Pyramids - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Explore pyramid shapes, their properties, and real-world examples with interactive activities
What is a Pyramid?
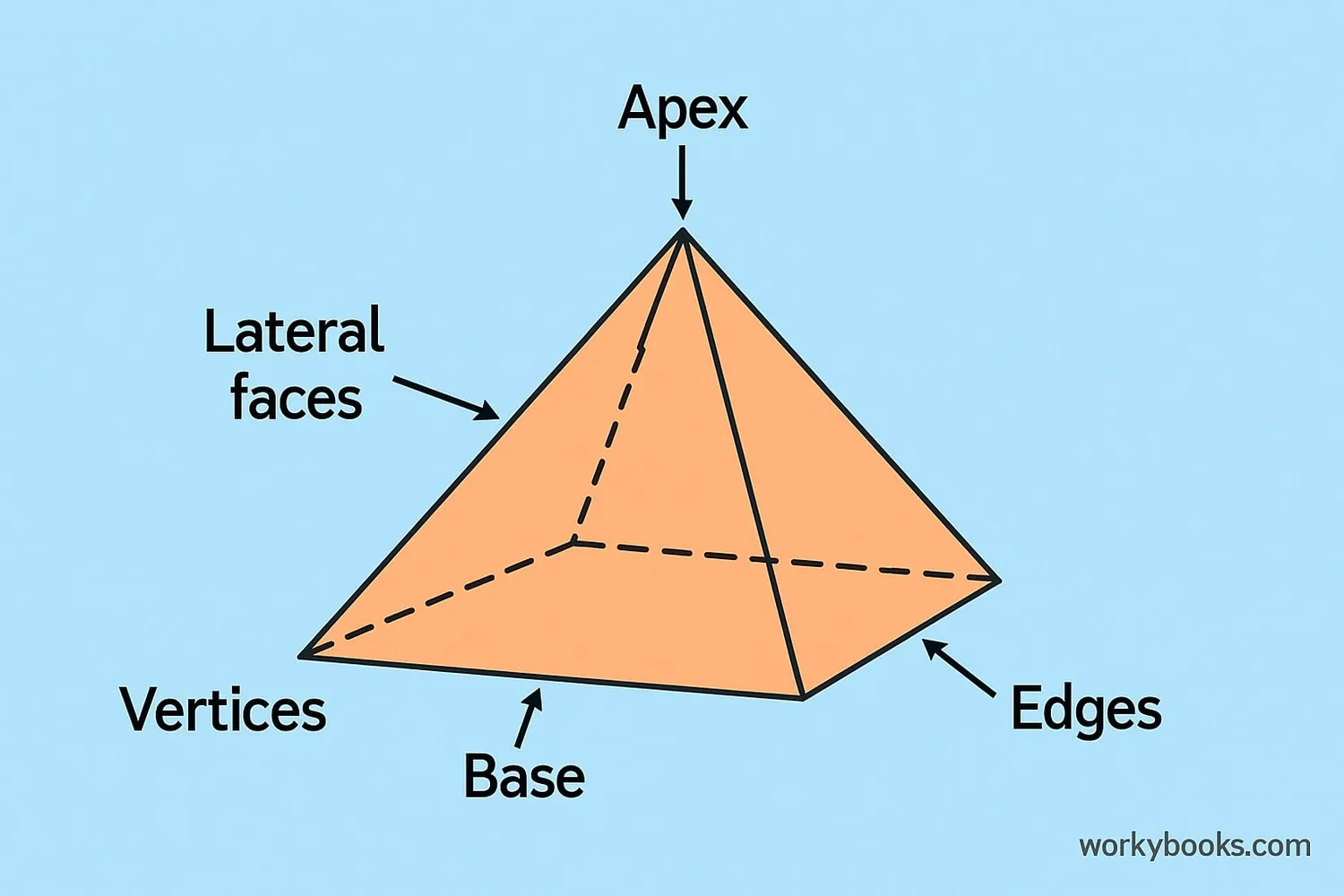
A pyramid is a three-dimensional shape with a polygon base and triangular faces that meet at a single point called the apex. The base can be any polygon (triangle, square, pentagon, etc.), and the sides are always triangles.
