Square Root of 75 - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn how to calculate the square root of 75 with easy explanations and step-by-step methods
What is Square Root?
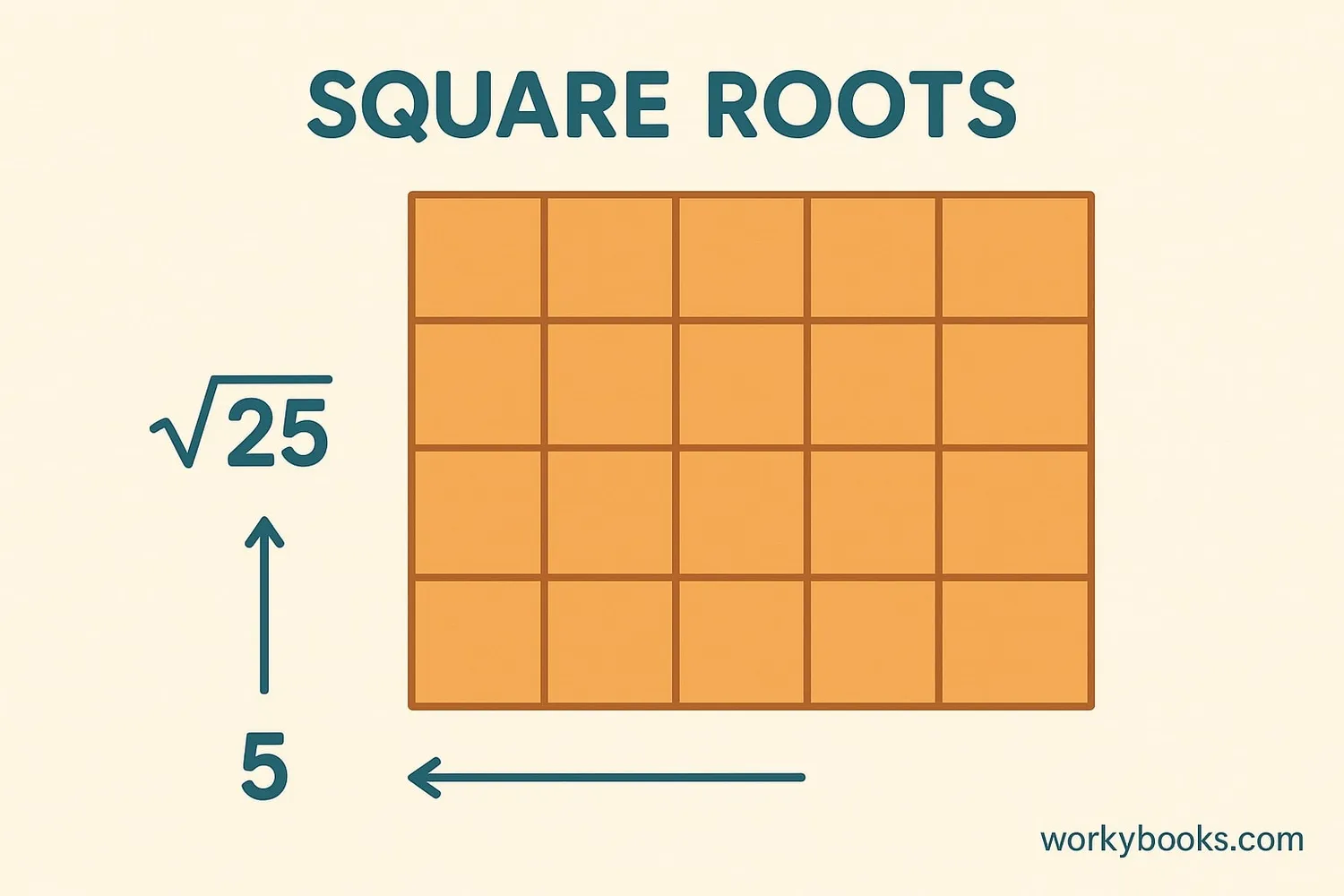
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 25 is 5 because 5 × 5 = 25. We use the radical symbol (√) to represent square roots.
Important terms to know:
Radicand: The number under the radical symbol (in √75, 75 is the radicand).
Perfect Square: A number whose square root is a whole number (like 25, 36, or 49).
Imperfect Square: A number whose square root is not a whole number (like 75).
Square Root Definition
For any number a, the square root b satisfies b² = a.
Key Concept
Finding the square root is the opposite operation of squaring a number.
