Alkaline Earth Metals - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the elements that help build strong bones and so much more!
What Are Alkaline Earth Metals?
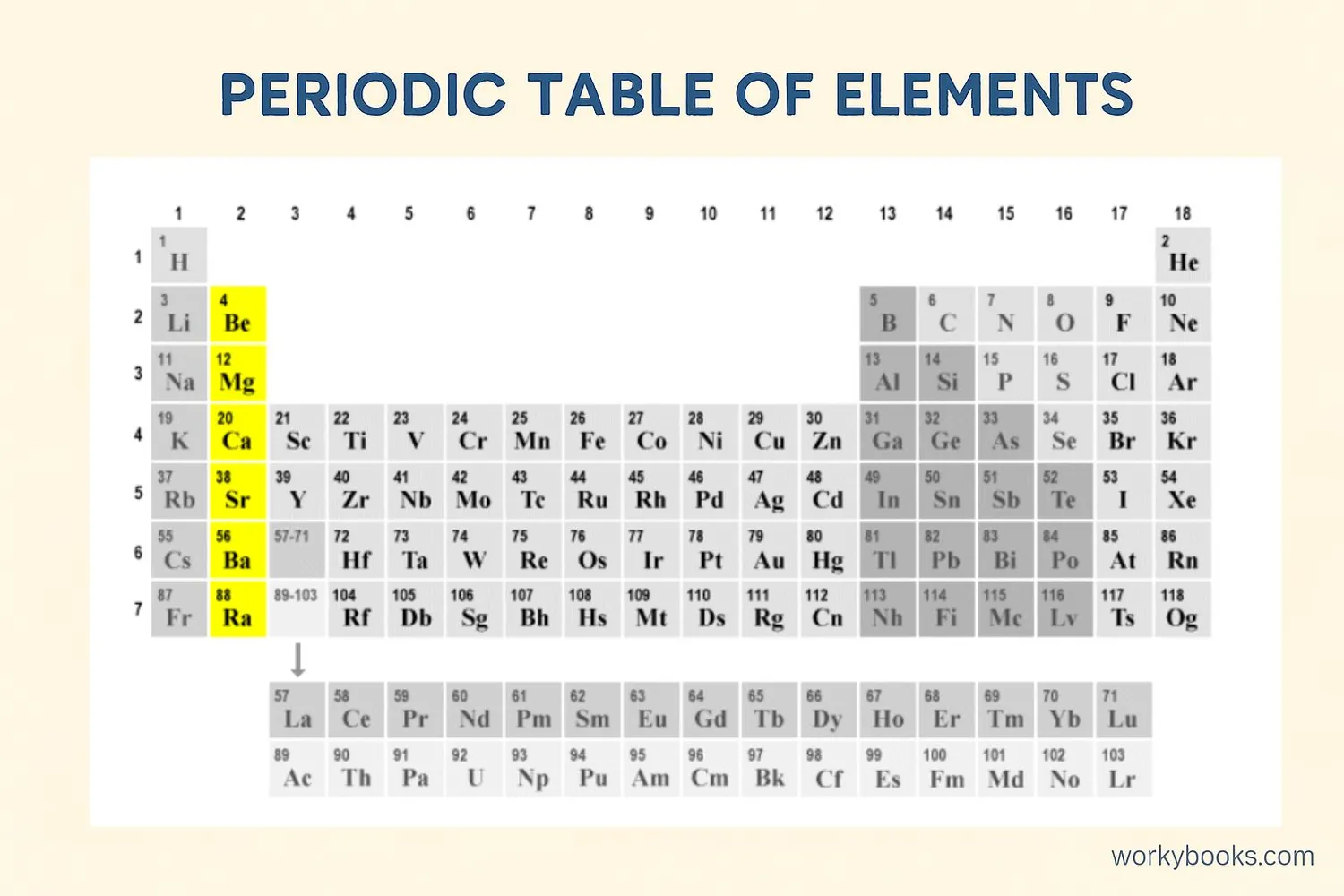
Alkaline earth metals are a group of chemical elements found in Group 2 of the periodic table. They're called "alkaline" because they form alkaline solutions (opposite of acidic) when they react with water, and "earth" because early scientists found them in Earth's crust.
These metals include beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra). They're all shiny, silvery-white metals that are somewhat reactive at standard temperature and pressure.
Quick Fact!
Calcium is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust and is essential for strong bones and teeth in living organisms!
