Number Properties - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Understanding How Numbers Work with Special Math Rules
What Are Number Properties?
Number properties are special rules that numbers follow in mathematics. Think of them as the personality traits of numbers! These rules help us understand how numbers behave when we add, subtract, multiply, or divide them.
Just like people have certain characteristics that make them unique, numbers have properties that always stay true no matter what numbers we use. Learning these properties helps make math easier and more predictable!
Math Fact!
Number properties work for all real numbers - that means they're true for whole numbers, fractions, decimals, and even negative numbers!
Commutative Property
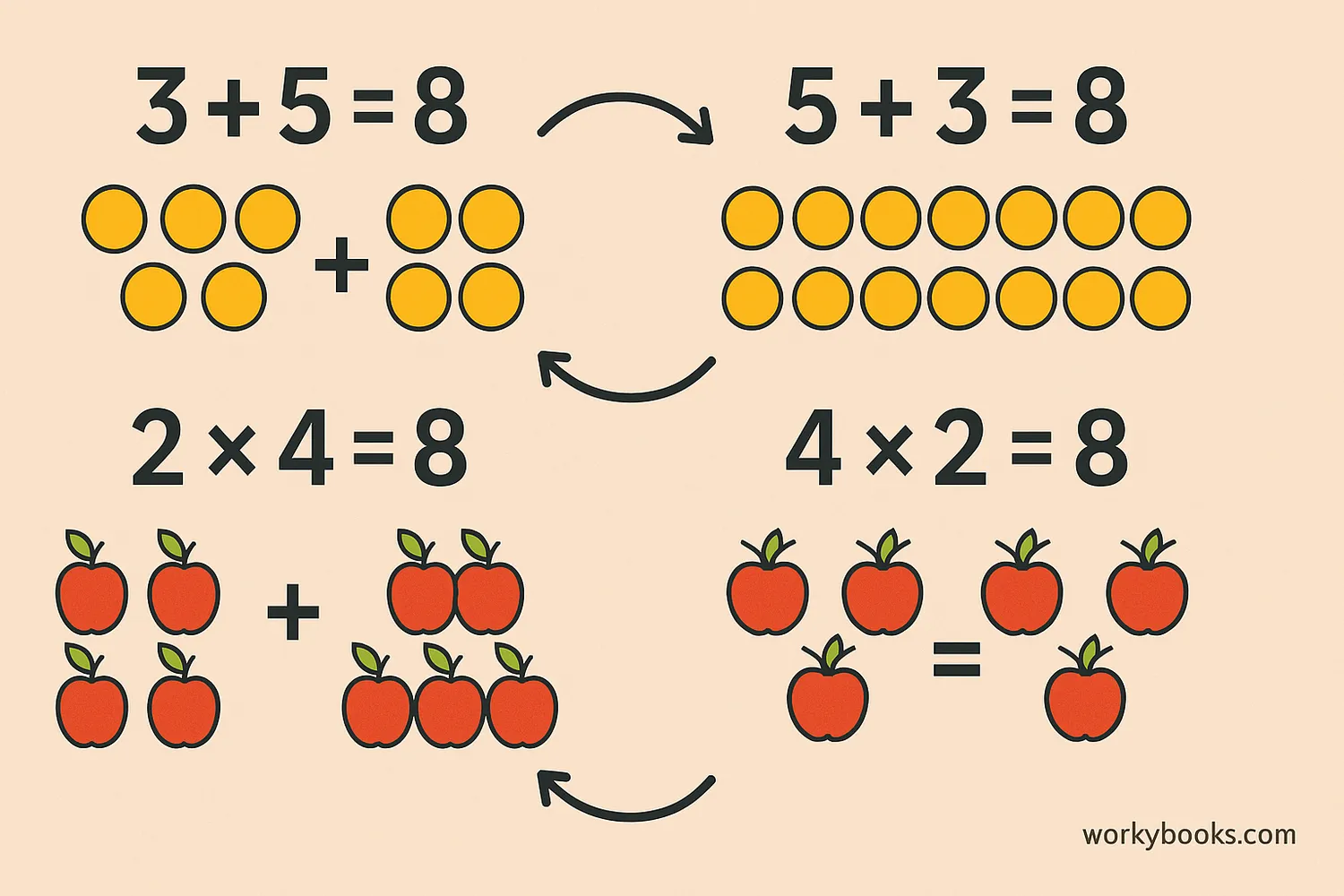
The commutative property tells us that we can change the order of numbers when we add or multiply them without changing the result. The word "commutative" comes from "commute," which means to travel or change places.
5 + 3 = 8 and 3 + 5 = 8
The order changed, but the sum stayed the same!
4 × 6 = 24 and 6 × 4 = 24
The order changed, but the product stayed the same!
Remember!
