Value - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about place value, absolute value, and numerical value with examples and activities
What is Value in Math?
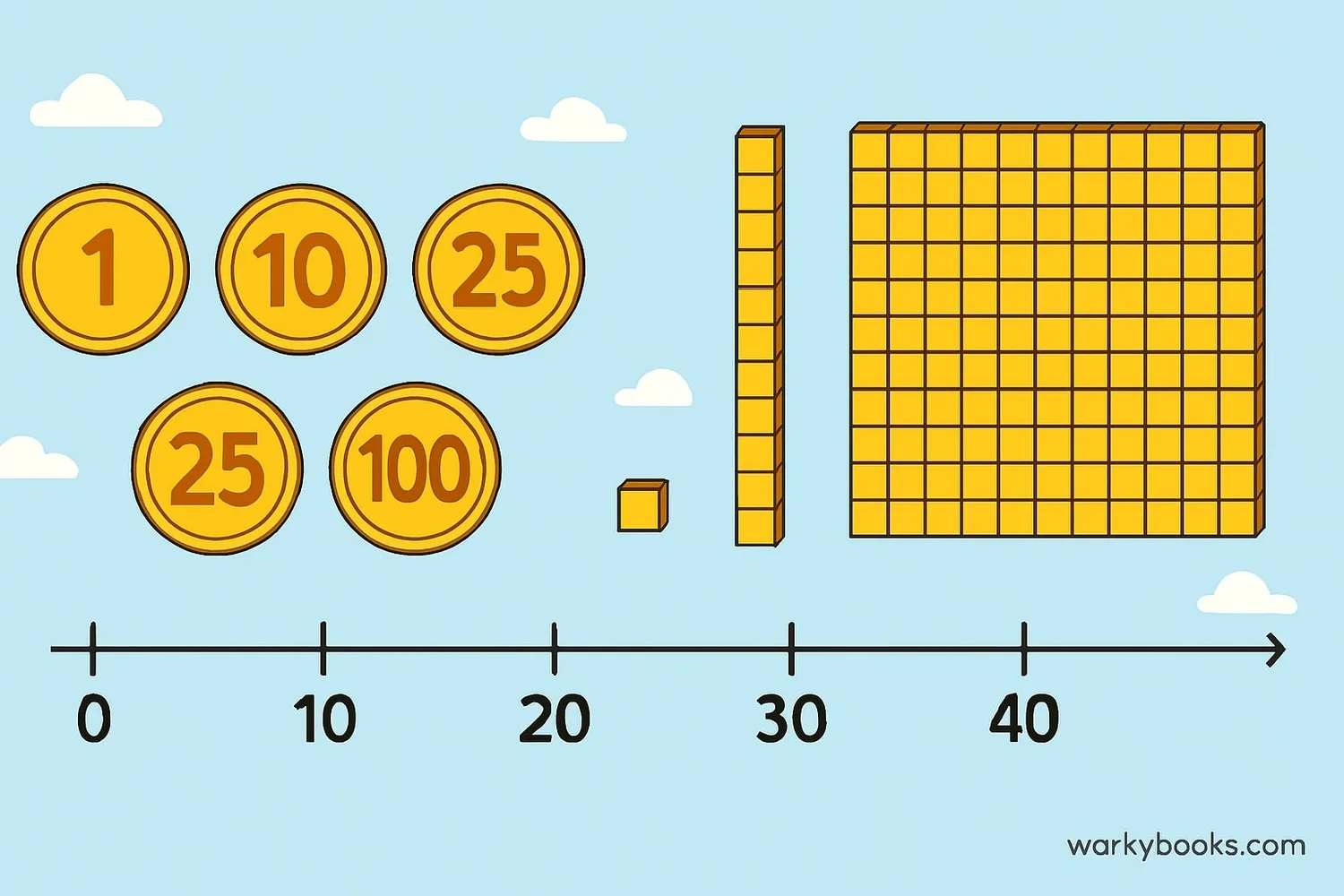
In math, value means how much something is worth. It can be the amount a number represents, or how much a digit is worth in a larger number. Understanding value helps us work with numbers and solve problems.
Think of value like this: The digit 5 has different values depending on where it is. In the number 5, it's worth 5 ones. In the number 50, it's worth 5 tens (50). In the number 500, it's worth 5 hundreds (500).
There are different types of value in math:
- Place Value - What a digit is worth based on its position
- Absolute Value - How far a number is from zero
- Numerical Value - The actual number that something represents
Key Concept
Value tells us how much a number or digit is worth. It changes based on where the digit is placed in a larger number.
Understanding Place Value

Place value is the value of a digit based on its position in a number. Each position has a different value:
- The 3 is in the hundreds place → 3 × 100 = 300
- The 2 is in the tens place → 2 × 10 = 20
- The 5 is in the ones place → 5 × 1 = 5
Remember
Moving left increases the value by 10 times. Moving right decreases the value to one-tenth.
