Avogadro's Number - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how chemists count atoms and molecules
What is Avogadro's Number?

Avogadro's number is a fundamental constant in chemistry that represents the number of particles (atoms, molecules, or ions) in one mole of a substance. It's named after the Italian scientist Amedeo Avogadro, who made important contributions to molecular theory.
The value of Avogadro's number is:
Think of it like this: Instead of counting grains of sand on a beach one by one, we count them in buckets. Avogadro's number is like a special "chemistry bucket" that holds exactly 602,200,000,000,000,000,000,000 particles!
Chemistry Fact!
If you had a mole of pennies, you could give every person on Earth 300 trillion dollars each!
The Mole Concept
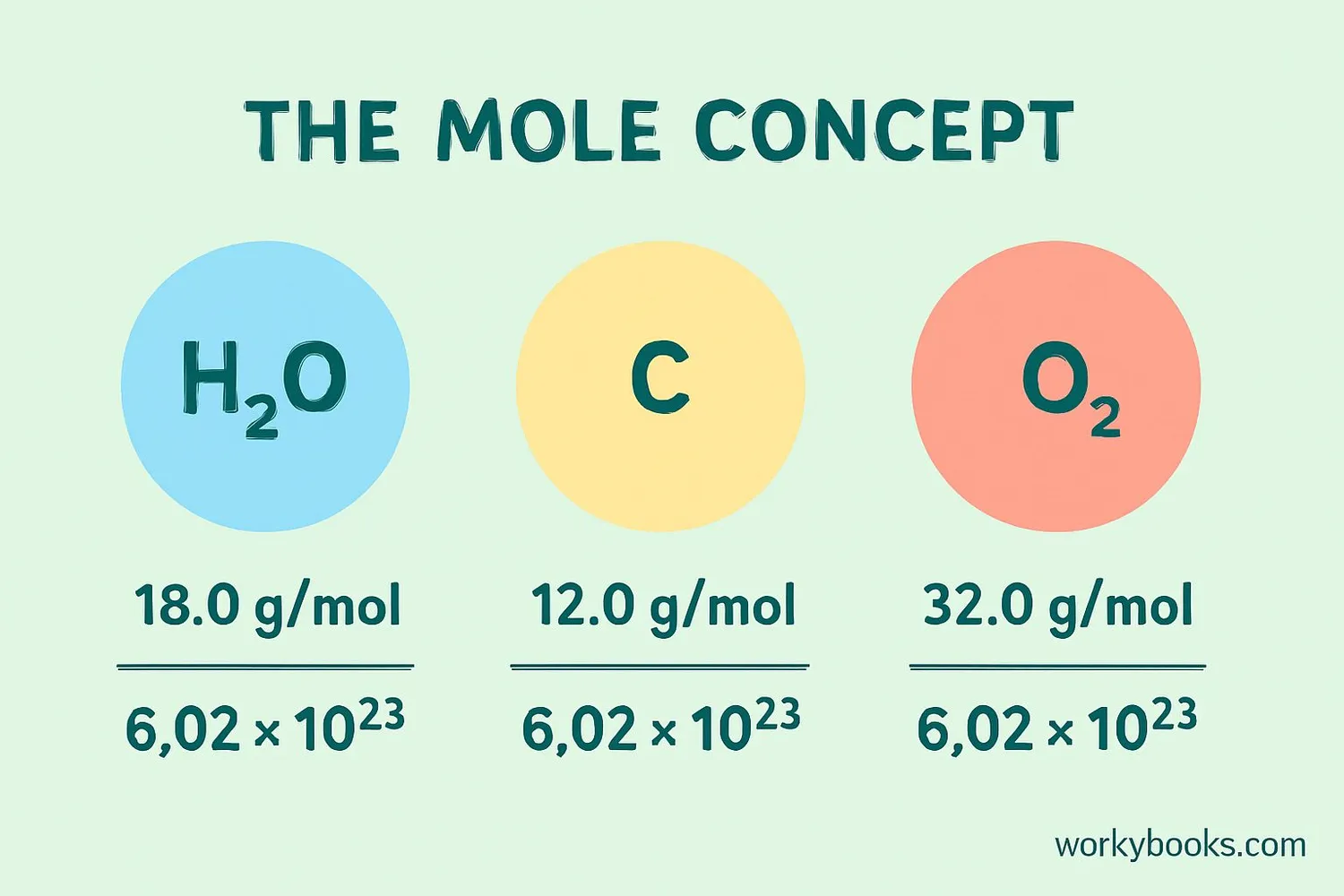
The mole is the basic unit for measuring the amount of a substance in chemistry. One mole of any substance contains exactly Avogadro's number of particles (6.022 × 10²³). This concept is crucial for:
• Converting between atomic/molecular scale and laboratory scale
• Understanding chemical reactions and stoichiometry
• Calculating molecular masses and formula weights
Atomic Mass
Elements have atomic masses measured in atomic mass units (u)
Molar Mass
One mole of an element has a mass in grams equal to its atomic mass
Avogadro's Number
One mole contains 6.022 × 10²³ particles (atoms or molecules)
For example:
• Carbon has an atomic mass of 12 u
• Therefore, 1 mole of carbon atoms has a mass of 12 grams
• And contains 6.022 × 10²³ carbon atoms
This relationship allows chemists to measure quantities of substances in the lab that correspond to manageable numbers of atoms or molecules.
