Number - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Understanding Numbers and How We Use Them in Mathematics
What is a Number?

A number is a mathematical idea that represents quantity, value, or count. Think of numbers as special symbols that help us answer questions like "How many?" or "How much?"
Numbers are all around us! We use them to count objects, tell time, measure ingredients for recipes, and even when playing games. Numbers help us understand and describe our world in a precise way.
Math Fact!
The symbols we use for numbers (0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9) are called digits. These digits can be combined to make any number, no matter how big or small!
Types of Numbers
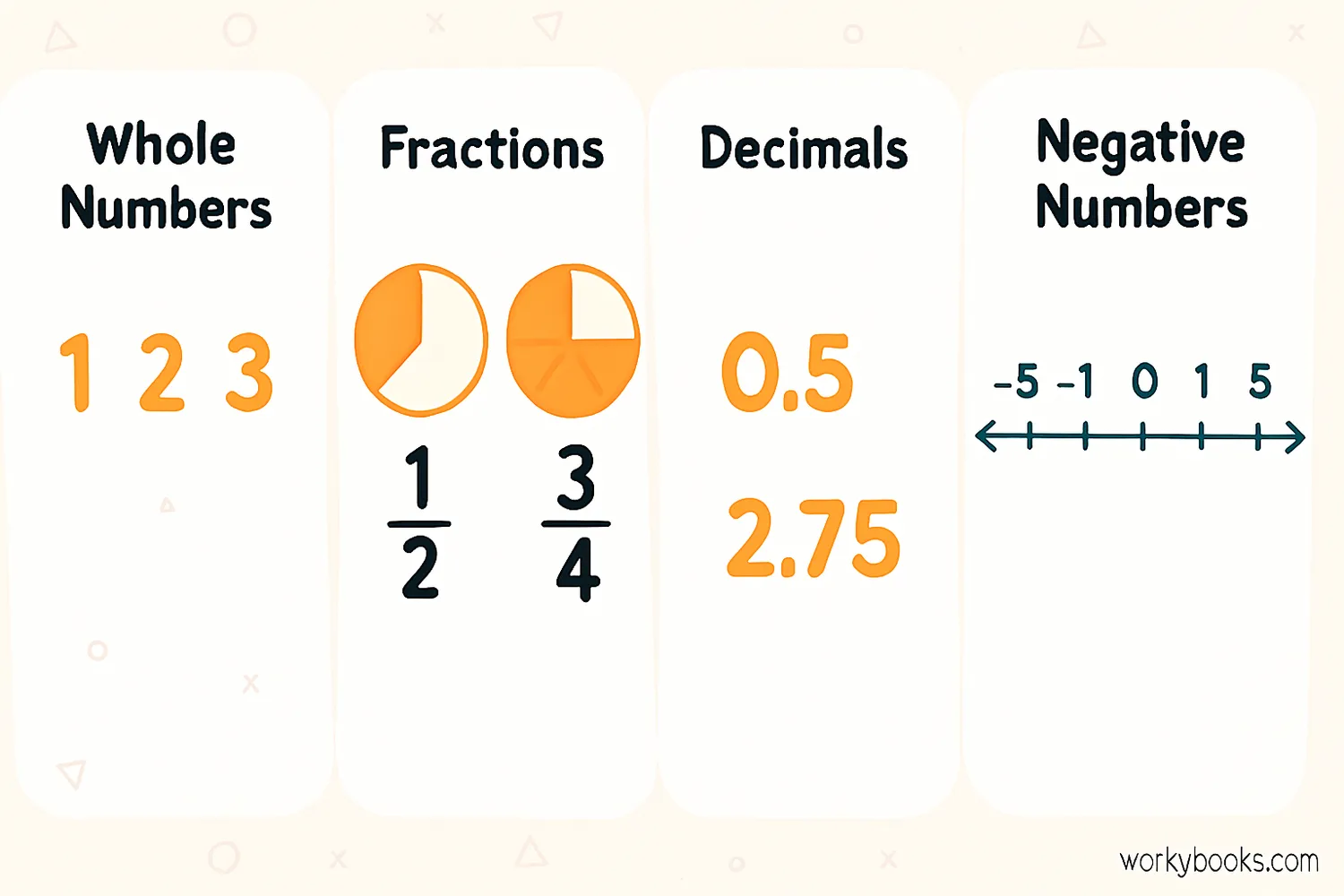
Numbers come in different types, each with special properties and uses. As you learn more math, you'll discover these different number families:
Counting Numbers
1, 2, 3, 4... (also called natural numbers)
Whole Numbers
0, 1, 2, 3, 4... (counting numbers plus zero)
Integers
...-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3... (positive and negative whole numbers)
Fractions
Parts of whole numbers like ½ or ¾
Decimals
Numbers with decimal points like 2.5 or 0.75
Each type of number helps us solve different kinds of problems. Counting numbers help us count objects, fractions help us share things equally, and negative numbers help us measure things like temperature below zero.
