Morse Code - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how people communicated using dots and dashes before phones!
What is Morse Code?
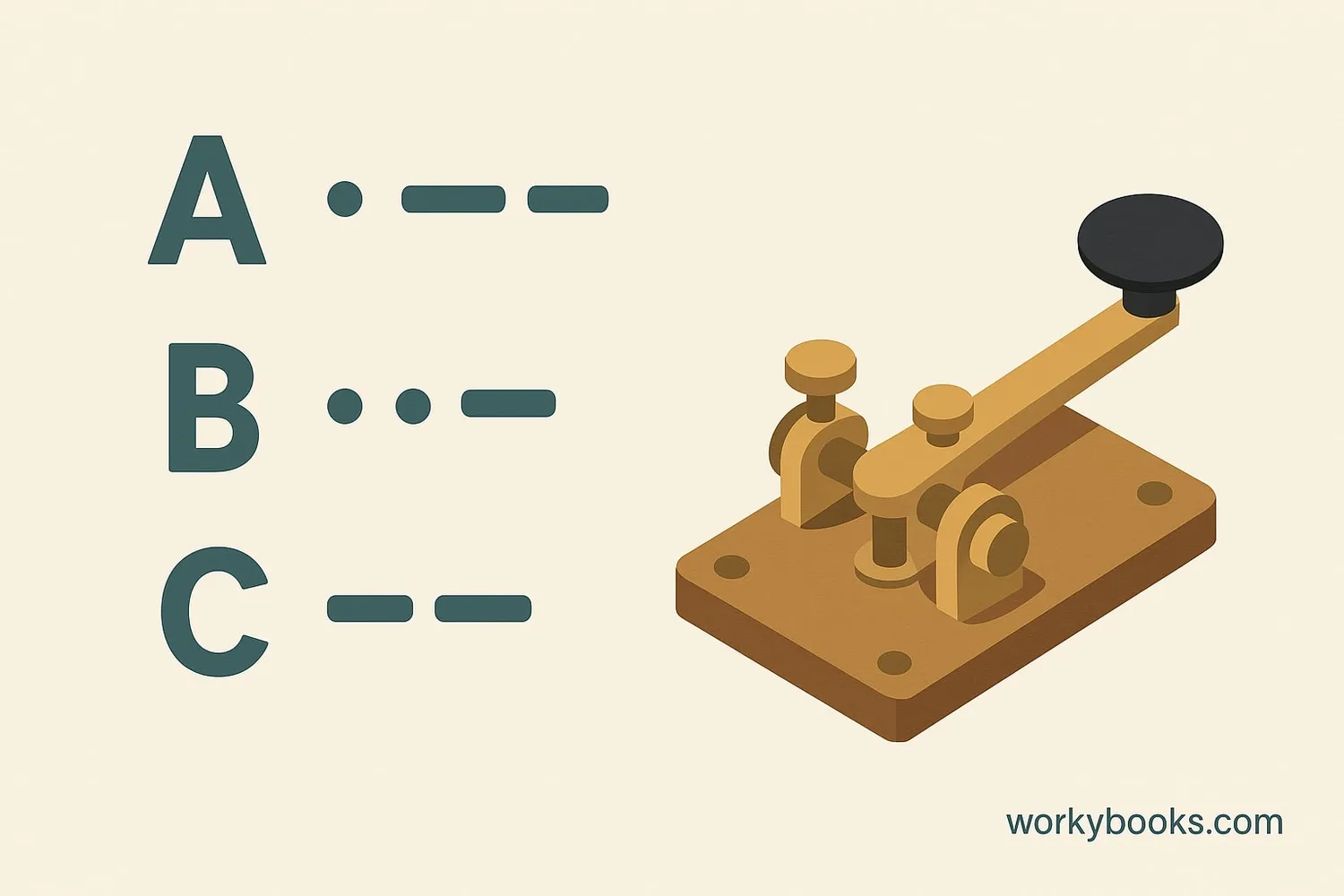
Morse code is a method of communication that uses dots and dashes to represent letters, numbers, and punctuation. Invented by Samuel Morse in the 1830s, it was originally used with telegraph machines to send messages over long distances.
Think of Morse code as a special language made of short signals (• called "dits") and long signals (— called "dahs"). By combining these signals in different patterns, you can spell out any word! This was especially important before telephones when people needed to send messages quickly across oceans and continents.
Communication Fact!
