Multiplying Decimals - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn how to multiply decimals with step-by-step instructions and practice problems!
What are Decimals?
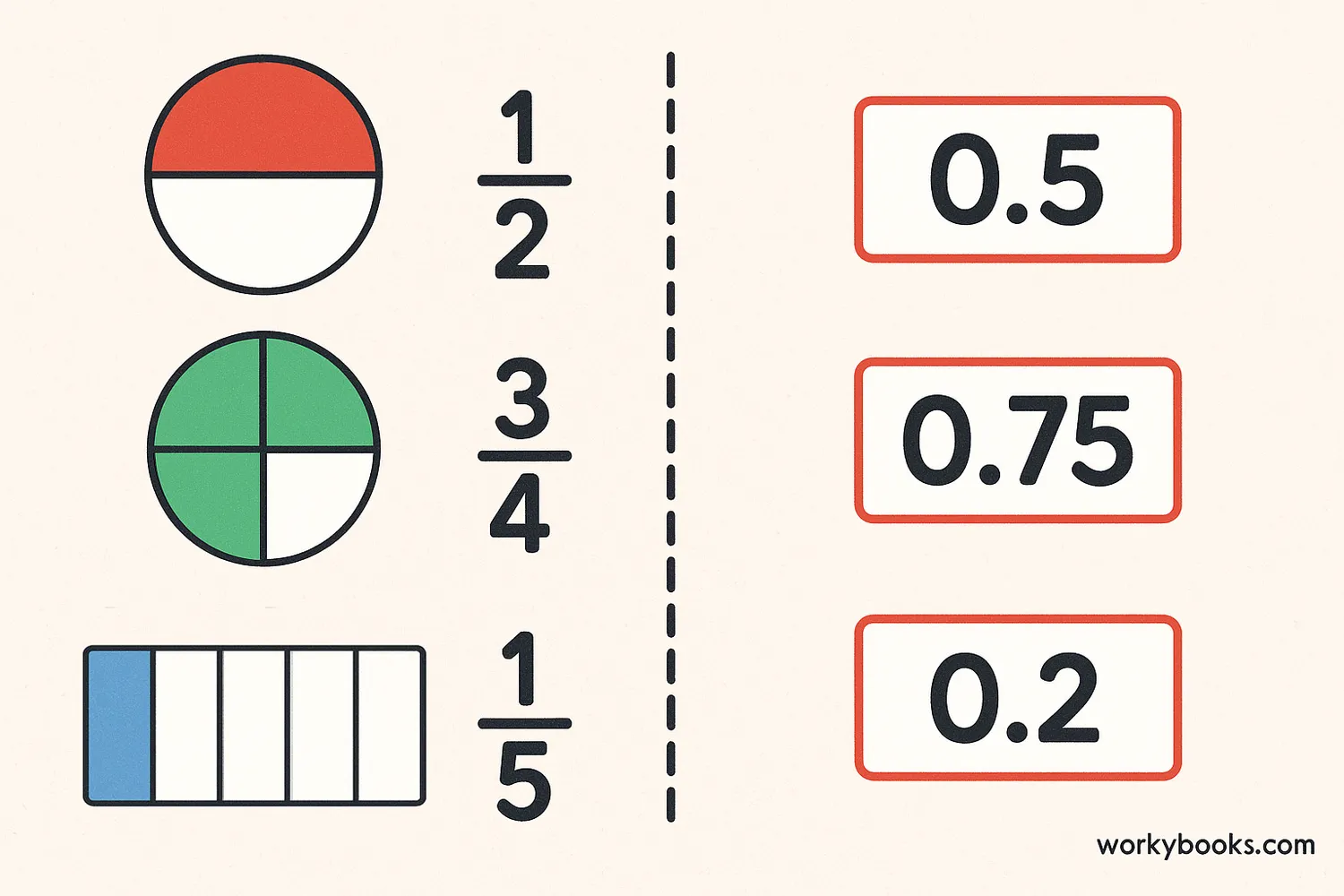
Decimals are numbers that have a whole number part and a fractional part separated by a decimal point. The digits to the right of the decimal point represent values less than one.
For example, the number 3.75 has a whole number part (3) and a fractional part (0.75). The decimal 0.75 means 75 hundredths, which is the same as the fraction 75/100 or 3/4.
Math Fact!
The word "decimal" comes from the Latin word "decimus" meaning "tenth". This is because our decimal system is based on powers of ten.