Here are the key parts of a pyramid:
- Base: The bottom polygon that the pyramid sits on
- Apex: The top point where all triangular faces meet
- Faces: Flat surfaces of the pyramid (base + triangular sides)
- Edges: Lines where two faces meet
- Vertices: Corner points where edges meet
Key Concept
All pyramids have one base and triangular sides that meet at the apex. The base gives the pyramid its name (triangular pyramid, square pyramid, etc.).
Types of Pyramids
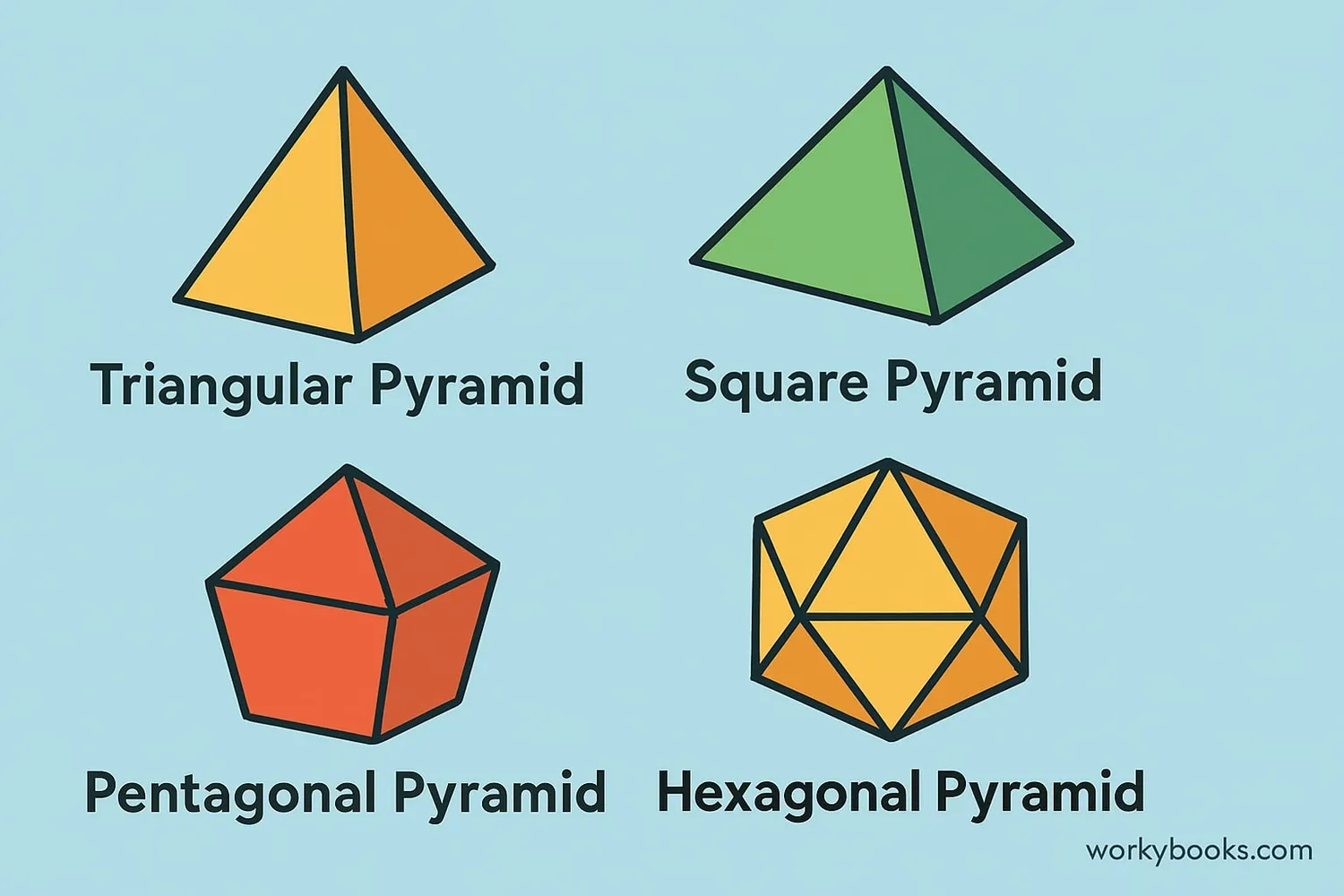
Pyramids come in different types based on their base shape and orientation:
By Base Shape
- Triangular: Base is a triangle (also called tetrahedron)
- Square: Base is a square
- Pentagonal: Base is a pentagon
- Hexagonal: Base is a hexagon
By Alignment
- Right pyramid: Apex directly above center of base
- Oblique pyramid: Apex not above center
By Regularity
- Regular: Base is regular polygon, apex centered
- Irregular: Base is irregular polygon