How to Find the Square Root of 75
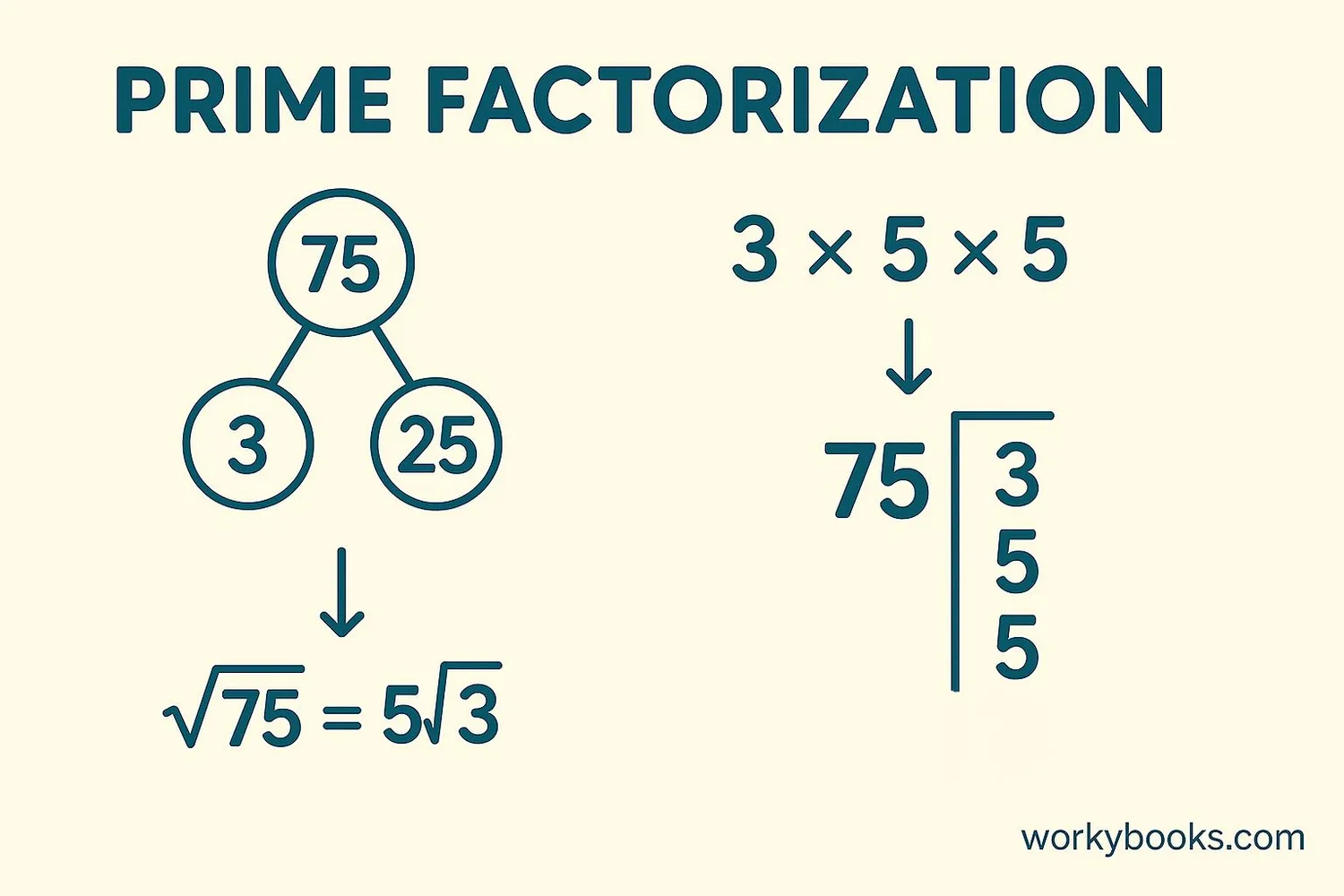
Since 75 is not a perfect square, we can find its square root using different methods. Let's explore the two most common methods:
1. Prime Factorization Method
2. Long Division Method
Remember
The square root of 75 can be expressed as √75 or 5√3. Both forms are correct, but 5√3 is the simplified radical form.
Is √75 Rational or Irrational?