Calculations & Examples
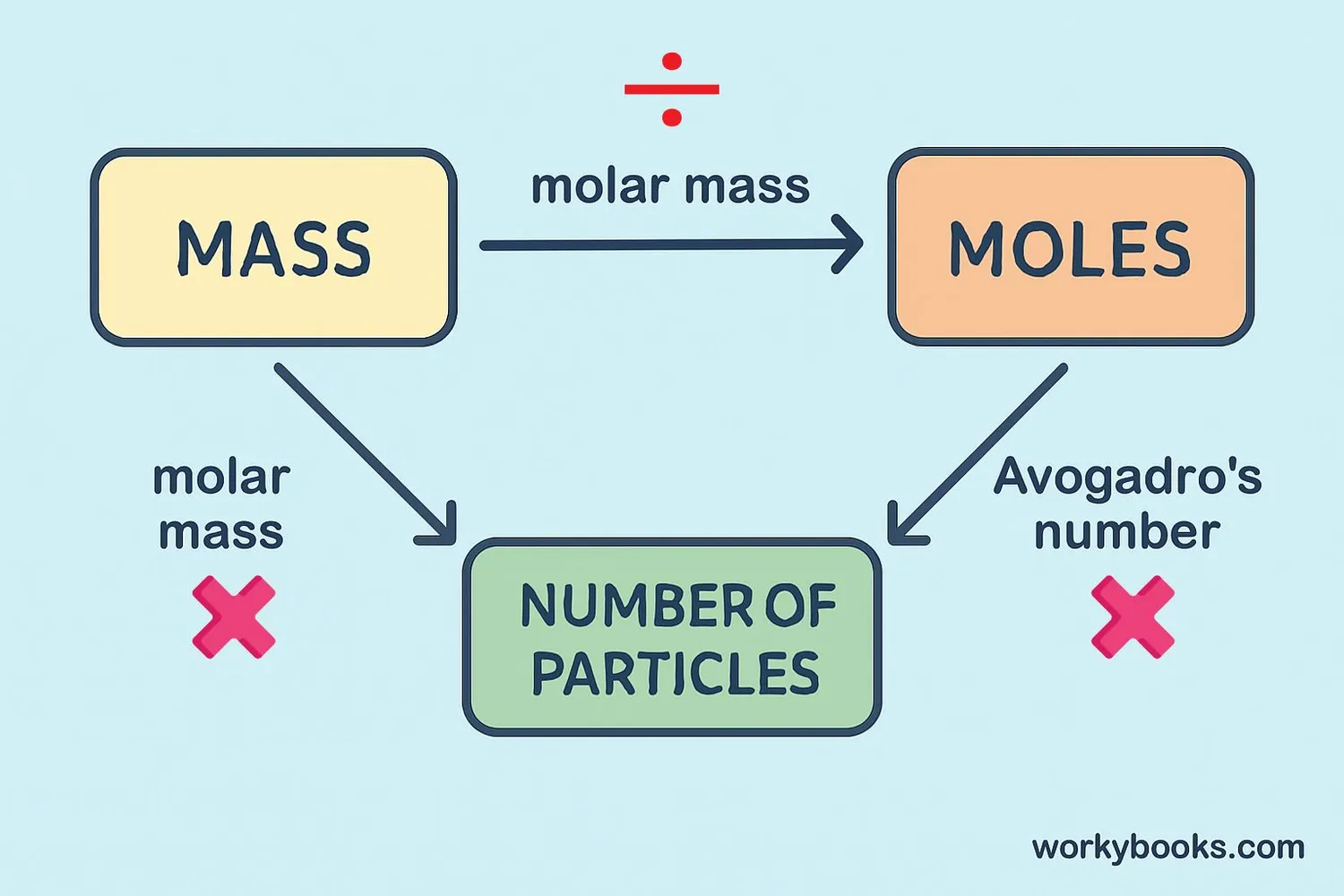
Avogadro's number allows us to perform important calculations in chemistry. Here's how we use it:
Key Formulas:
• Number of moles = Mass of substance (g) ÷ Molar mass (g/mol)
• Number of particles = Moles × Avogadro's number
• Mass of substance = Moles × Molar mass
Example 1: Water Molecules
How many molecules are in 18g of water (H₂O)?
Example 2: Carbon Atoms
How many atoms are in 24g of carbon?
Example 3: Oxygen Gas
What is the mass of 3.011 × 10²³ molecules of O₂?
Mass = 0.5 mol × 32g/mol = 16g
These calculations are fundamental to chemistry and allow scientists to measure precise quantities for chemical reactions, pharmaceutical development, and materials science.
Avogadro's Number Quiz
Test your understanding of Avogadro's number and the mole concept with this quiz!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about Avogadro's number:
Chemistry Trivia
Discover fascinating facts about Avogadro's number and chemistry:
Precision Measurement
The official value of Avogadro's number was established in 2019 by measuring a perfect silicon-28 sphere. Scientists polished it to near-perfect roundness with less than 0.3 nanometers of roughness!
Historical Name
Avogadro never actually calculated the number named after him. The constant was first estimated in 1865 by Johann Josef Loschmidt, who calculated the number of molecules in a cubic centimeter of gas.
Massive Scale
If you had a mole of basketballs, they would cover the entire surface of the Earth to a depth of more than 80 kilometers! That's about 10 times deeper than the deepest ocean trench.
Counting Time
If you could count 10 atoms per second, it would take you about 2 billion years to count just one mole of atoms! That's nearly half the age of our planet.