Remember
The most common pyramid is the square pyramid, which has a square base and four triangular faces.
Properties of Pyramids
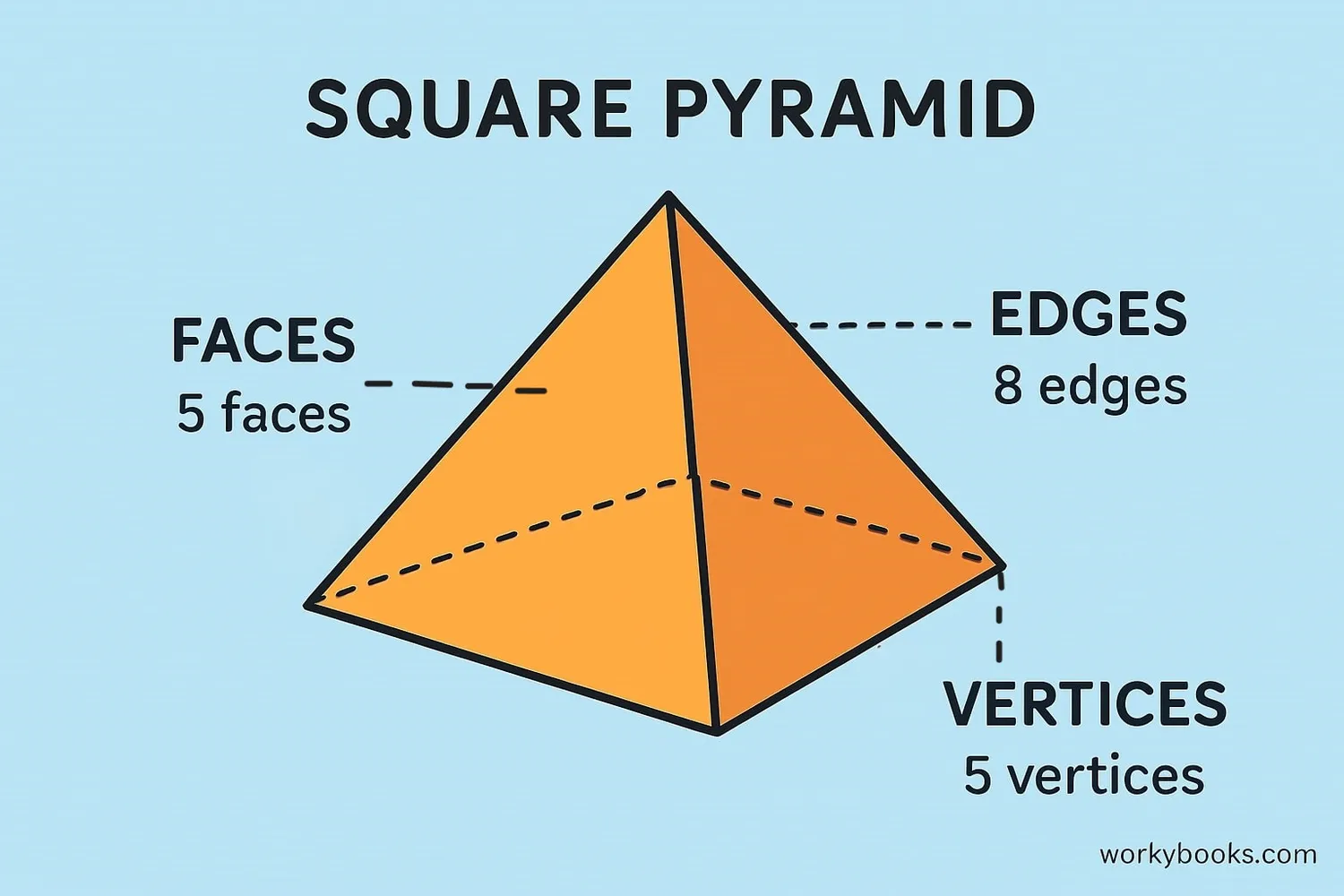
Pyramids have special properties that help us identify and work with them:
Faces: A pyramid has n+1 faces (n triangular sides + 1 base)
Edges: A pyramid has 2n edges (n edges around base + n edges from base to apex)
Vertices: A pyramid has n+1 vertices (n base corners + 1 apex)
For example, a square pyramid has:
- 5 faces (4 triangles + 1 square)
- 8 edges (4 around base + 4 from base to apex)
- 5 vertices (4 base corners + 1 apex)
Key Concept
All pyramids follow Euler's Formula: Faces + Vertices = Edges + 2
Volume and Surface Area
Volume Formula
Where B is the base area and h is the height (distance from base to apex perpendicular to base)
Surface Area Formula
Where B is the base area and LSA is the lateral surface area (sum of areas of all triangular faces)