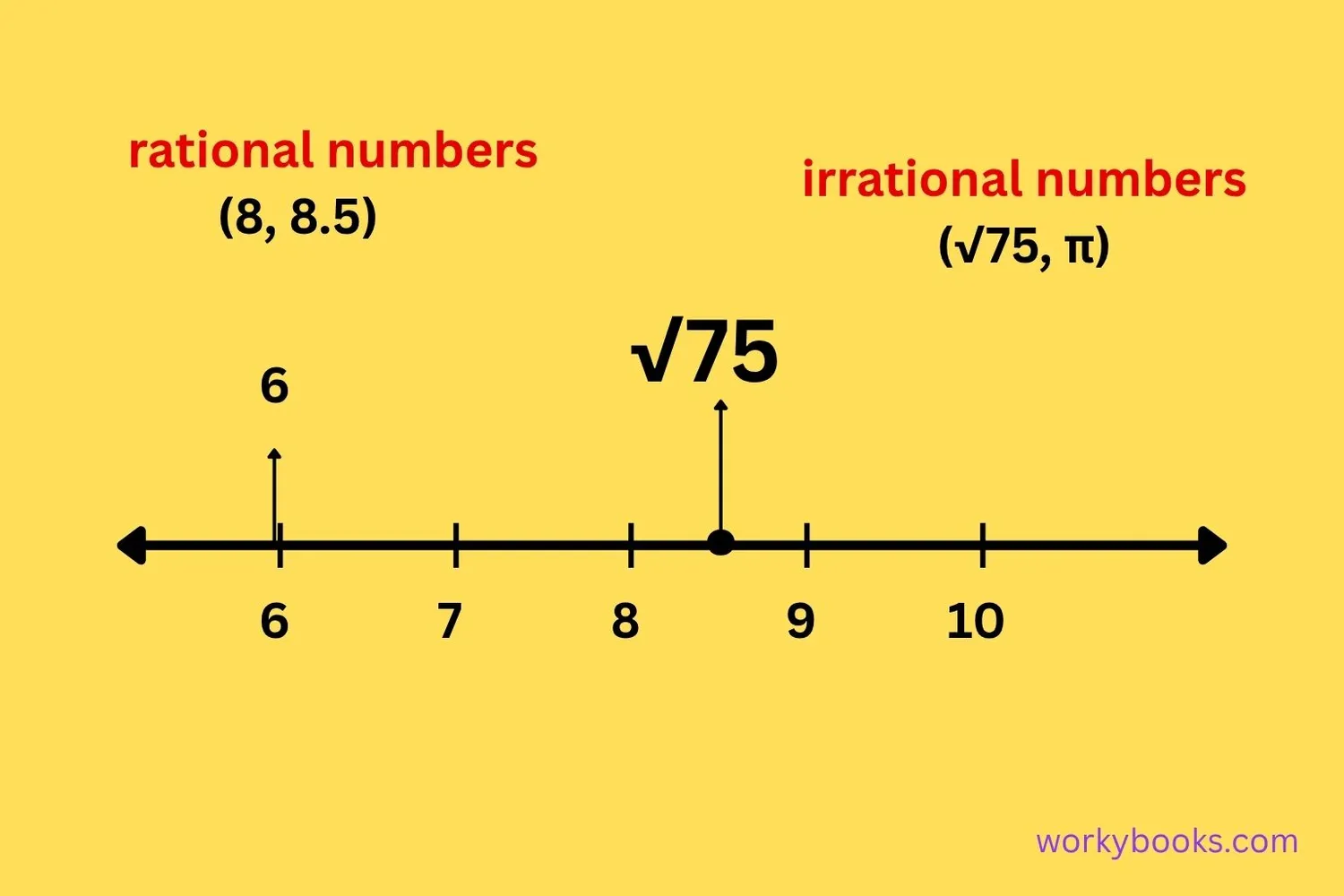
A rational number can be expressed as a simple fraction (a/b where a and b are integers). An irrational number cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and has a decimal that goes on forever without repeating.
Since 75 is not a perfect square, √75 is irrational. Here's why:
- √75 = √(3×5²) = 5√3
- √3 is known to be irrational (approximately 1.7320508... with non-repeating decimals)
- Multiplying a rational number (5) by an irrational number (√3) gives an irrational result
The decimal representation of √75 is approximately 8.660254037... and the digits go on forever without repeating.
Key Concept
The square root of any number that is not a perfect square is irrational.
Examples & Applications

Let's explore how the square root of 75 appears in real-world situations:
Example 1: If a square garden has an area of 75 square meters, what is the length of each side?
Solution: Side length = √75 ≈ 8.66 meters
Example 2: A right triangle has legs measuring 5 meters and √75 meters. What is the length of the hypotenuse?
Solution: Using Pythagorean theorem:
Example 3: A cube has a volume of 75 cubic inches. What is the length of one edge?
Solution: Edge length = ∛75 ≈ 4.22 inches (Note: This is a cube root, not square root)
Application Tip
Square roots are commonly used in geometry, physics, engineering, and computer graphics.
Square Roots Practice Quiz
Test your understanding with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about square roots:
Math Trivia
Discover interesting facts about square roots and mathematics:
Ancient Square Roots
The Babylonians had methods for approximating square roots as early as 2000 BCE. They used a method similar to the modern long division method.
Radical Symbol Origin
The radical symbol (√) was first used in 1525 by mathematician Christoph Rudolff. It's thought to be derived from the letter "r" for "radix," the Latin word for root.
Square Roots in Nature
Square roots appear in natural phenomena like the relationship between an animal's size and its metabolic rate, and in the physics of wave patterns and resonance.
Computing Square Roots
The current world record for computing the most digits of √3 is 10 trillion digits! This took 94 days of computation on a powerful computer.