Multiplying Decimals
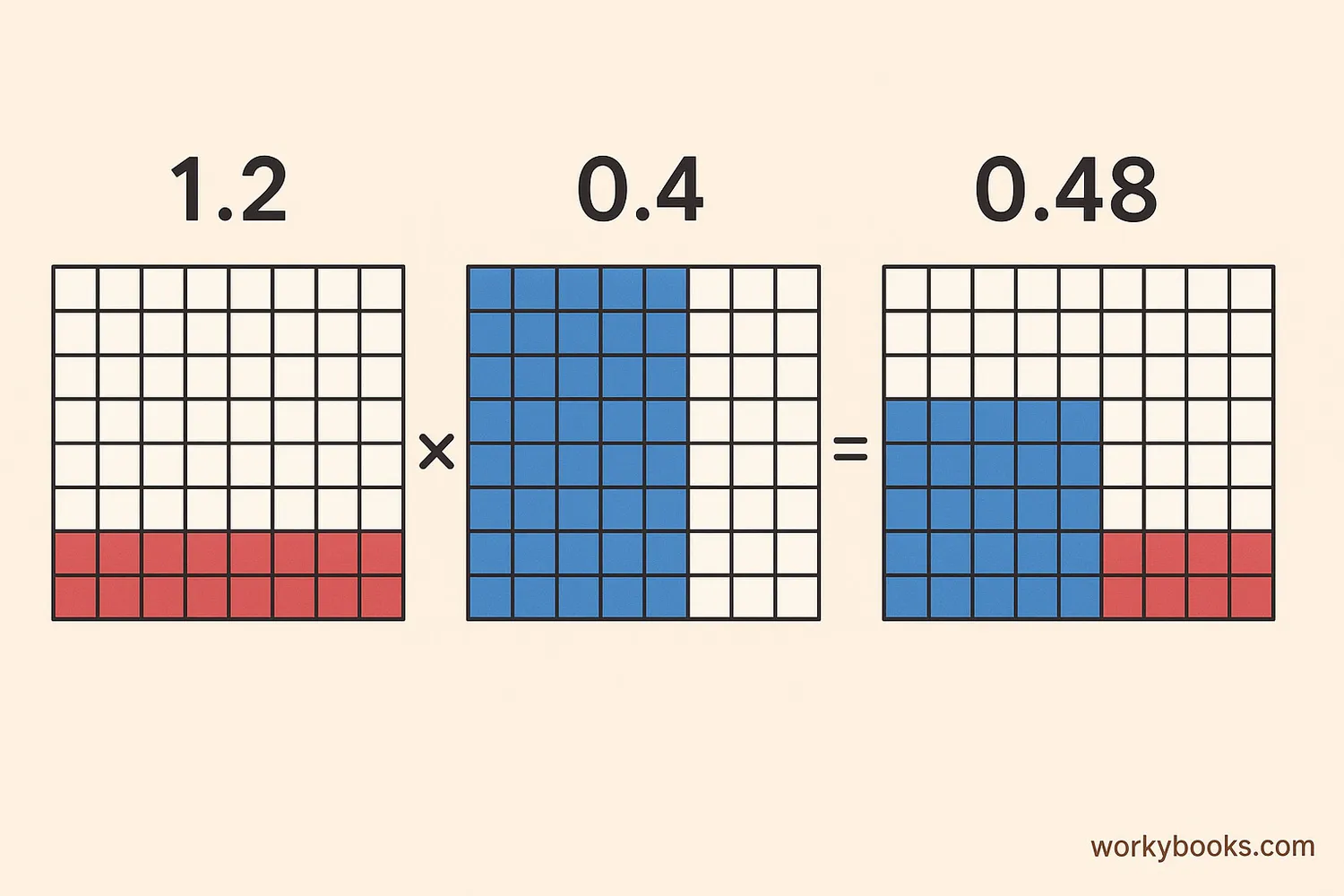
Multiplying decimals might seem tricky at first, but it's very similar to multiplying whole numbers. The key difference is that we need to correctly place the decimal point in our final answer.
When we multiply decimals, we're actually finding a part of a part. For example, 0.5 × 0.2 means "half of 0.2" which equals 0.1.
