Properties of Matter - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how everything around us is made of matter with different properties and states
What is Matter?
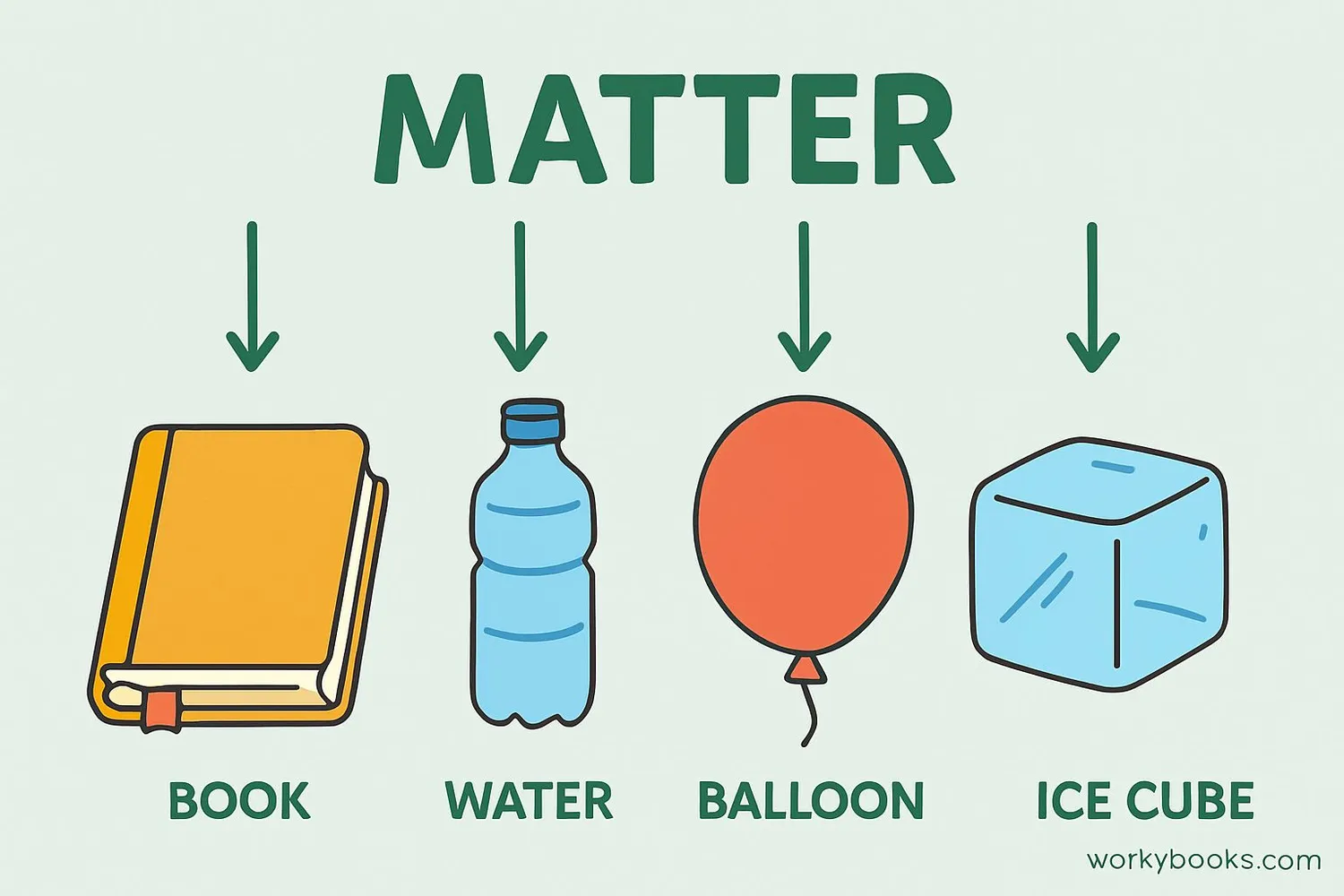
Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Everything you can see, touch, smell, or taste is made of matter. Your desk, your pencil, the air you breathe, and even you are made of matter!
Matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms and molecules. These particles are too small to see with just your eyes, but they're the building blocks of everything in the universe. Matter can exist in different states (solid, liquid, gas) and has different properties that help us identify and classify it.
Matter Fact!
All matter has two fundamental properties: mass (how much "stuff" is in it) and volume (how much space it takes up).
