Analog vs Digital Signals - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn how information travels through waves and numbers!
What Are Signals?
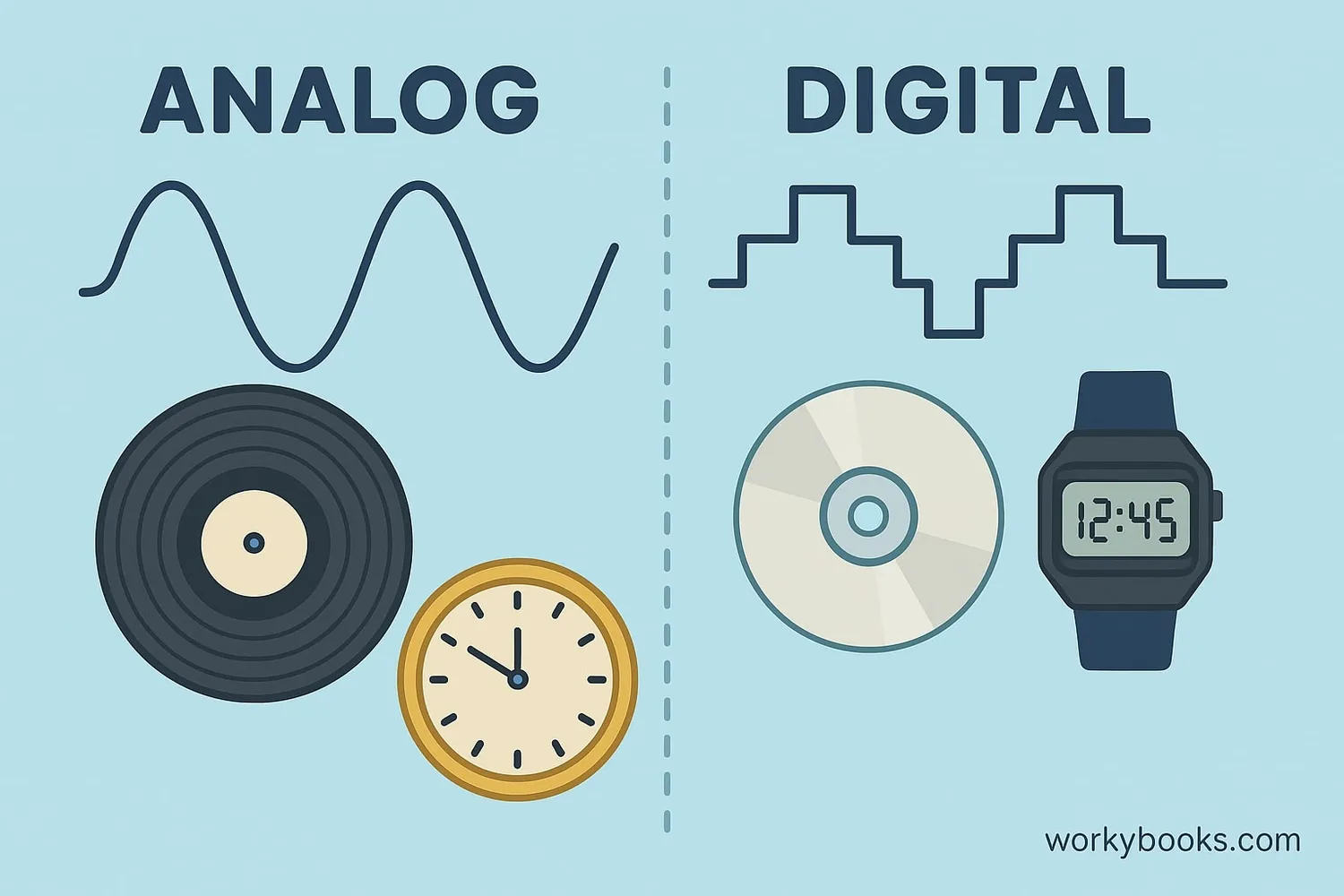
Signals are how information travels from one place to another. Think of them like messages that devices use to communicate. There are two main types of signals:
• Analog signals are continuous waves that can have any value. They represent information using smooth changes in properties like voltage, sound, or light.
• Digital signals are discrete signals that represent information using numbers (usually 0s and 1s). They jump between specific values rather than flowing smoothly.
Both types of signals help us send information, but they work in very different ways!
Signal Fact!
Your voice is an analog signal! When you speak, you create sound waves that travel through the air as continuous vibrations.
Analog Signals Explained

Analog signals are continuous waves that represent information by changing their properties smoothly over time. They can have an infinite number of values within a range.
Key characteristics of analog signals:
Continuous
No breaks or jumps - smooth transitions between values
Infinite Values
Can represent any value within a range
Natural
Most natural phenomena are analog
Noise Susceptible
Easily affected by interference
Examples of analog signals:
• Sound waves (music, voices)
• Light waves
• Temperature changes
• Traditional watch hands
• FM/AM radio signals
Analog signals are great for representing natural phenomena, but they can be affected by noise and distortion during transmission.