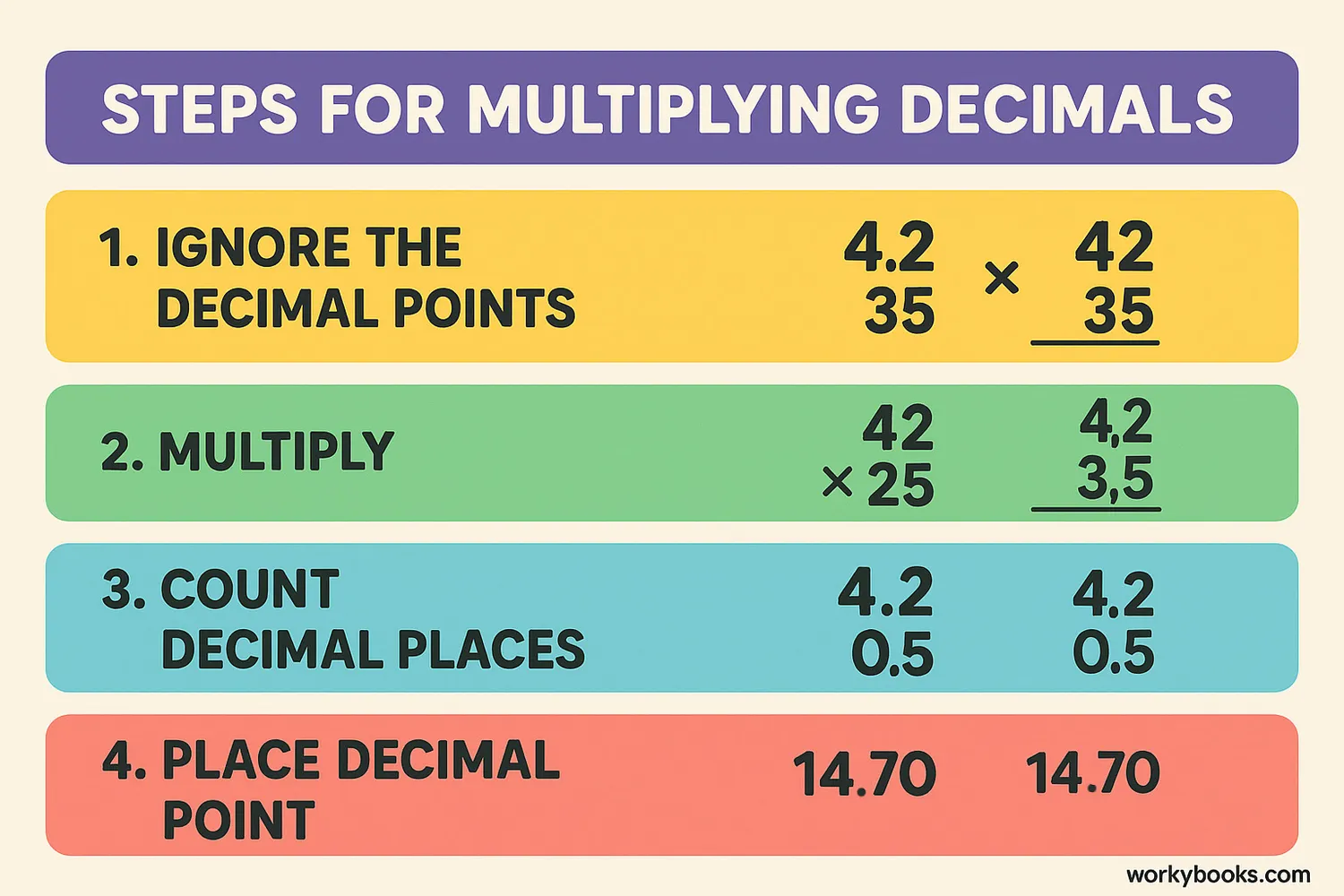
Multiply Normally
Ignore the decimals and multiply the numbers as if they were whole numbers
Count Decimal Places
Count the total number of decimal places in both factors
Place Decimal Point
Place the decimal point in the product so it has the same number of decimal places
Step-by-Step Examples
Let's work through some examples to see how decimal multiplication works in practice:
Example 1: 0.4 × 0.6
Example 2: 1.25 × 0.8
Example 3: 2.34 × 1.5
Practice Problems

Now it's your turn to try some practice problems. Remember the three steps: multiply normally, count decimal places, and place the decimal point.
Try These Problems:
Tip!
You can check your decimal multiplication by estimating. For example, 0.7 × 0.3 should be about 0.21 because 7×3=21 and you need two decimal places.
Decimal Multiplication Quiz
Test your decimal multiplication skills with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about multiplying decimals:
Math Trivia
Discover some interesting facts about decimals and mathematics!
Decimal History
The decimal system was first developed by ancient civilizations including the Egyptians, Babylonians, and Chinese. However, the modern decimal point was popularized by Scottish mathematician John Napier in the early 17th century.
Universal System
While most of the world uses the decimal system (base-10), some cultures have used other number systems. The ancient Mayans used a base-20 system, and computers use binary (base-2) and hexadecimal (base-16) systems.
Money and Decimals
Money is one of the most common everyday uses of decimals. When you see a price like $3.99, you're looking at a decimal number! The decimal point separates dollars from cents, with 100 cents making one whole dollar.
Metric System
The metric system is based on decimals, which makes conversions easy. For example, there are 100 centimeters in a meter and 1000 meters in a kilometer. This decimal-based system is used by most countries around the world.





