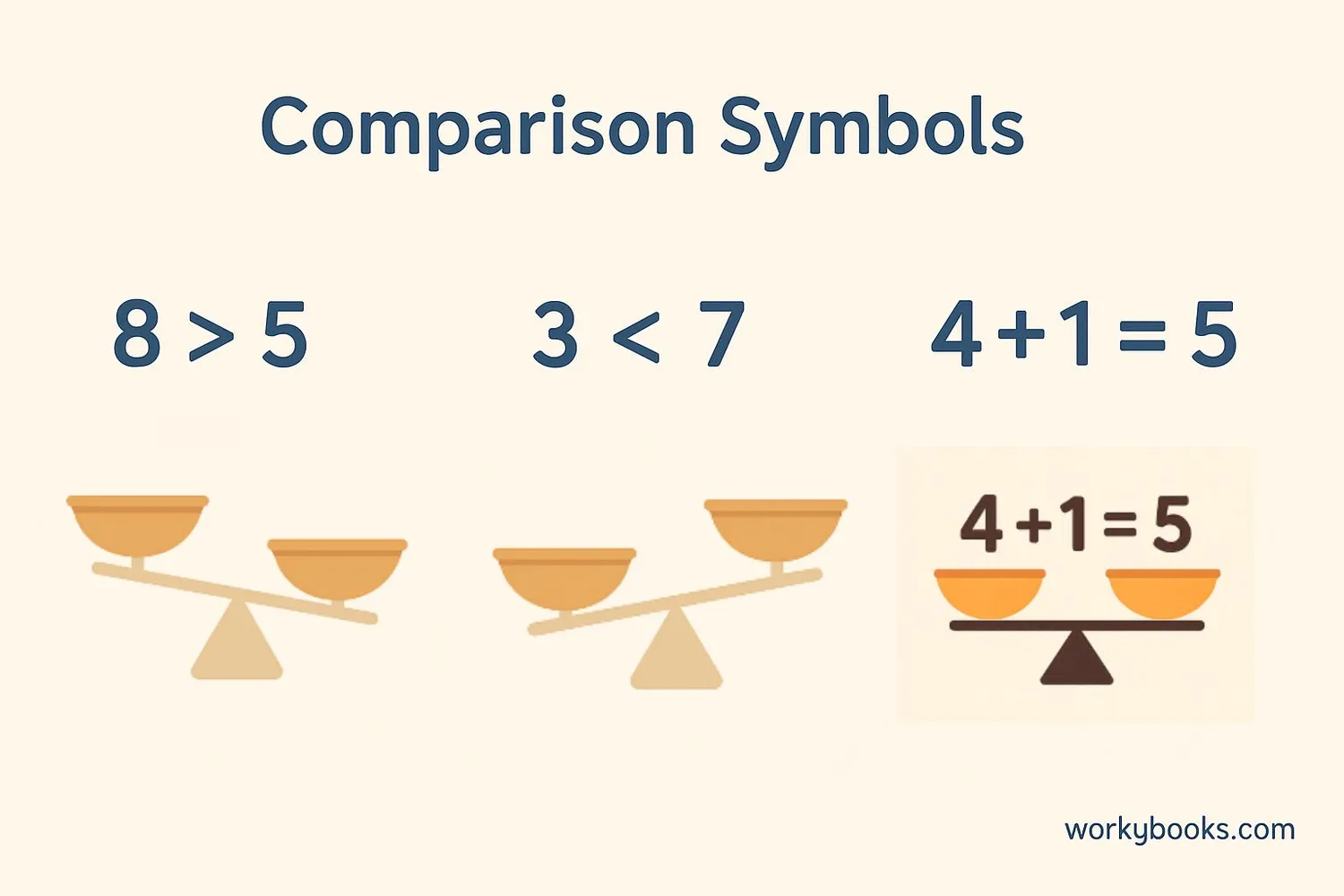
Comparison symbols help us show how numbers relate to each other. They tell us which number is larger, smaller, or if numbers are equal:
The equals sign shows that two amounts have the same value.
The greater than sign shows that the number on the left is larger than the number on the right.
The less than sign shows that the number on the left is smaller than the number on the right.
The not equal to sign shows that two amounts are different.
Remember
Think of the greater than and less than signs as hungry alligators that always want to eat the larger number!