Morse code was the primary way ships communicated at sea for over 100 years. The famous distress signal "SOS" is Morse code: ••• ——— •••
How Morse Code Works
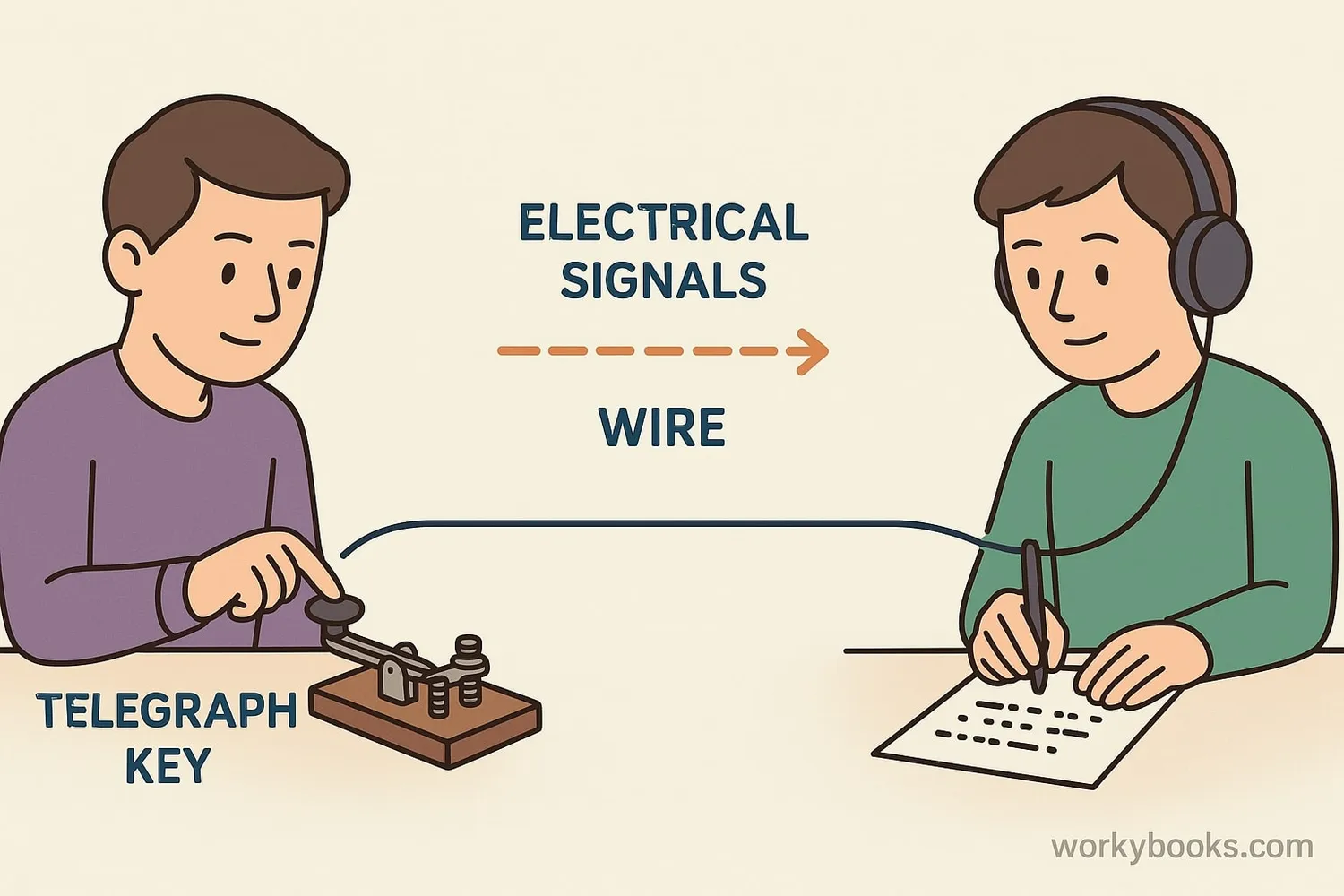
Morse code uses combinations of short and long signals to represent each letter of the alphabet and numbers 0-9. Here's how the system works:
Try Decoding This:
•• ——— •••
This is the international distress signal "SOS" which means "Save Our Souls" or simply "Help!"
| Letter | Morse Code | Letter | Morse Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | •— | N | —• |
| B | —••• | O | ——— |
| C | —•—• | P | •——• |
| D | —•• | Q | ——•— |
| E | • | R | •—• |
| F | ••—• | S | ••• |
| G | ——• | T | — |
| H | •••• | U | ••— |
| I | •• | V | •••— |
| J | •——— | W | •—— |
| K | —•— | X | —••— |
| L | •—•• | Y | —•—— |
| M | —— | Z | ——•• |
To send a message in Morse code:
1. Break your message into individual letters
2. Find each letter in the Morse code chart
3. Transmit the dots and dashes using a telegraph key, flashlight, or sound
4. Leave a short pause between letters and a longer pause between words
Binary Communication!
Morse code was one of the first binary communication systems, using just two different signals (dot and dash) to represent all information!
History & Modern Uses

Morse code revolutionized communication in the 19th and 20th centuries. Here's why it was so important and where it's still used today:
Maritime Safety
Used on ships for distress signals until the 1990s. The Titanic sent Morse code distress calls when it sank.
Aviation Navigation
Some navigation beacons still identify themselves with Morse code signals.
Amateur Radio
Ham radio operators use Morse code for long-distance communication.
Samuel Morse and his assistant Alfred Vail developed the code in the 1830s-1840s to work with their new invention - the telegraph. The first official message sent by Morse code was "What hath God wrought?" from Washington to Baltimore in 1844.
Even today, Morse code remains valuable because:
• It can be sent with simple equipment
• It works when voice communication isn't possible
• It can be understood through interference
• It requires very little power to transmit
Many military personnel and emergency responders still learn Morse code as a backup communication method.
Morse Code Quiz
Test your knowledge with this Morse code quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about Morse code:
Fun Morse Code Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about Morse code:
Titanic's Distress Call
The Titanic's radio operators sent the Morse code distress signal "CQD" (the older distress call) and the newer "SOS" as the ship sank in 1912. This was one of the first major uses of SOS.
POW Communication
American prisoners of war in Vietnam used Morse code to communicate by tapping on walls. Navy pilot Jeremiah Denton blinked "T-O-R-T-U-R-E" in Morse code during a televised interview to alert the world to POW conditions.
First Message
The first official Morse code message sent in 1844 was "What hath God wrought?" from Washington, D.C. to Baltimore. This phrase comes from the Bible (Numbers 23:23) and was chosen by Annie Ellsworth.
Morse in Your Pocket
Smartphones have built-in Morse code capabilities! Both Android and iOS support Morse code input methods. Google's Gboard keyboard includes a Morse code keyboard option for typing using dots and dashes.