The commutative property does NOT work for subtraction or division. 8 - 3 is not the same as 3 - 8, and 12 ÷ 4 is not the same as 4 ÷ 12.
Associative Property
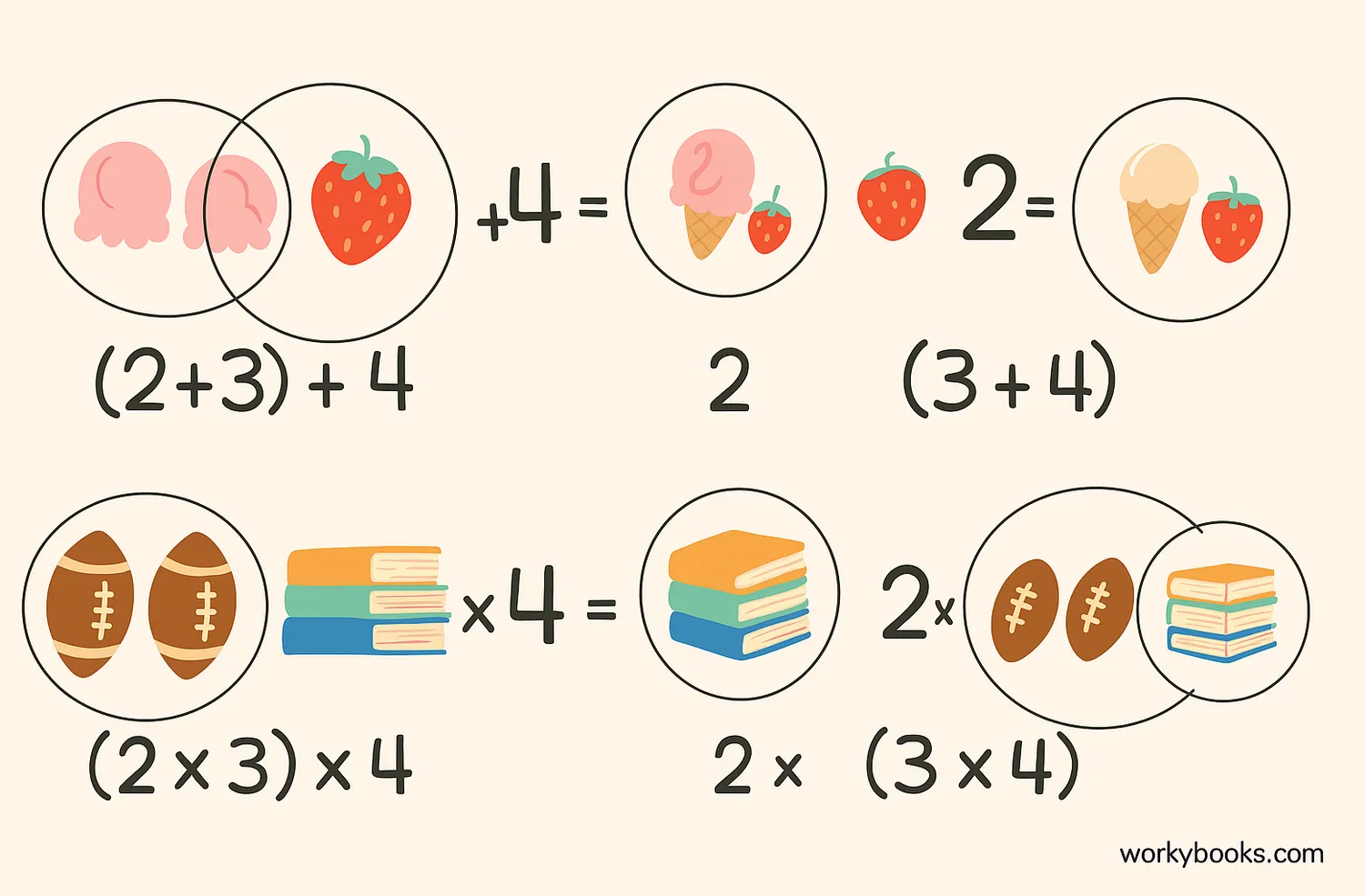
The associative property tells us that how we group numbers when we add or multiply them doesn't change the result. The word "associative" comes from "associate," which means to group together.
(2 + 3) + 4 = 2 + (3 + 4)
5 + 4 = 2 + 7
9 = 9
(2 × 3) × 4 = 2 × (3 × 4)
6 × 4 = 2 × 12
24 = 24
Remember!
Like the commutative property, the associative property does NOT work for subtraction or division. Changing the grouping in subtraction or division changes the result.