Number Sense
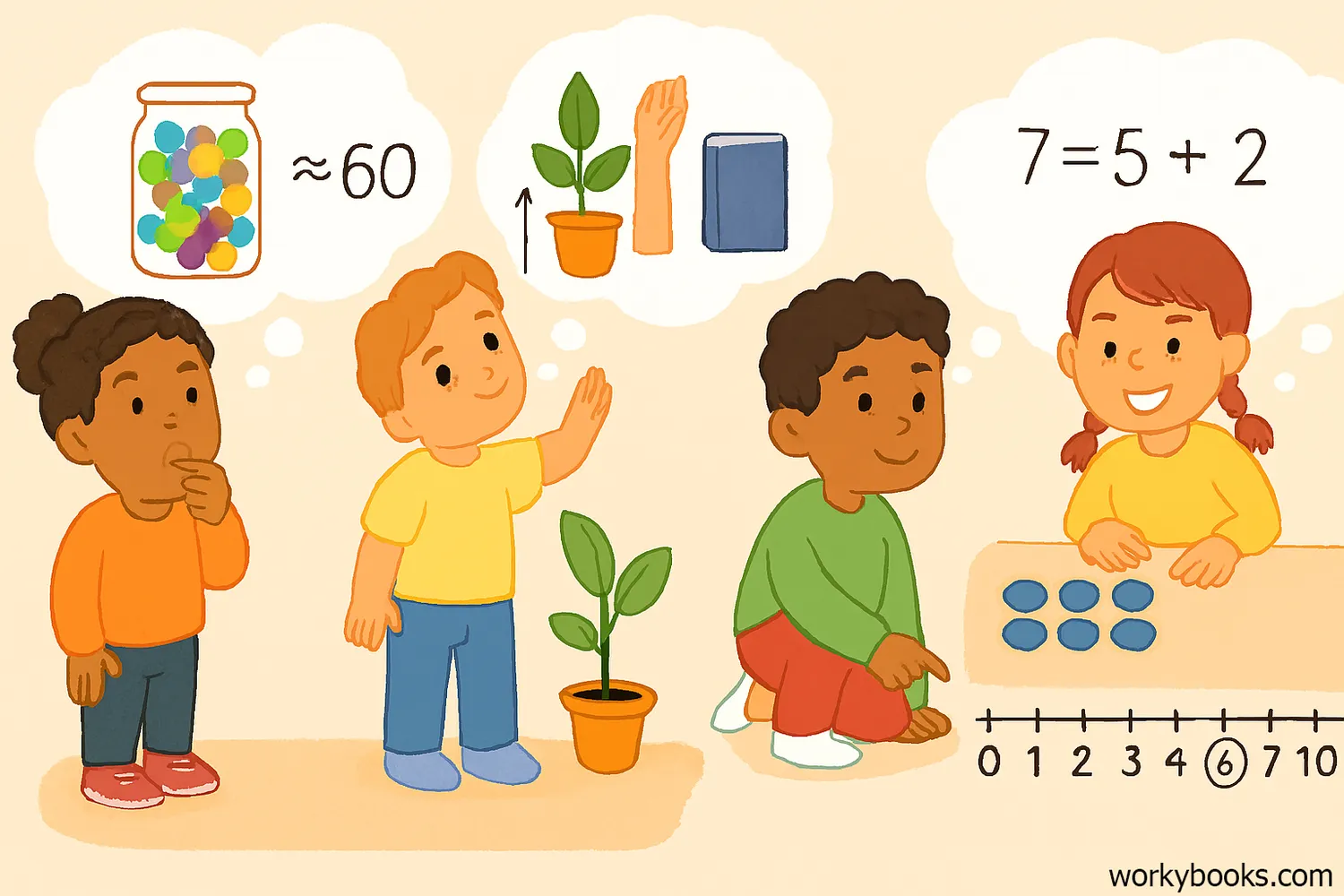
Number sense is our ability to understand numbers and how they work together. It's like having a "feel" for numbers! People with good number sense can:
Compare Numbers
Understand which is larger or smaller
Estimate
Make good guesses about quantities
Break Numbers Apart
See that 7 can be 5+2 or 6+1
Developing strong number sense helps you become better at math because you understand what numbers mean, not just how to calculate with them. It's the foundation for all higher math skills!
Did You Know?
Number sense begins developing in infancy! Even babies have a basic understanding of small quantities and can tell the difference between one, two, and three objects.