Geometry Symbols
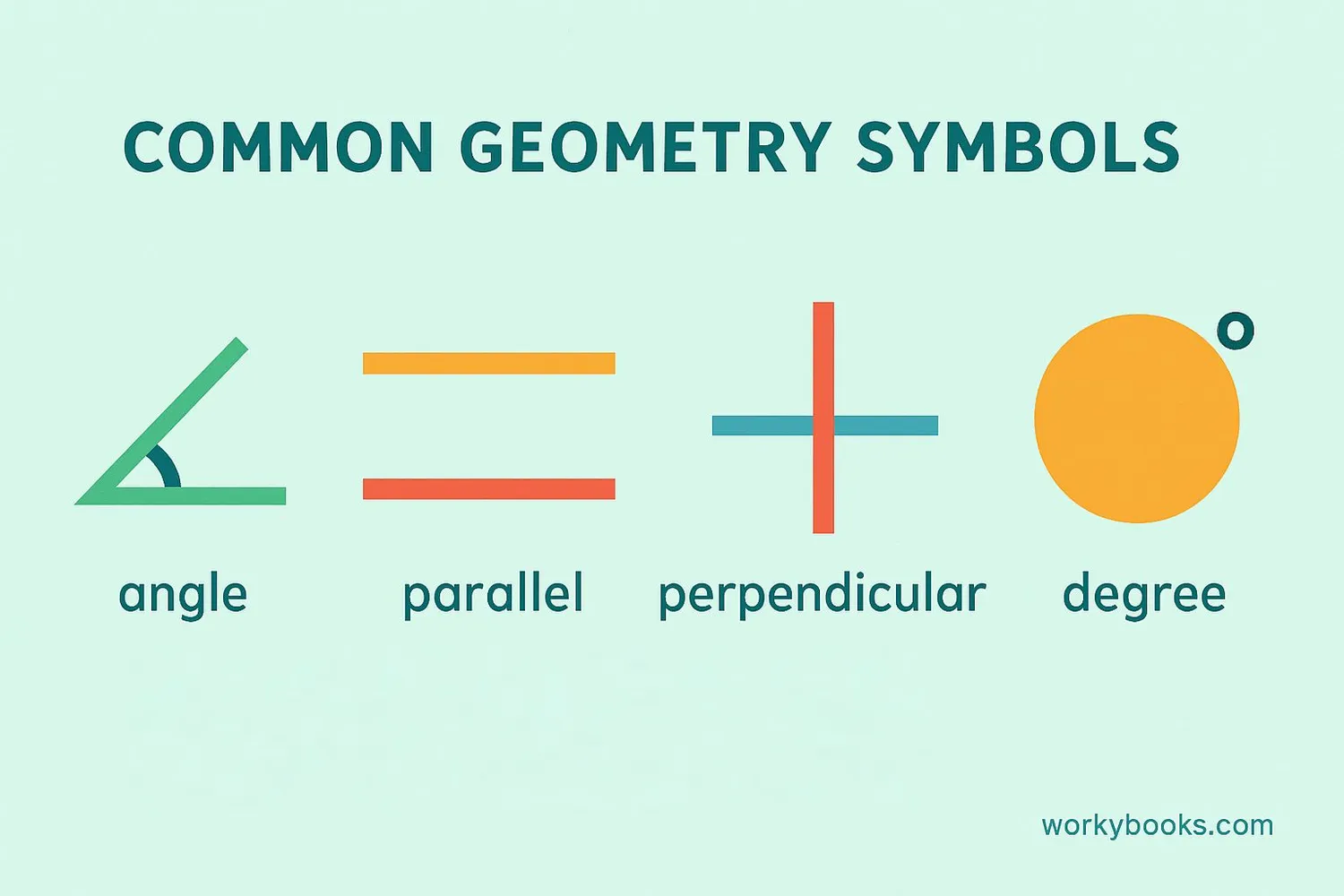
Geometry has its own special symbols that help us describe shapes, angles, and measurements:
The angle symbol shows the space between two intersecting lines.
The degree symbol is used to measure angles and temperature.
The parallel symbol shows that two lines will never meet.
The perpendicular symbol shows that two lines meet at a right angle.
Remember
Geometry symbols help us describe the world around us, from the shapes of buildings to the angles of sports fields.
Math Symbols Quiz
Test your knowledge of math symbols with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about math symbols:
Math Symbols Trivia
Discover interesting facts about math symbols:
Oldest Math Symbols
The plus (+) and minus (−) signs first appeared in print in Johannes Widmann's 1489 book "Mercantile Arithmetic." Before that, mathematicians wrote out words like "plus" and "minus."
Origin of the Equals Sign
The equals sign (=) was invented in 1557 by Robert Recorde, who said he chose two parallel lines because "no two things can be more equal." Before this, people wrote out the word "equals."
Multiplication Symbol
The multiplication symbol (×) was introduced by mathematician William Oughtred in 1631. German mathematician Gottfried Leibniz preferred the dot (·) for multiplication because he thought × looked too much like the letter x.
Division Symbol
The division symbol (÷) is called an obelus. It was first used by Swiss mathematician Johann Rahn in 1659. The symbol combines a dot above and below a horizontal line, representing fractions.