Distributive Property
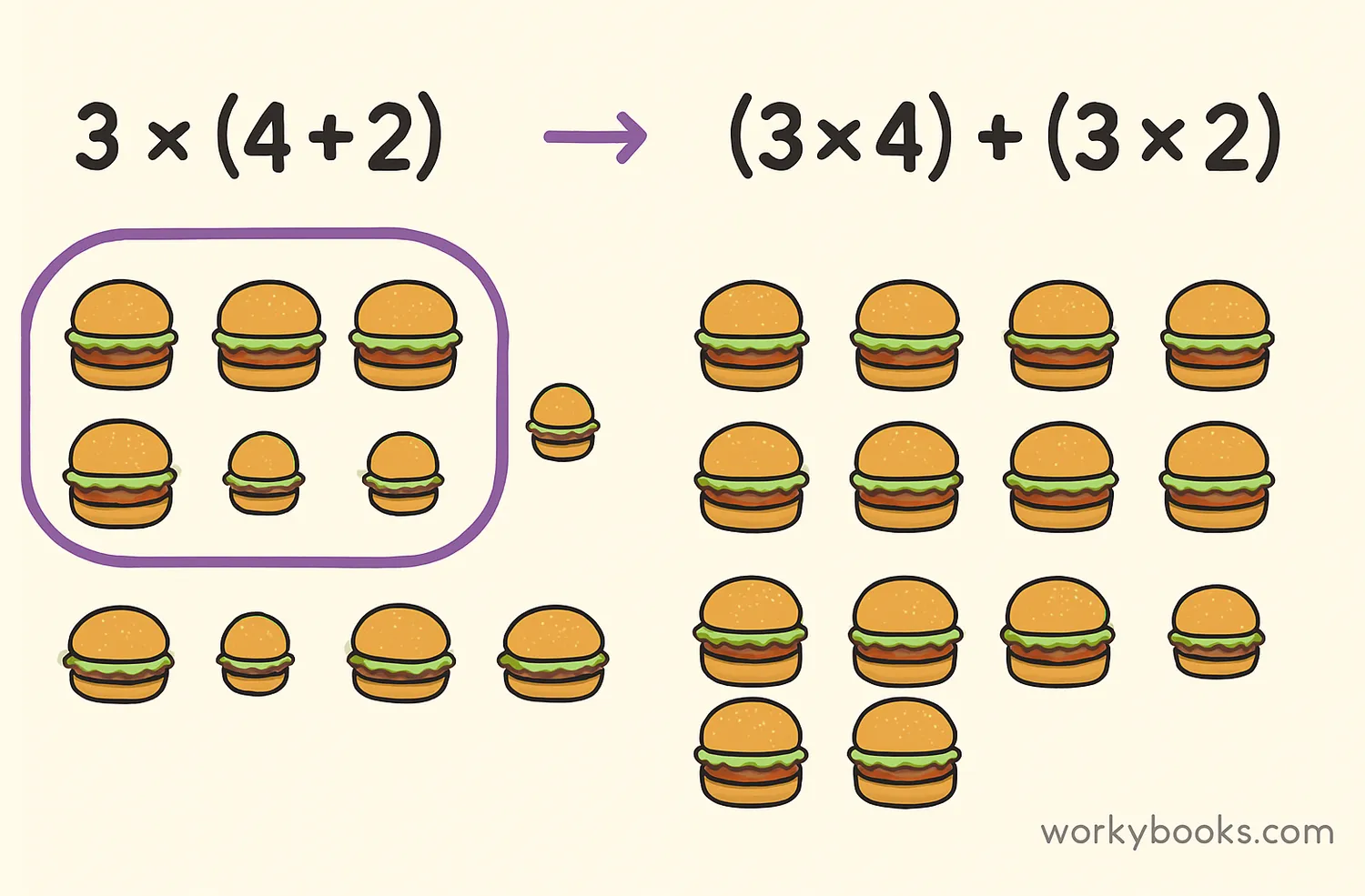
The distributive property tells us that multiplying a number by a sum is the same as multiplying the number by each part of the sum and then adding the results. It "distributes" the multiplication over addition.
3 × (4 + 2) = (3 × 4) + (3 × 2)
3 × 6 = 12 + 6
18 = 18
The distributive property helps us solve problems with larger numbers more easily. For example:
7 × 13 = 7 × (10 + 3) = (7 × 10) + (7 × 3) = 70 + 21 = 91
Did You Know?