Properties of Matter
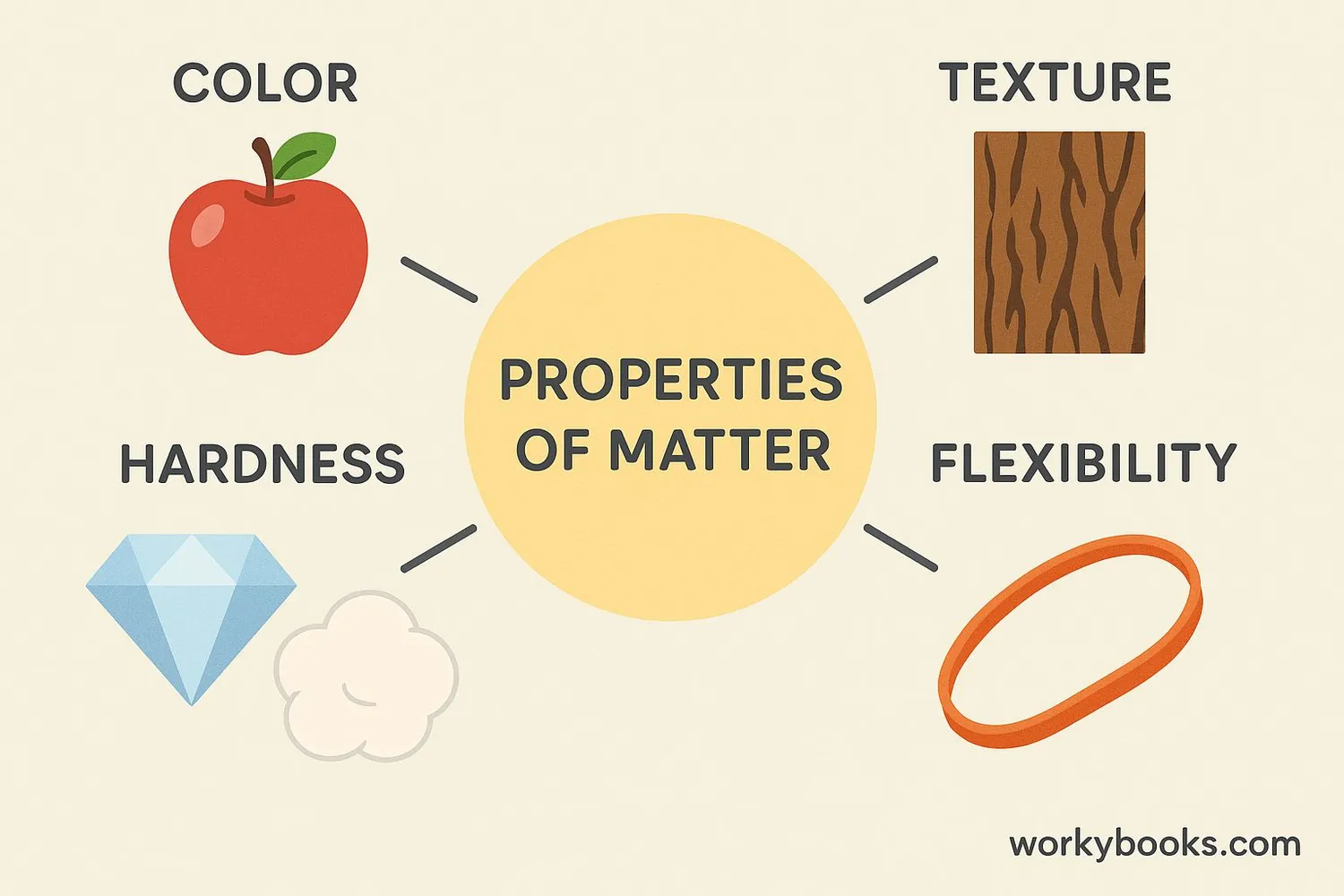
Properties of matter are the characteristics that describe matter and help us identify different substances. These properties can be divided into two main categories: physical properties and chemical properties.
Physical Properties
Physical properties can be observed or measured without changing the substance into something else. Examples include:
| Property | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Color | How an object reflects light | Apples are red, bananas are yellow |
| Texture | How a surface feels | Sandpaper is rough, silk is smooth |
| Hardness | Resistance to being scratched | Diamonds are hard, talc is soft |
| Mass | Amount of matter in an object | Measured in grams or kilograms |
| Volume | Amount of space an object occupies | Measured in liters or cubic centimeters |
| Density | Mass per unit volume (mass ÷ volume) | Lead is dense, Styrofoam is not dense |
Chemical Properties
Chemical properties describe how a substance behaves when it reacts with other substances and changes into new substances. Examples include:
Flammability
Ability to burn
Reactivity
How easily it reacts with other substances
Oxidation
Ability to react with oxygen (rusting)
Density Demonstration!
When you pour oil and water together, the oil floats on top because it's less dense than water. This is why oil spills float on ocean water!