Absolute Value
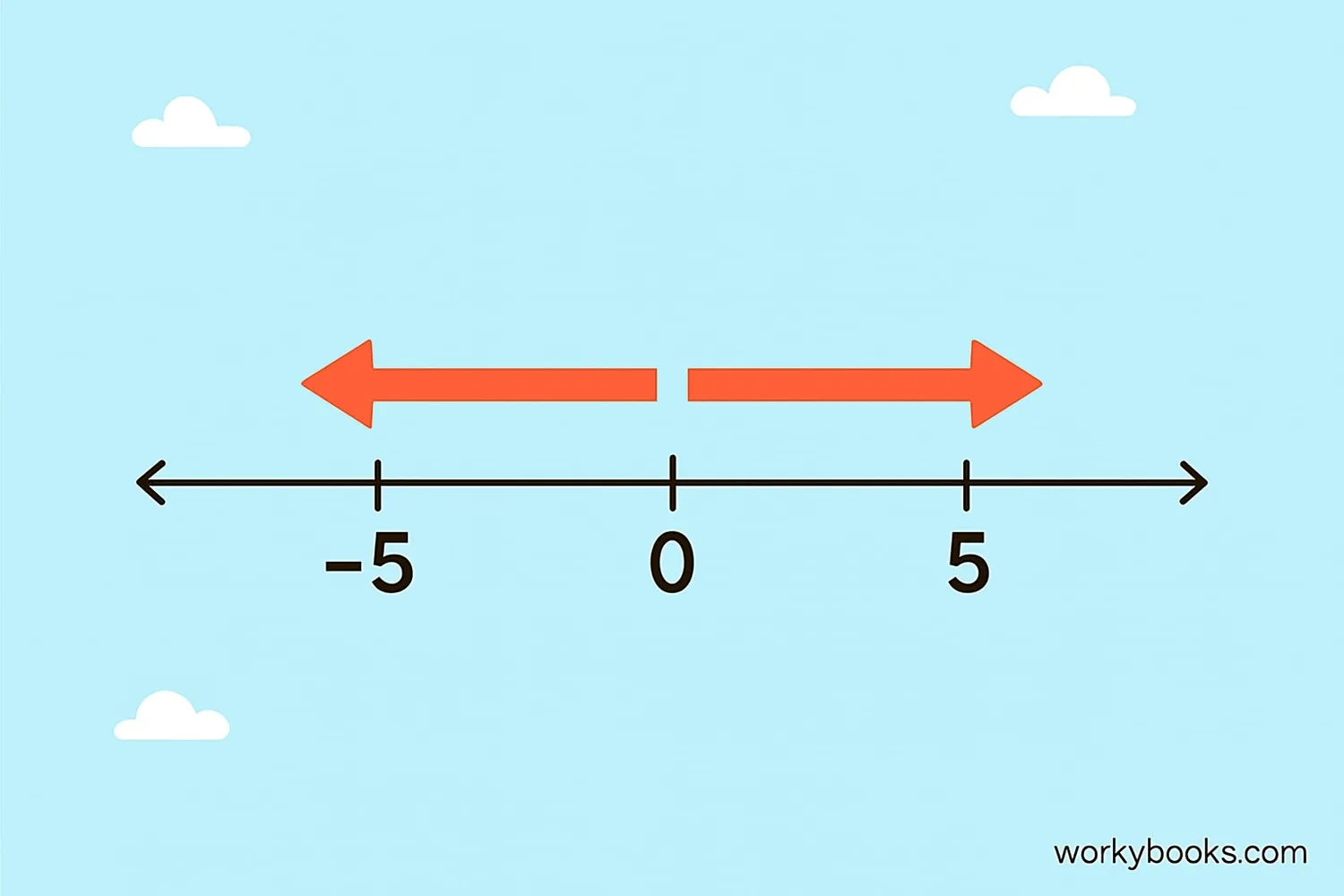
Absolute value is how far a number is from zero on the number line. It's always positive and written with vertical bars like this: | -5 | = 5.
Absolute Value Formula
The absolute value is always positive or zero, never negative.
- Measure distances (distance is always positive)
- Understand how far apart numbers are
- Solve equations with positive and negative numbers
Key Concept
Absolute value makes negative numbers positive because distance is always positive.
Numerical Value

Numerical value is the actual number that a digit or expression represents. It's the specific quantity that a number stands for.
To find the numerical value of a digit in a number:
- Identify the digit's position (ones, tens, hundreds, etc.)
- Multiply the digit by the value of its position
- 7 is in the hundreds place
- 7 × 100 = 700
- Numerical value = 700
- 4 is in the tenths place
- 4 × 0.1 = 0.4
- Numerical value = 0.4
- 3 is in the hundreds place
- 3 × 100 = 300
- Numerical value = 300
Remember
The same digit has different numerical values depending on its position in a number.
Value in Math Quiz
Test your understanding of value in math with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about value in math:
Number Value Trivia
Discover interesting facts about numbers and values:
Ancient Number Systems
The concept of place value was first developed by Babylonian mathematicians around 2000 BCE. They used a base-60 system that influenced how we measure time and angles today.
Zero's Importance
The invention of zero as a placeholder was crucial for developing place value systems. Without zero, we couldn't distinguish between numbers like 25, 205, and 250.
Large Numbers in Science
Scientists use place value to work with extremely large and small numbers. For example, the distance to the sun is about 149,600,000,000 meters, and a hydrogen atom is about 0.000000000053 meters wide.
The Largest Number
The largest named number is "googolplex" - that's 1 followed by a googol of zeros (a googol is 10100). Understanding place value helps us comprehend these enormous numbers.