The distributive property also works with multiplication over subtraction: a × (b - c) = (a × b) - (a × c)
Identity Property
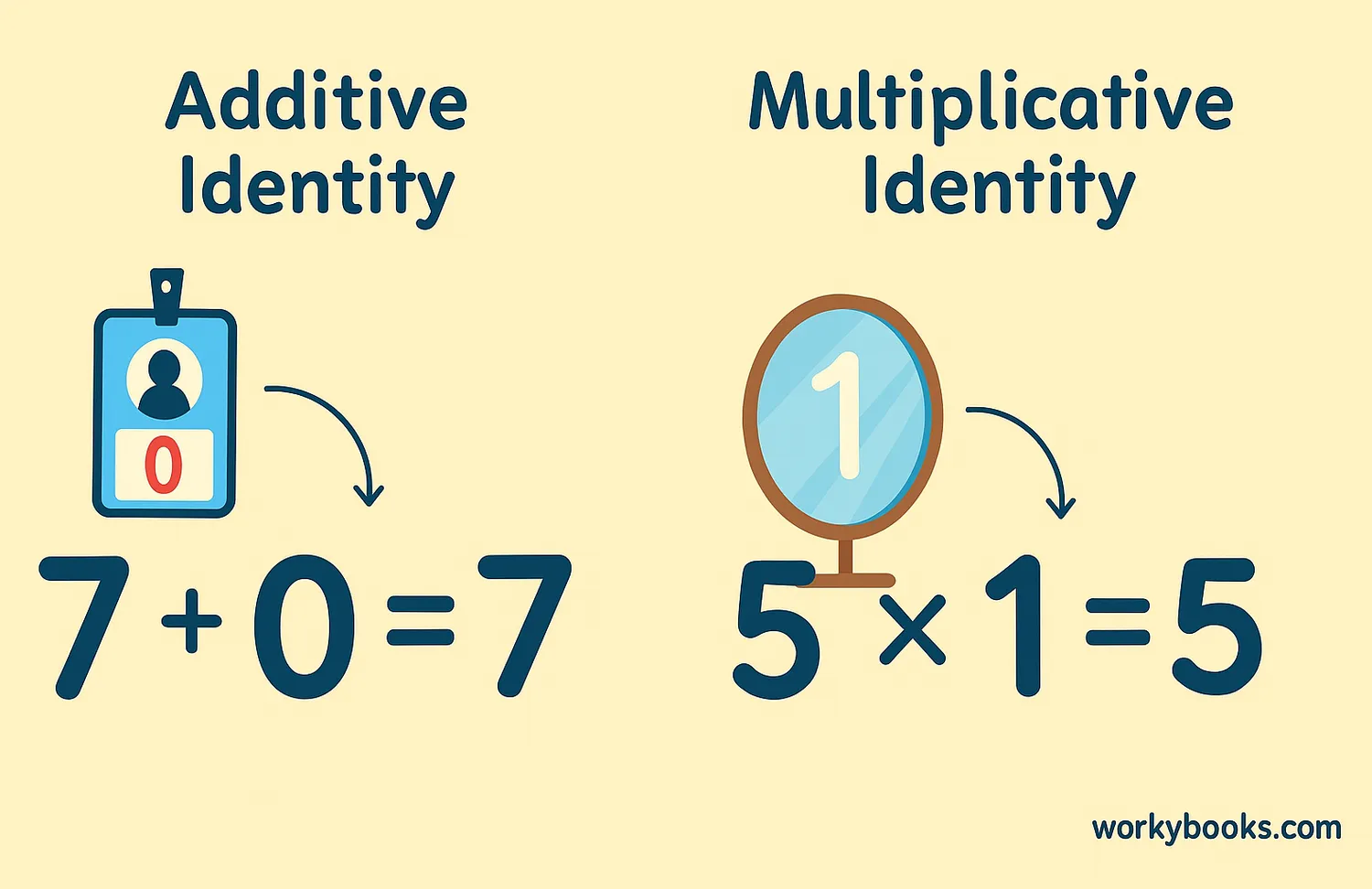
The identity property tells us that there are special numbers that don't change other numbers when we use them in operations. These numbers protect the "identity" of the original number.
Additive Identity
Adding zero to any number doesn't change it: a + 0 = a
Example: 7 + 0 = 7
Multiplicative Identity
Multiplying any number by one doesn't change it: a × 1 = a
Example: 5 × 1 = 5
Special Numbers
Zero is called the additive identity, and one is called the multiplicative identity. These numbers are special because they don't change other numbers in their operations.
Number Properties Quiz
Test your knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned about number properties.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about number properties:
Math Facts About Number Properties
Discover some fascinating facts about number properties and mathematics!
Historical Origins
The concept of number properties dates back to ancient mathematicians. The commutative property was first recorded by the Egyptians around 1800 BC, while the distributive property was formally described by Greek mathematicians.
Special Zero
Zero is a special number in mathematics. It wasn't always recognized as a number - ancient number systems like Roman numerals didn't have a symbol for zero. The concept of zero as a number originated in India around the 5th century.
Algebra Connection
Number properties form the foundation of algebra. When we solve equations like x + 3 = 7 by subtracting 3 from both sides, we're using properties of equality that are based on the number properties we learn in elementary school.
Real-World Applications
Number properties are used every day in many professions. Accountants use them for financial calculations, engineers use them in design work, and computer scientists use them when writing algorithms and programming.