Example: Find the volume of a square pyramid with base side 5cm and height 8cm.
Solution:
Base area = 5 × 5 = 25 cm²
Volume = 1/3 × 25 × 8 = 200/3 ≈ 66.67 cm³
Tip
The volume of a pyramid is exactly one-third the volume of a prism with the same base and height.
Real-World Examples
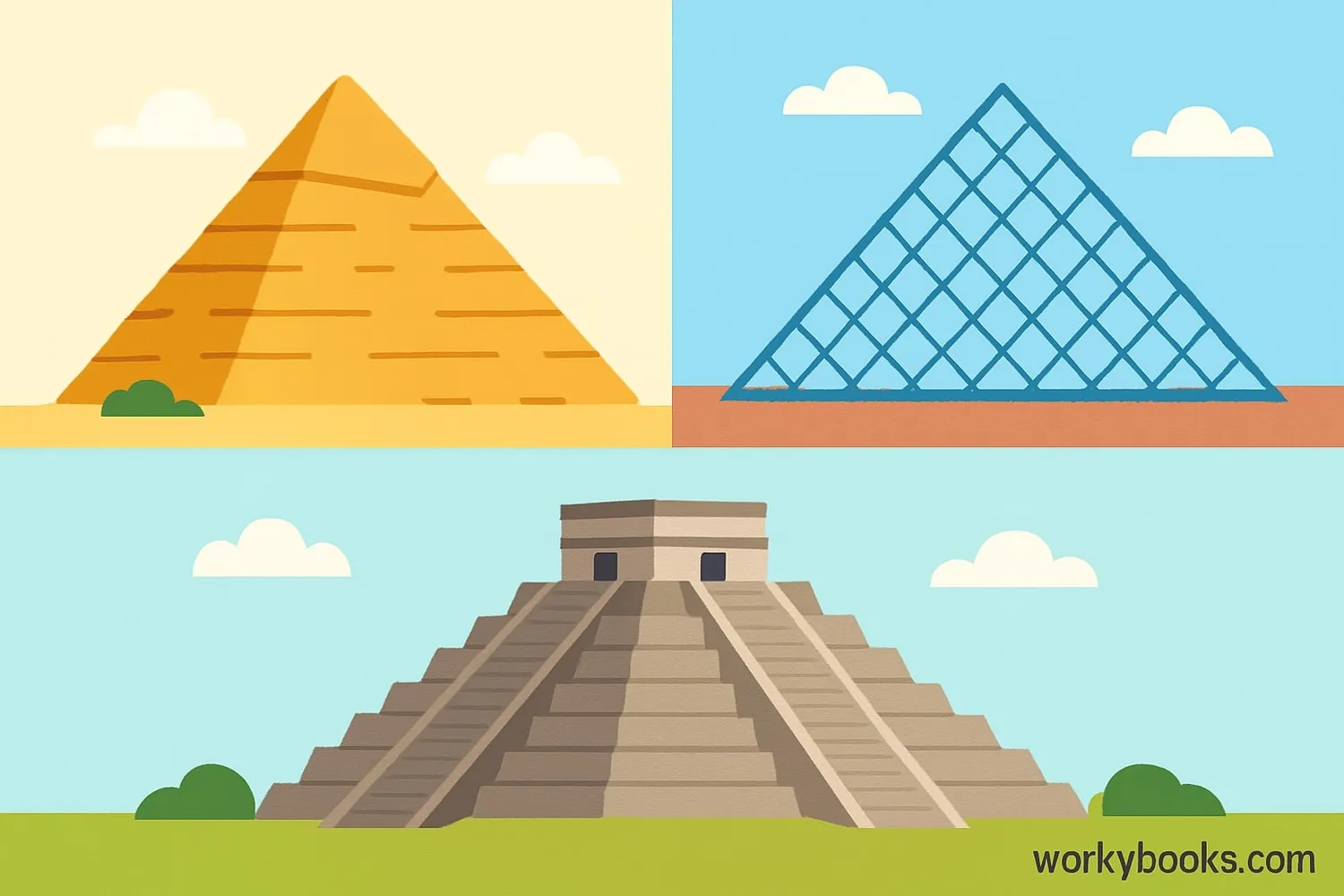
Pyramids aren't just math concepts - they're all around us! Here are some famous examples:
Great Pyramid of Giza: The largest Egyptian pyramid, built around 2580 BC. It's 481 feet tall with a square base of 756 feet on each side.
Chichen Itza: A Mayan pyramid in Mexico with 365 steps (one for each day of the year).
Louvre Pyramid: A modern glass pyramid in Paris, France, serving as the entrance to the Louvre Museum.
Luxor Hotel: A pyramid-shaped hotel in Las Vegas, Nevada.
Food Pyramid: The nutrition guide shaped like a pyramid to show food groups.
Did You Know?
The Great Pyramid of Giza was the tallest human-made structure in the world for over 3,800 years!
Pyramid Knowledge Quiz
Test what you've learned with this 5-question quiz. Choose the best answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about pyramids:
Pyramid Trivia
Discover fascinating facts about pyramids:
Ancient Precision
The Great Pyramid of Giza is aligned with true north with only 1/15th of a degree error. Its base is level to within just 2.1 cm despite covering 5.3 hectares!
Pyramid Power?
Some people believe pyramids have special energy properties, but scientists haven't found evidence for "pyramid power." The shape is efficient for construction though!
Mathematical Marvel
The ratio of a pyramid's circumference to its height equals 2π (about 6.28). This shows ancient Egyptians understood advanced math concepts.
Modern Pyramids
The largest modern pyramid is the Luxor Hotel in Las Vegas at 350 feet tall. The Transamerica Pyramid in San Francisco is 853 feet tall with 48 floors!