Digital Signals Explained
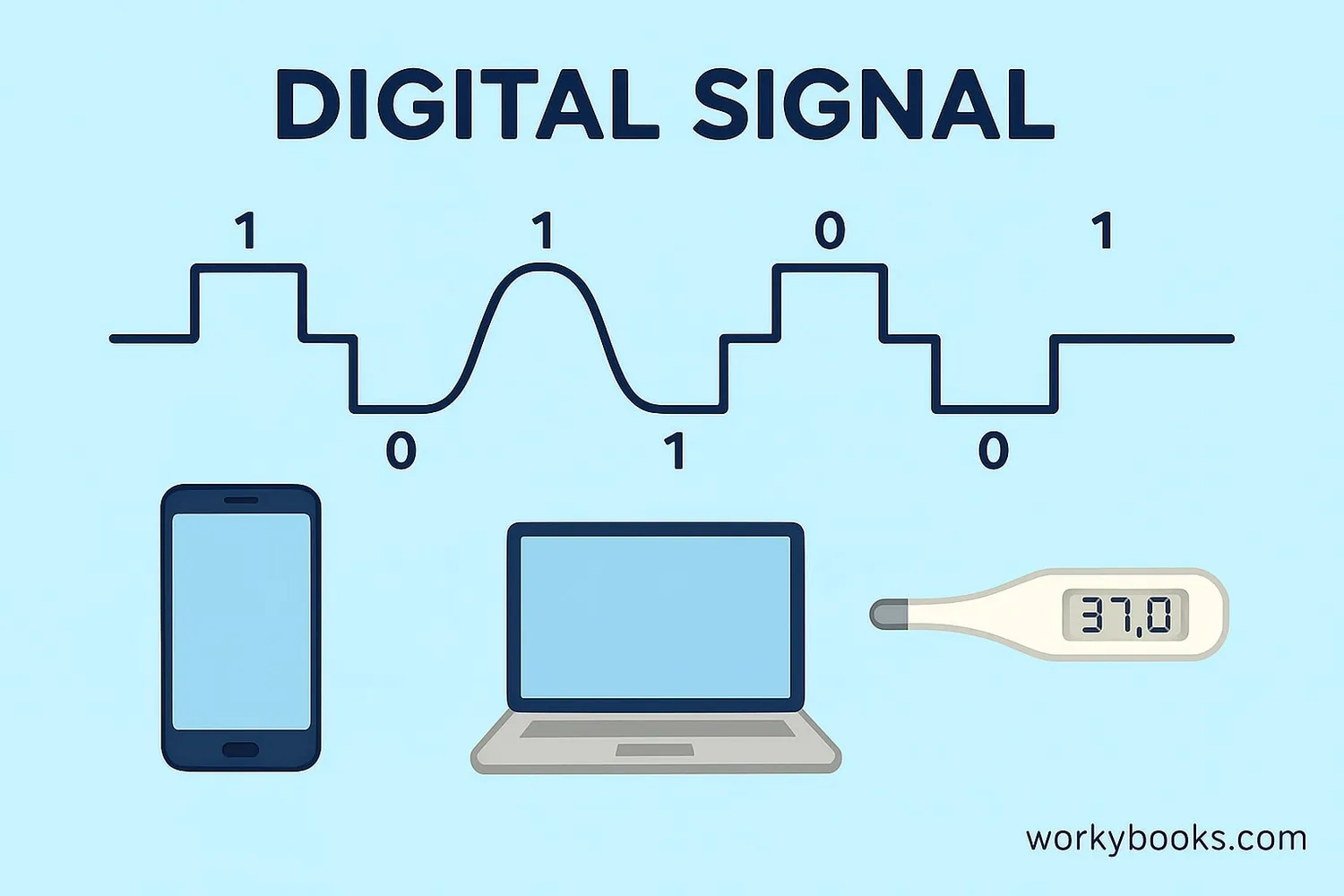
Digital signals represent information using discrete values (usually 0 and 1). They jump between specific levels rather than changing continuously.
Key characteristics of digital signals:
Discrete
Values jump between specific levels
Binary
Information represented as 0s and 1s
Noise Resistant
Easier to clean up from interference
Computable
Easy for computers to process
Examples of digital signals:
• Computer data
• Digital audio (CDs, MP3s)
• Digital photos
• Text messages
• Wi-Fi signals
Digital signals are created through a process called sampling and quantization, where continuous analog signals are measured at regular intervals and converted to numbers.