States of Matter
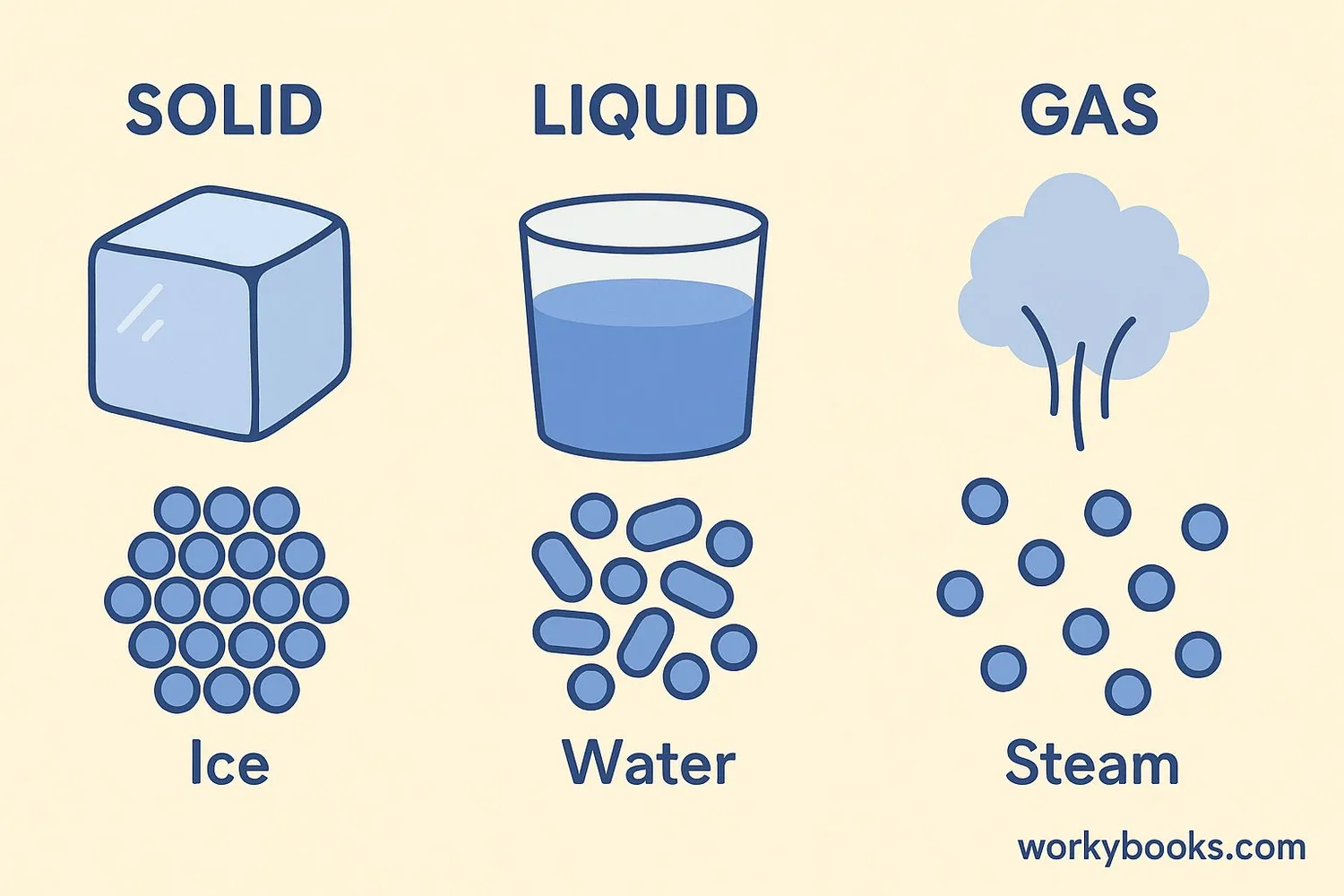
Matter exists in different states, primarily solid, liquid, and gas. The state of matter depends on how close its particles are and how they move. Matter can change from one state to another when heat is added or removed.
Solid
Has definite shape and volume. Particles are packed tightly together and vibrate in place.
Liquid
Has definite volume but takes the shape of its container. Particles are close but can slide past each other.
Gas
No definite shape or volume. Particles are far apart and move quickly in all directions.
Changes between states of matter have special names:
• Solid to Liquid: Melting (ice to water)
• Liquid to Gas: Evaporation (water to steam)
• Gas to Liquid: Condensation (steam to water)
• Liquid to Solid: Freezing (water to ice)
• Solid to Gas: Sublimation (dry ice to carbon dioxide gas)
• Gas to Solid: Deposition (frost forming)
Water Cycle Connection!
The water cycle is a perfect example of matter changing states: evaporation (liquid to gas), condensation (gas to liquid), and precipitation (liquid falling as rain or solid falling as snow).
Properties of Matter Quiz
Test your knowledge about matter with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about matter:
Fun Matter Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about matter!
Space Matter
The most common state of matter in the universe is plasma, not solid, liquid, or gas! Stars like our sun are made of plasma.
Super Dense
A teaspoon of a neutron star would weigh about 10 million tons! That's heavier than all the cars in the United States combined.
Water Exception
Water is unusual because its solid form (ice) is less dense than its liquid form. That's why ice floats in water!
Mostly Empty Space
Atoms are mostly empty space! If an atom were the size of a football stadium, the nucleus would be the size of a marble in the center.





