Bromine - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the fascinating reddish-brown liquid element and its important role in our world
What is Bromine?

Bromine is a fascinating chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It's one of only two elements that are liquid at room temperature (the other is mercury). Bromine is a member of the halogen group on the periodic table, which also includes fluorine, chlorine, iodine, and astatine.
The name "bromine" comes from the Greek word "bromos," which means stench, because bromine has a strong, unpleasant odor. It was discovered in 1826 by two chemists working independently: Antoine-Jérôme Balard in France and Carl Löwig in Germany.
Bromine at a Glance
Element Fact!
Bromine is the only nonmetallic element that is liquid at ordinary temperatures! It evaporates easily, giving off orange vapors that have a strong smell.
Properties & Characteristics
Bromine has several unique physical and chemical properties that make it interesting to scientists:
Physical State
Reddish-brown liquid at room temperature
Odor
Strong, unpleasant, choking odor
Reactivity
Highly reactive, especially with metals
Toxicity
Corrosive and toxic element
Molecular Form
Exists as diatomic molecules (Br₂)
Bromine is less reactive than fluorine or chlorine but more reactive than iodine. It reacts with many metals to form bromides, which are compounds containing bromine. For example, when bromine reacts with aluminum, it forms aluminum bromide.
Because bromine is so reactive, it's never found as a free element in nature. Instead, it's found in compounds dissolved in sea water, salt lakes, and underground brine wells.
Safety Note!
Bromine is corrosive and toxic. It can cause serious burns on skin and damage to eyes and respiratory system. Scientists always use special safety equipment when working with bromine.
Uses & Importance
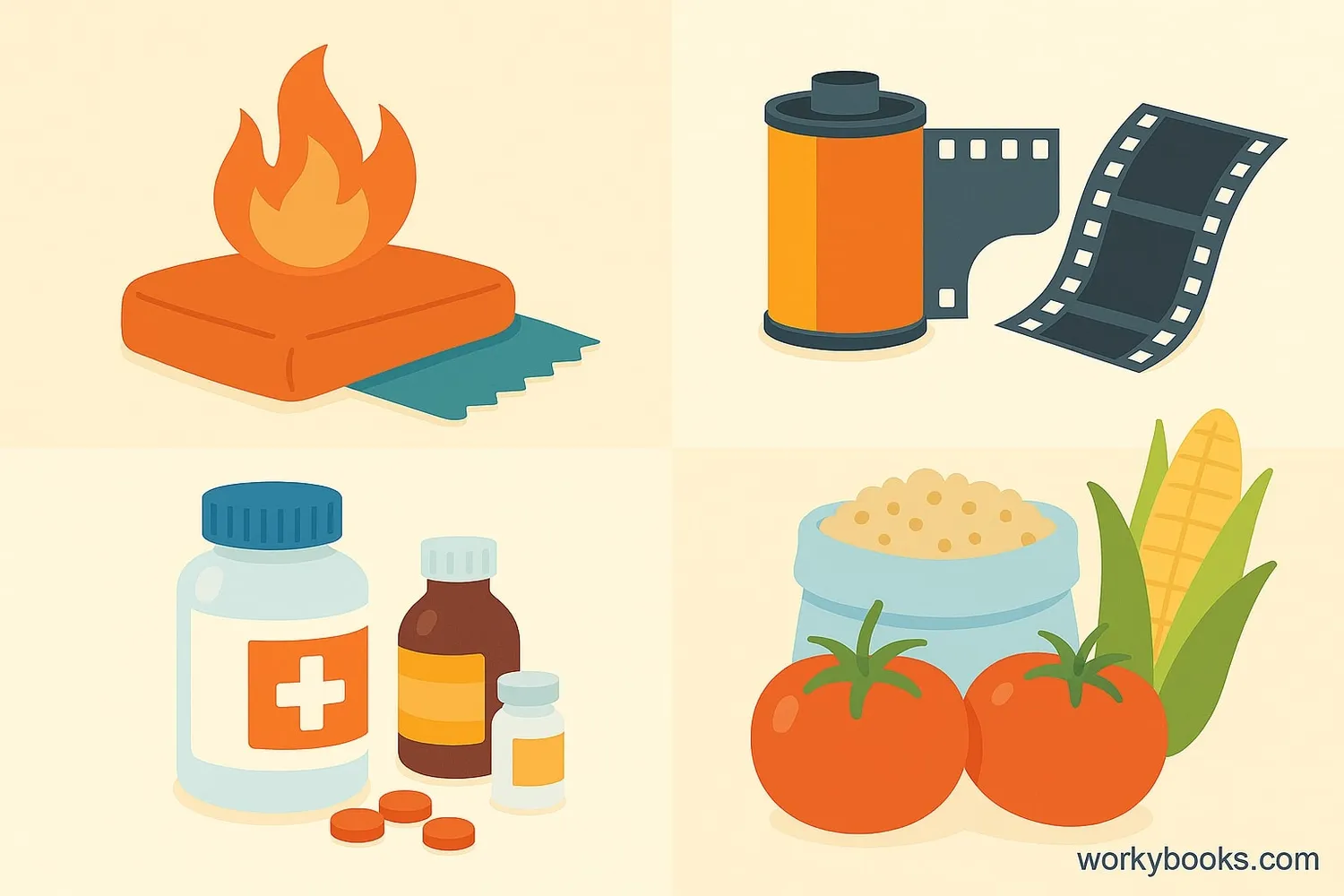

Despite its potentially dangerous properties, bromine and its compounds have many important uses in our daily lives:
Flame Retardants
Brominated compounds are used to make materials less flammable
Photography
Silver bromide is light-sensitive and used in photographic film
Medicines
Some bromine compounds are used in sedatives and other medications
Agriculture
Used in pesticides to protect crops from pests
Water Treatment
Sometimes used to disinfect water in swimming pools and hot tubs
Bromine is also used in drilling fluids for oil and gas wells, in dyes, and in making certain types of plastics. The pharmaceutical industry uses bromine compounds to manufacture various drugs, including those used to treat pneumonia and Alzheimer's disease.
Environmental Note!
While bromine has many useful applications, some brominated flame retardants can persist in the environment. Scientists are researching safer alternatives that break down more easily.
Bromine Element Quiz
Test your knowledge about bromine with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about bromine:
Element Trivia
Discover some fascinating facts about bromine!
Major Producer
The United States and Israel are the world's leading producers of bromine. Israel extracts most of its bromine from the Dead Sea, which has an extremely high salt content.
What's in a Name?
The name "bromine" comes from the Greek word "bromos," which means "stench" - a reference to its strong, unpleasant odor that can irritate eyes and throat.
Historical Use
In the 19th century, potassium bromide was widely used as a sedative and to prevent seizures. However, it could cause bromism (bromine poisoning) with side effects like skin rashes and neurological problems.
Color Test
Bromine water (a solution of bromine in water) is often used as a test for unsaturation in organic compounds. When added to an unsaturated compound, the reddish-brown color of bromine water disappears.





