Natural Numbers - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about counting numbers with clear explanations, examples, and practice activities
What Are Natural Numbers?

Natural numbers are the counting numbers we use every day. They start from 1 and go up forever: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and so on. These are the first numbers you learned when you started counting!
Natural numbers are also called counting numbers because we use them to count objects. For example, if you have 3 apples or 5 pencils, you're using natural numbers.
Natural numbers are different from:
- Whole numbers - These include 0 along with natural numbers (0, 1, 2, 3...)
- Integers - These include negative numbers too (-2, -1, 0, 1, 2...)
Key Concept
Natural numbers = Counting numbers = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ... and so on forever!
Properties of Natural Numbers

Natural numbers have special properties that make them unique:
1. They start at 1: The smallest natural number is 1. There is no largest natural number - they go on forever!
2. They are positive: Natural numbers are always greater than zero. They don't include negative numbers or fractions.
3. They are whole: Natural numbers don't have fractions or decimals. You can't have 2.5 apples when counting!
4. They are ordered: Each natural number has a clear next number (2 comes after 1, 3 comes after 2, etc.).
5. They are infinite: No matter how big a number you think of, you can always add 1 to make a bigger natural number.
Remember
Zero (0) is not a natural number. Natural numbers begin at 1.
Operations with Natural Numbers
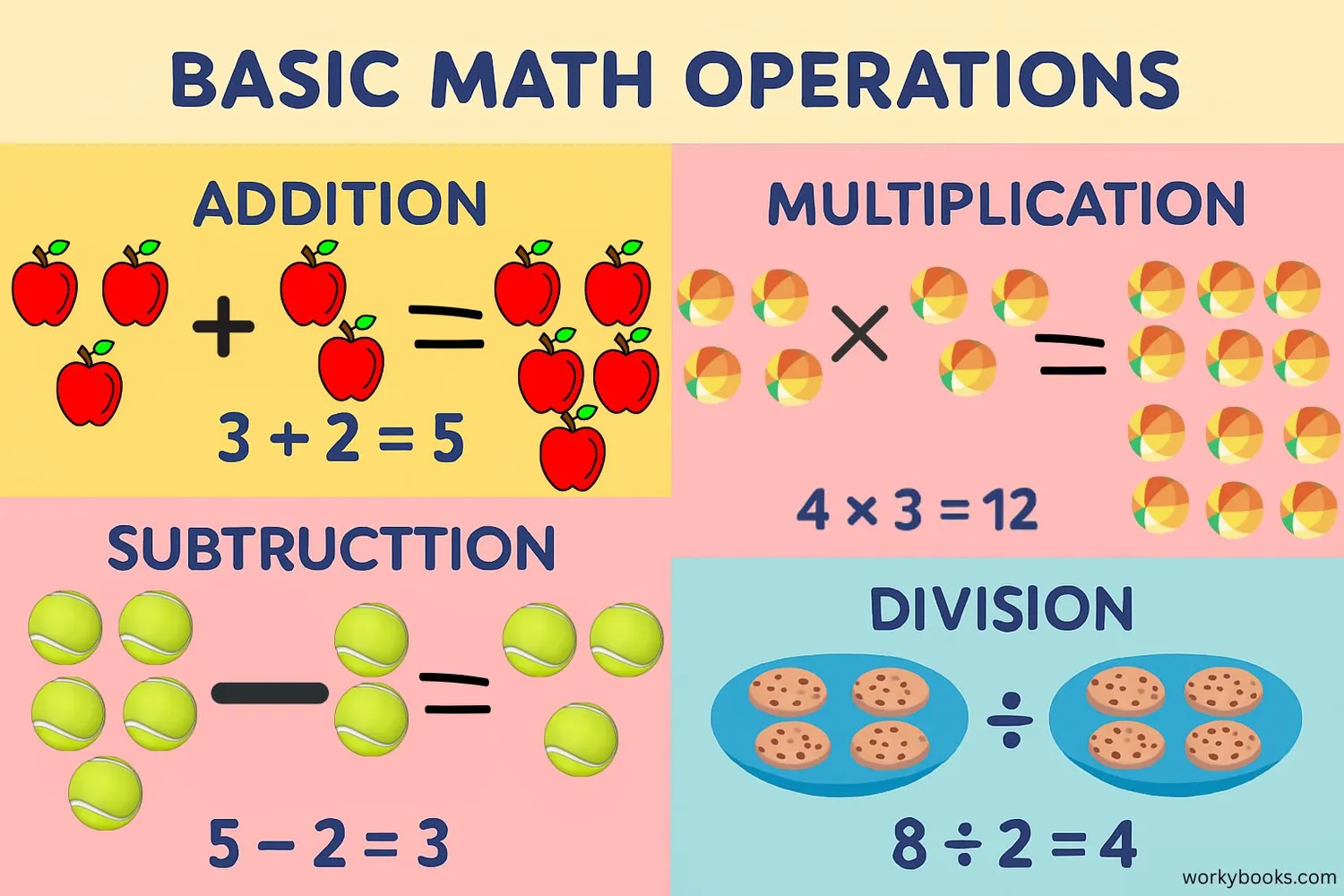
We can perform four basic operations with natural numbers:
Addition (+): Combining numbers to find a total
Example: 3 + 4 = 7 (adding 3 apples and 4 apples gives 7 apples)
Subtraction (-): Taking one number away from another
Example: 8 - 3 = 5 (if you have 8 cookies and eat 3, you have 5 left)
Multiplication (×): Repeated addition
Example: 4 × 3 = 12 (4 groups of 3 pencils each equals 12 pencils)
Division (÷): Sharing or grouping equally
Example: 10 ÷ 2 = 5 (10 candies shared equally between 2 friends gives each 5 candies)
Important Note
Subtraction and division with natural numbers don't always give natural numbers as results (e.g., 3 - 5 or 5 ÷ 2).