Properties of Alkaline Earth Metals
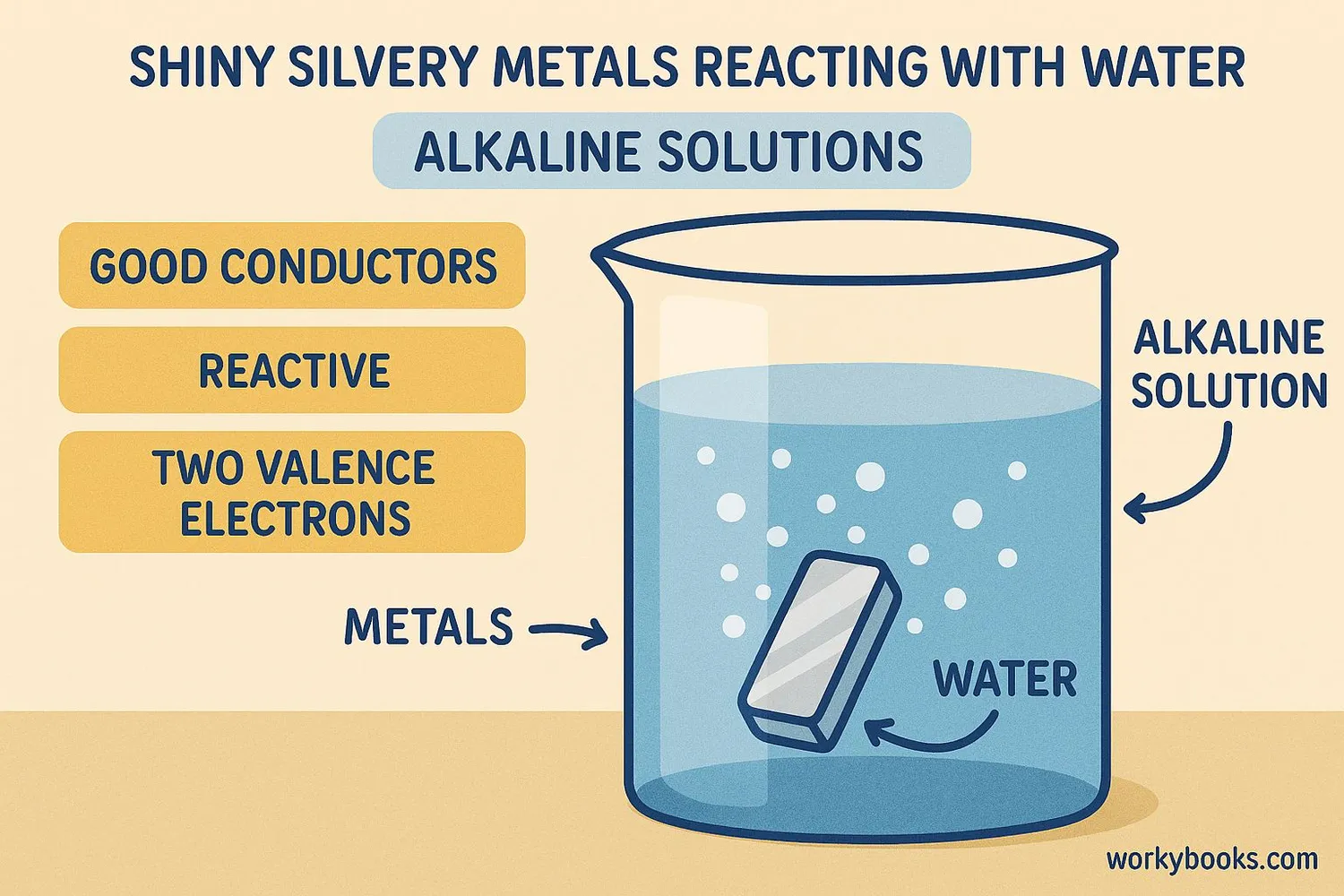
Alkaline earth metals share several important properties:
Physical Properties
Shiny, silvery-white, relatively soft metals (harder than alkali metals)
Reactivity
Less reactive than alkali metals but still quite reactive
Electrons
Have two electrons in their outer shell (valence electrons)
Conductivity
Good conductors of electricity
Melting Points
Higher melting points than alkali metals
As we move down the group from beryllium to radium:
• Atomic radius increases
• Reactivity increases
• Melting and boiling points decrease
• Density increases
Chemical Behavior
These metals readily lose their two valence electrons to form +2 cations, making them good reducing agents in chemical reactions.
Alkaline Earth Metal Examples

Let's look at each alkaline earth metal and where we can find them:
| Element | Symbol | Atomic Number | Common Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beryllium | Be | 4 | Emeralds, aquamarine, aerospace materials |
| Magnesium | Mg | 12 | Epsom salt, green vegetables, alloys |
| Calcium | Ca | 20 | Dairy products, bones, limestone, chalk |
| Strontium | Sr | 38 | Fireworks (red color), ceramic magnets |
| Barium | Ba | 56 | Medical imaging, glass production, rat poison |
| Radium | Ra | 88 | Formerly in glow-in-the-dark paints, radioactive |
Did You Know?
Marie Curie and her husband Pierre discovered radium in 1898. It was once used in glow-in-the-dark watch dials before its radioactivity was understood to be dangerous.
Uses of Alkaline Earth Metals

Alkaline earth metals have many important uses in our daily lives and industries:
Calcium
Essential for bones and teeth; used in cement, plaster, and cheese making
Beryllium
Used in aerospace materials, X-ray equipment, and nuclear reactors
Strontium
Produces red color in fireworks; used in ceramic magnets and glow-in-dark paints
Magnesium
Used in antacids, Epsom salts, lightweight alloys, and flares
Barium
Used in medical imaging of digestive system, glass production, and rat poison
These metals are also important in:
• Agriculture (soil treatment)
• Medicine (treatments and diagnostics)
• Manufacturing (alloys and materials)
• Electronics (components and devices)
Alkaline Earth Metals Quiz
Test your knowledge with this quiz about alkaline earth metals! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about alkaline earth metals:
Interesting Facts
Discover some amazing facts about alkaline earth metals!
Calcium Abundance
Calcium is the fifth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and makes up about 3% of the crust's composition. It's also essential for living organisms.
Magnesium in Photosynthesis
Magnesium is at the center of chlorophyll molecules, making it essential for photosynthesis in plants. Without magnesium, plants couldn't convert sunlight into energy!
Beryllium in Gemstones
Beryllium is found in some of the world's most beautiful gemstones, including emeralds and aquamarine, which are both forms of the mineral beryl.
Radium Discovery
Marie Curie discovered radium in 1898. It was once used in glow-in-the-dark paint for watch dials until its radioactivity was understood to be dangerous.





