Perpendicular Bisector - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about this important geometric concept with clear explanations and interactive activities
What is a Perpendicular Bisector?
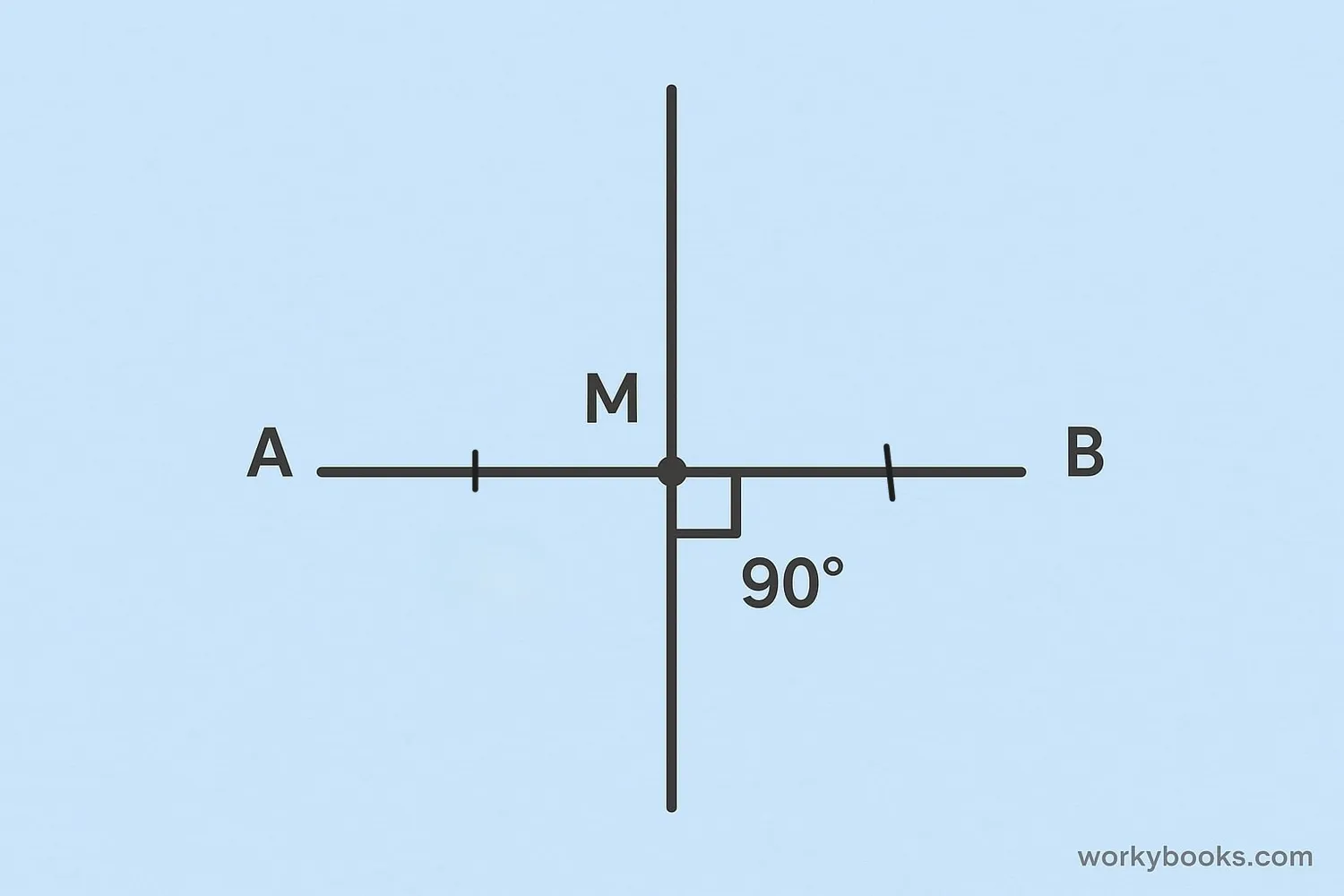
A perpendicular bisector is a special line that:
1. Crosses a line segment at a 90-degree angle (perpendicular)
2. Splits the segment into two equal parts (bisector)
Imagine you have a straight path between two trees. The perpendicular bisector would be another path that crosses exactly at the middle point between the trees and forms perfect right angles with the first path.