Natural Numbers on a Number Line
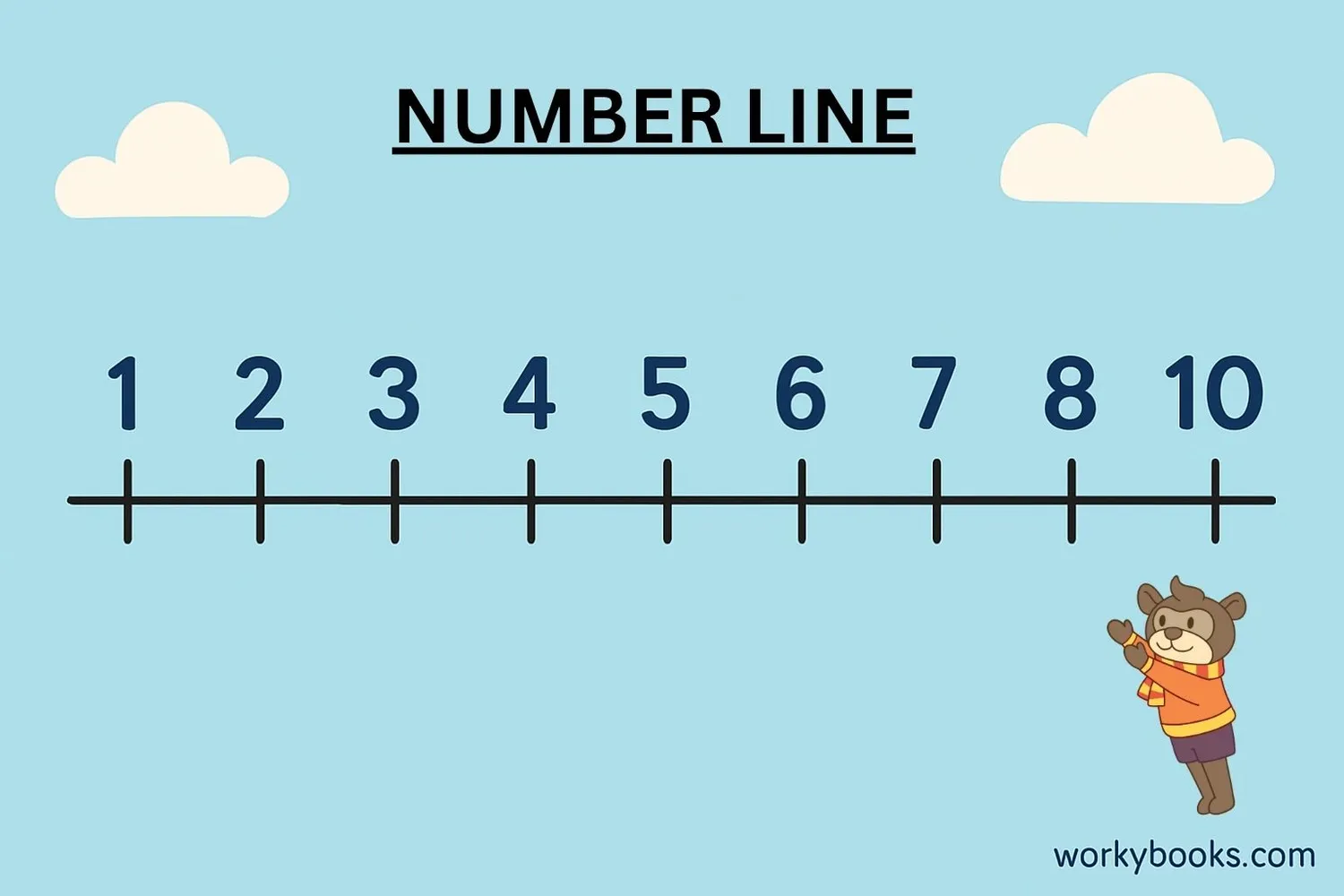
A number line helps us visualize natural numbers and their relationships:
1. Equal spacing: Each natural number is the same distance apart on the line.
2. Increasing order: Numbers get larger as you move to the right.
3. No end: The line continues forever to the right with higher numbers.
4. No left of 1: There are no natural numbers to the left of 1 on the line.
Number lines help us understand:
- Which number is greater or smaller
- How far apart numbers are
- Addition (moving right) and subtraction (moving left)
Try This
Draw your own number line from 1 to 10 and practice jumping forward for addition and backward for subtraction!
Natural Numbers Quiz
Test your understanding of natural numbers with these questions. Choose the best answer for each.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about natural numbers:
Number Trivia
Discover interesting facts about numbers and counting:
First Number System
The earliest known number system was used by the Sumerians around 3000 BC. They used a base-60 system (sexagesimal) which is why we have 60 seconds in a minute and 60 minutes in an hour.
Prime Numbers
Prime numbers are natural numbers greater than 1 that can only be divided by 1 and themselves. The smallest prime number is 2, which is also the only even prime number.
Finger Counting
Many ancient cultures developed counting systems based on fingers. Some cultures could count up to 10,000 using finger positions and gestures!
Really Big Numbers
The largest named number is the "googolplex," which is a 1 followed by a googol zeros. A googol is already a 1 followed by 100 zeros - that's more than all the particles in the universe!