Number System
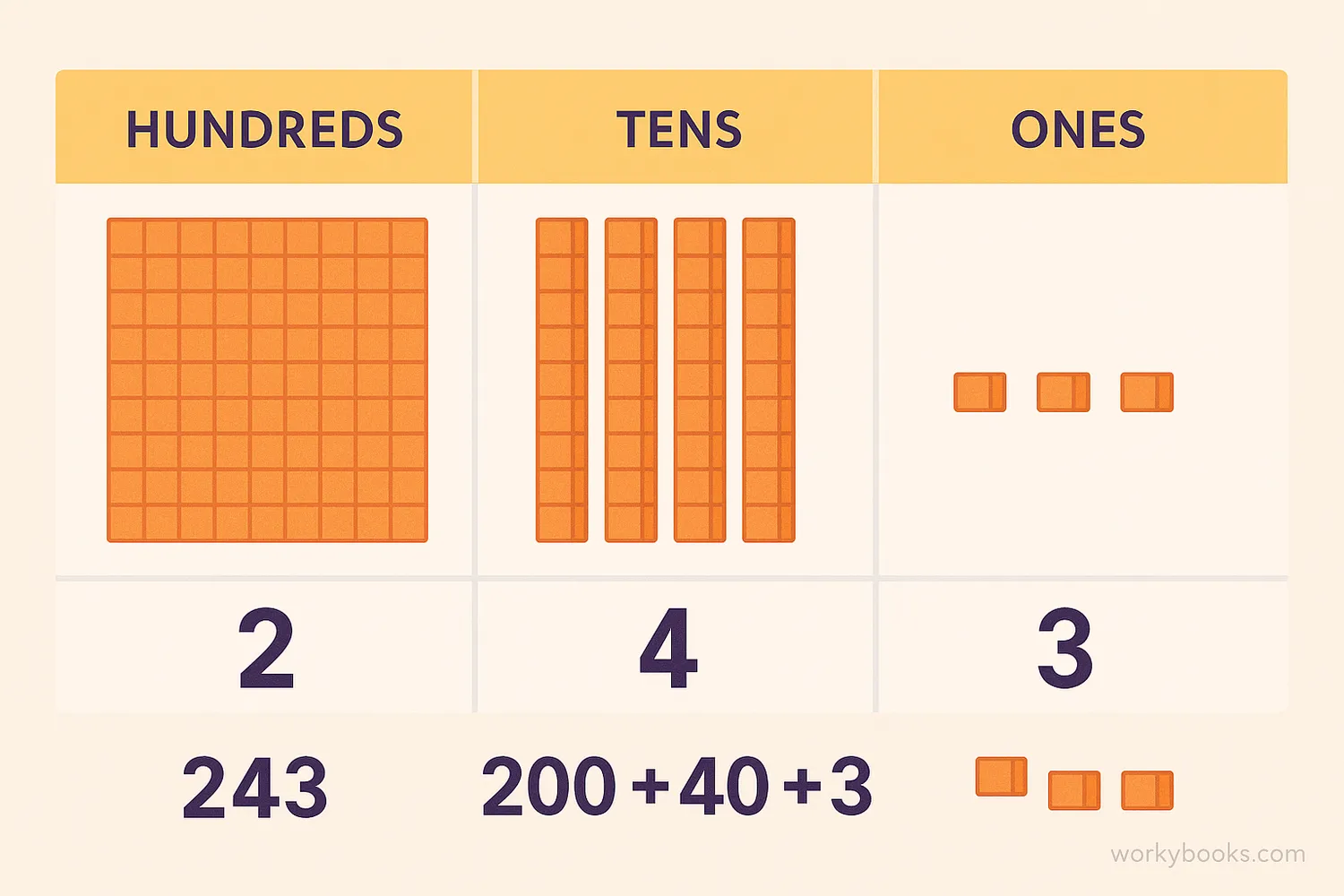
Our number system is called a base-10 or decimal system. This means we use ten digits (0-9) and organize numbers based on powers of ten. The position of a digit in a number determines its value - this is called place value.
Ones Place
The rightmost digit (0-9)
Tens Place
10 times the value of the digit
Hundreds Place
100 times the value of the digit
Thousands Place
1,000 times the value of the digit
Decimal Point
Separates whole numbers from parts
For example, in the number 3,452:
• The 2 is in the ones place (2)
• The 5 is in the tens place (50)
• The 4 is in the hundreds place (400)
• The 3 is in the thousands place (3,000)
History Fact!
The number system we use today is called the Hindu-Arabic numeral system. It was developed in India around the 6th century and later adopted by Arabic mathematicians before spreading to Europe.
Number Quiz
Test your knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned about numbers.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about numbers:
Math Facts About Numbers
Discover some fascinating facts about numbers and number systems!
Zero's Journey
The concept of zero took a long time to develop! Ancient Babylonians had a placeholder zero around 300 BCE, but the number zero as we know it today was developed in India around the 5th century CE.
Really Big Numbers
A "googol" is the number 1 followed by 100 zeros! It's so large that there aren't even that many particles in the entire observable universe. The company Google got its name from this number.
Prime Numbers
Prime numbers (numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves) are like the building blocks of all numbers. Every whole number greater than 1 is either prime or can be made by multiplying primes together!
Nature's Numbers
The Fibonacci sequence (0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13...) appears often in nature! You can find these numbers in the arrangement of leaves on a stem, the pattern of seeds in a sunflower, and the spiral of a nautilus shell.