Key Differences
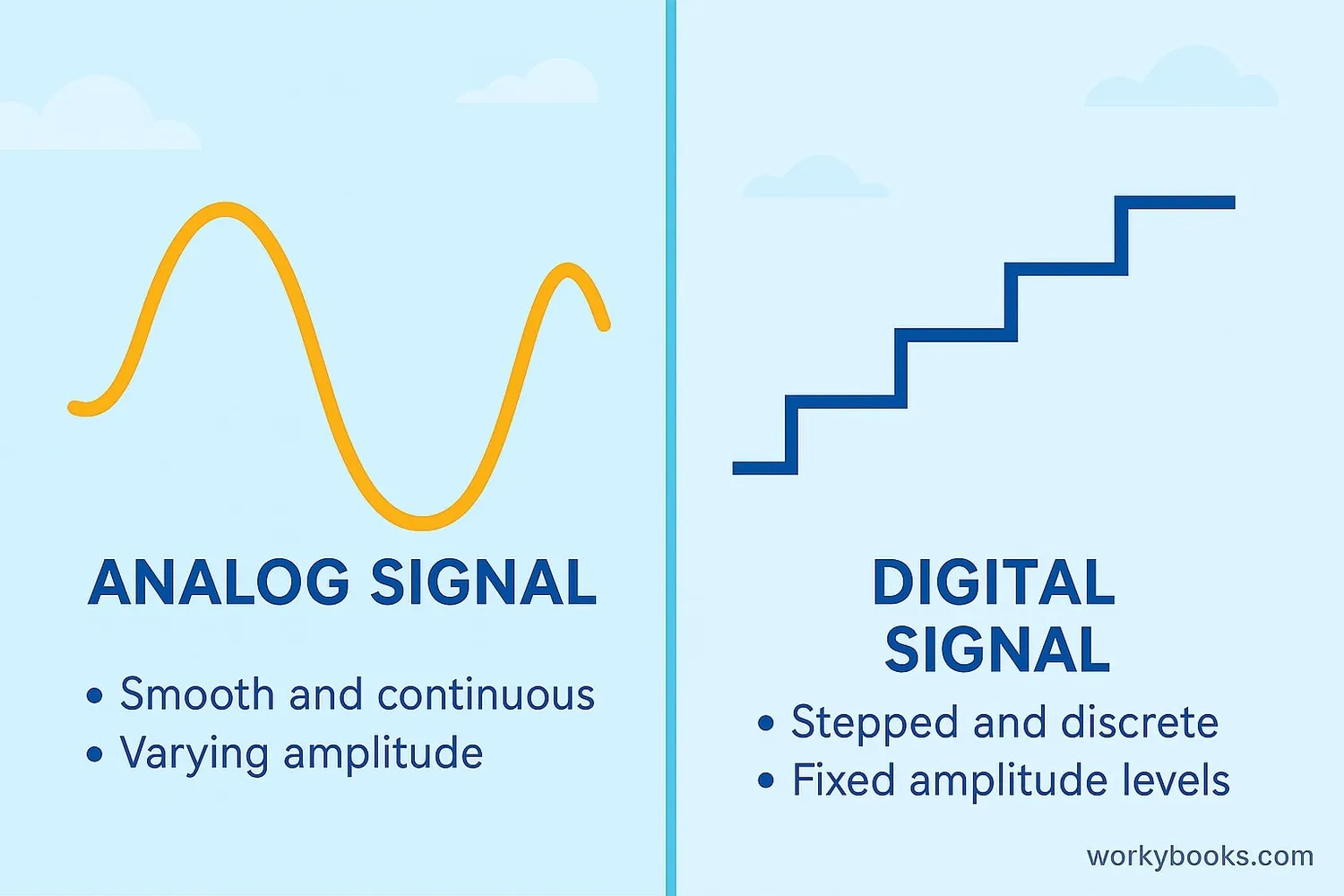
Understanding how analog and digital signals differ helps us see why each is useful in different situations:
| Feature | Analog Signal | Digital Signal |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Continuous wave | Discrete steps |
| Values | Infinite possibilities | Specific values (0/1) |
| Noise Resistance | Easily distorted | More resistant to noise |
| Storage | Tape, vinyl records | CDs, hard drives, flash memory |
| Processing | Difficult with computers | Easy with computers |
| Transmission | Radio waves, copper wires | Fiber optics, digital networks |
Conversion Between Signals
We often convert between analog and digital signals using special devices:
• ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) turns analog signals into digital data
• DAC (Digital-to-Analog Converter) turns digital data back into analog signals
Signals Quiz
Test your knowledge about analog and digital signals with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about analog and digital signals:
Fun Signal Trivia
Discover some fascinating facts about signals!
Historical First
The first digital signal was sent in 1844 by Samuel Morse - the famous "What hath God wrought" Morse code message!
Music Quality
CD-quality audio uses 44,100 samples per second! That's why digital music can sound just as good as analog recordings.
Space Communication
Voyager 1, over 14 billion miles away, communicates with Earth using digital signals that take over 21 hours to reach us!
Brain Signals
Your brain uses both analog and digital signals! Neurons send digital "spikes" of electricity, but their timing is analog.