Every line segment has exactly one perpendicular bisector. This special line is very useful in geometry for finding equal distances and creating symmetrical shapes.
Key Concept
Perpendicular bisectors create symmetry. Any point on the bisector is exactly the same distance from both endpoints of the segment.
Perpendicular Bisector Theorem
The Perpendicular Bisector Theorem states:
Perpendicular Bisector Theorem
• If point P is on the perpendicular bisector of segment AB,
• Then PA = PB (the distance to A equals the distance to B)
Example: Imagine two houses (A and B). The perpendicular bisector of the line connecting them is the set of all points that are exactly the same distance from both houses. This could be useful for placing something equally accessible to both!
Remember
The theorem works both ways: If a point is equidistant from two points, it must lie on their perpendicular bisector.
How to Construct a Perpendicular Bisector
You can construct a perpendicular bisector using just a compass and straightedge. Here's how:
Draw a line segment AB
Place compass on A, set width greater than half of AB, draw arcs above and below
Without changing compass width, place on B and draw arcs intersecting the first ones
Draw a straight line through the two intersection points - this is your perpendicular bisector!
This method works because the points where the arcs intersect are exactly the same distance from both A and B, so the line connecting them must be the perpendicular bisector.
Perpendicular Bisector in a Triangle
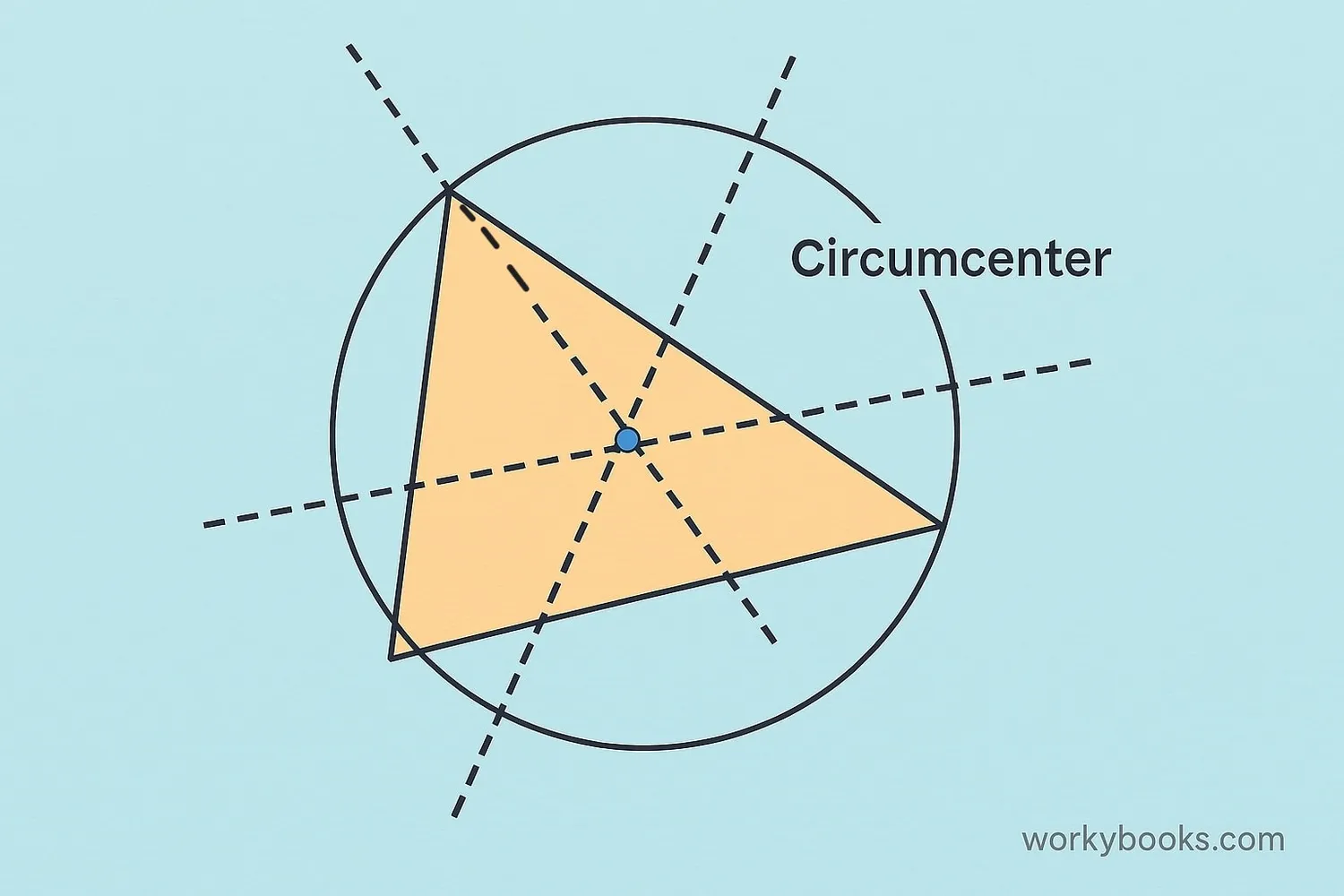
In a triangle, the perpendicular bisectors of the three sides have a special relationship:
• All three perpendicular bisectors intersect at a single point called the circumcenter
• This circumcenter is equidistant from all three vertices of the triangle
• You can draw a circle (circumcircle) centered at the circumcenter that passes through all three vertices
Different triangles:
• In acute triangles: circumcenter is inside the triangle
• In right triangles: circumcenter is at the midpoint of the hypotenuse
• In obtuse triangles: circumcenter is outside the triangle
Remember
The circumcenter is the center of the only circle that passes through all three vertices of a triangle.
Perpendicular Bisector of a Chord
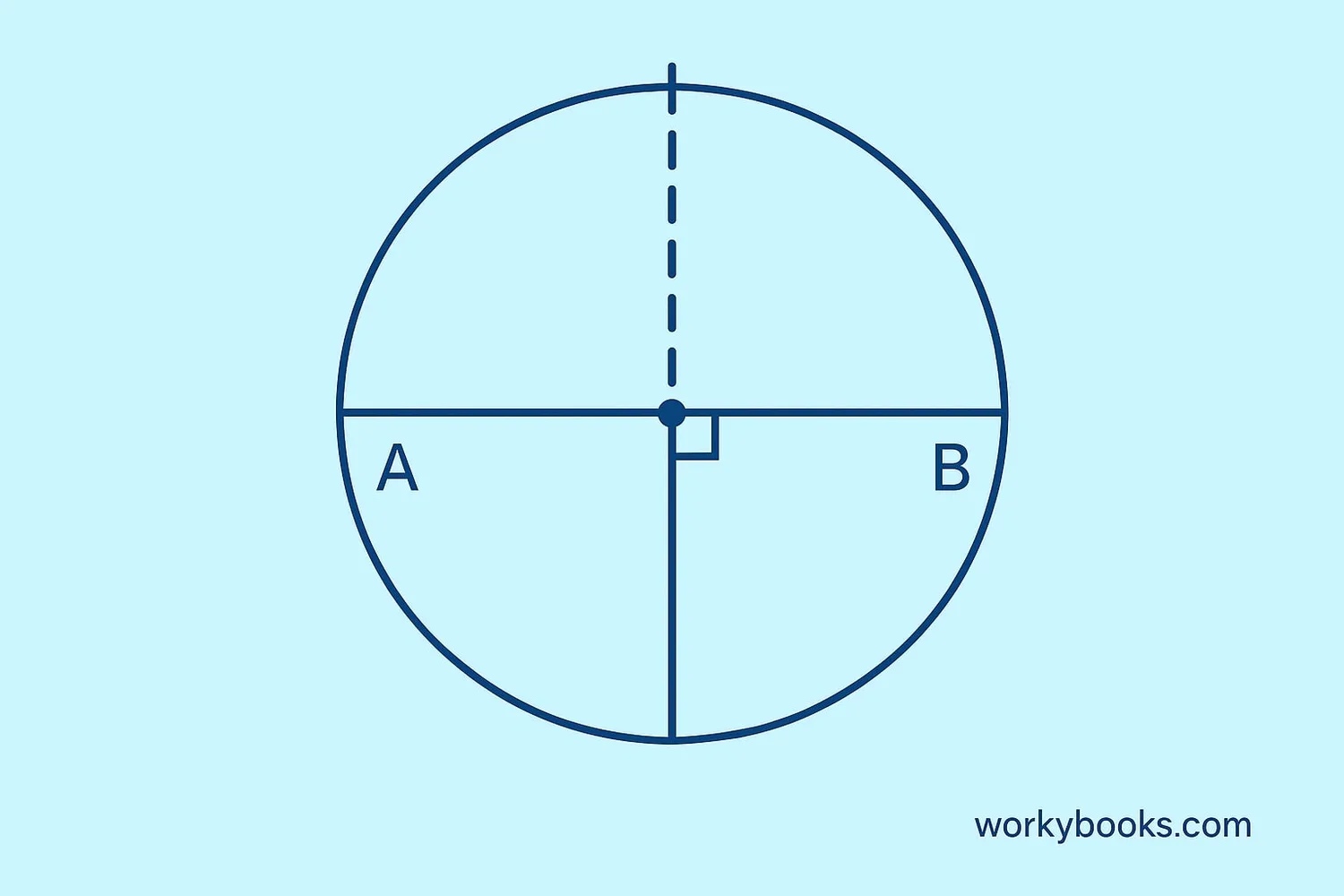
A chord is a straight line connecting two points on a circle. The perpendicular bisector of any chord has special properties:
• The perpendicular bisector of a chord passes through the center of the circle
• If a radius is perpendicular to a chord, it bisects the chord
• The center of a circle is the intersection point of the perpendicular bisectors of any two chords
Example: If you know two chords of a circle, you can find the center by constructing the perpendicular bisectors of both chords. Where they intersect is the circle's center!
Key Concept
In a circle, the perpendicular distance from the center to a chord determines the chord's length. The shorter the distance, the longer the chord.
Converse of the Perpendicular Bisector Theorem
The converse of the Perpendicular Bisector Theorem states:
Converse Theorem
• If PA = PB (distance to A equals distance to B)
• Then point P must lie on the perpendicular bisector of segment AB
This theorem is useful for proving that points lie on certain lines and for solving location problems where equal distances are important.
Application
This theorem helps find the set of all points that are equal distance from two fixed points - which forms the perpendicular bisector.
Perpendicular Bisector Quiz
Test your knowledge with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about perpendicular bisectors:
Geometry Trivia
Discover interesting facts about geometry and perpendicular bisectors:
Ancient Origins
The concept of perpendicular bisectors dates back to ancient Egypt, where surveyors called "rope-stretchers" used these principles to re-establish field boundaries after Nile floods.
Circle Connection
In a circle, the perpendicular bisector of any chord always passes through the center. This property was used by ancient astronomers to calculate planetary orbits.
GPS Technology
Modern GPS systems use perpendicular bisector principles to determine your exact location by calculating intersection points from multiple satellites.
Natural Symmetry
Many natural formations like snowflakes, honeycombs, and crystal structures exhibit perpendicular bisector relationships in their symmetrical patterns.





