Single Replacement Reactions - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how elements trade places in chemical reactions!
What is a Single Replacement Reaction?
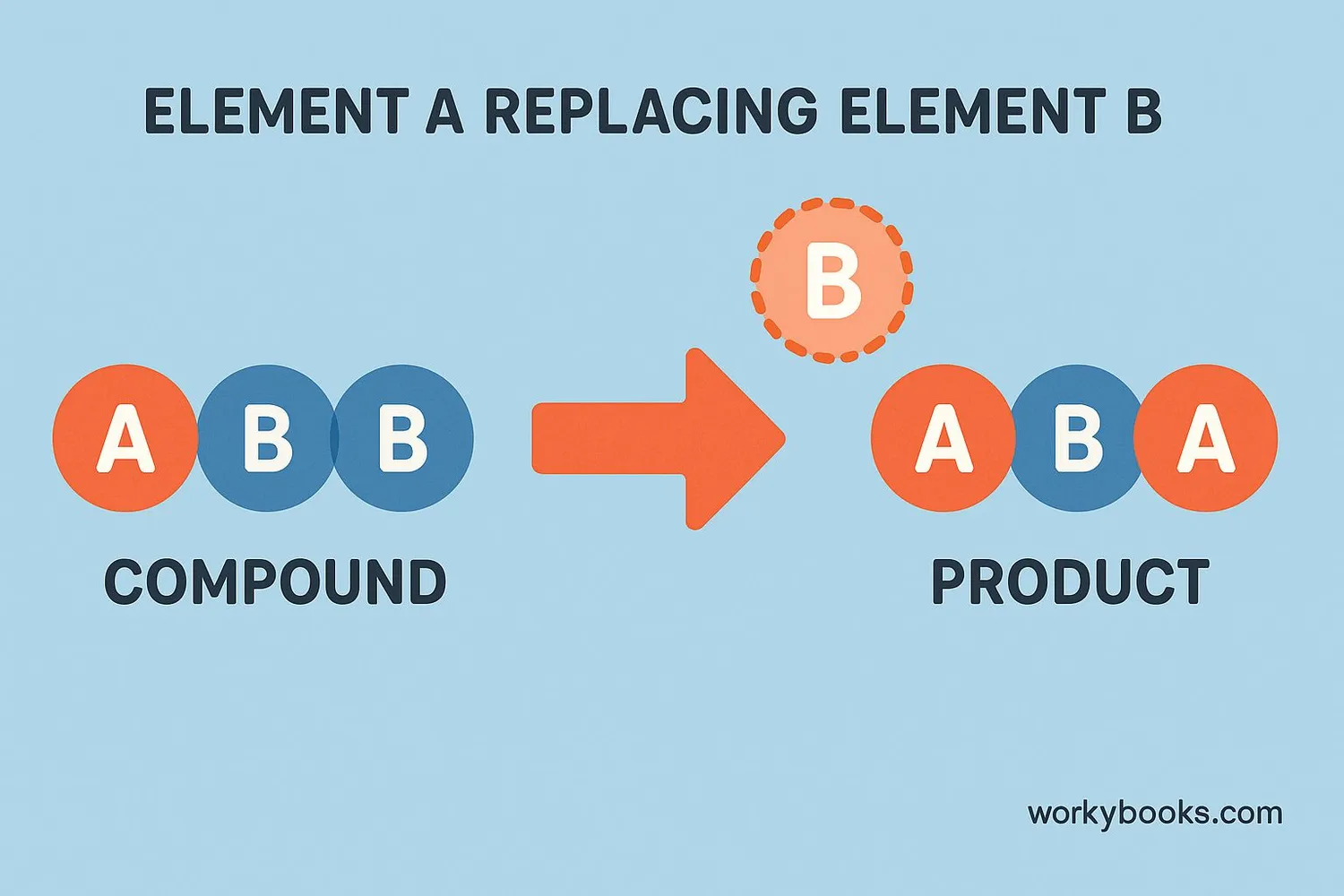
A single replacement reaction is a type of chemical reaction where one element replaces another element in a compound. It's like a trade or swap where a more reactive element kicks out a less reactive element from its compound.
The general formula for a single replacement reaction is:
A + BC → AC + B
Where element A replaces element B in the compound BC. For the reaction to work, element A must be more reactive than element B.
Remember This!
In single replacement reactions, think of it as a competition - the more reactive element wins and takes the place of the less reactive element in the compound.
How Single Replacement Reactions Work
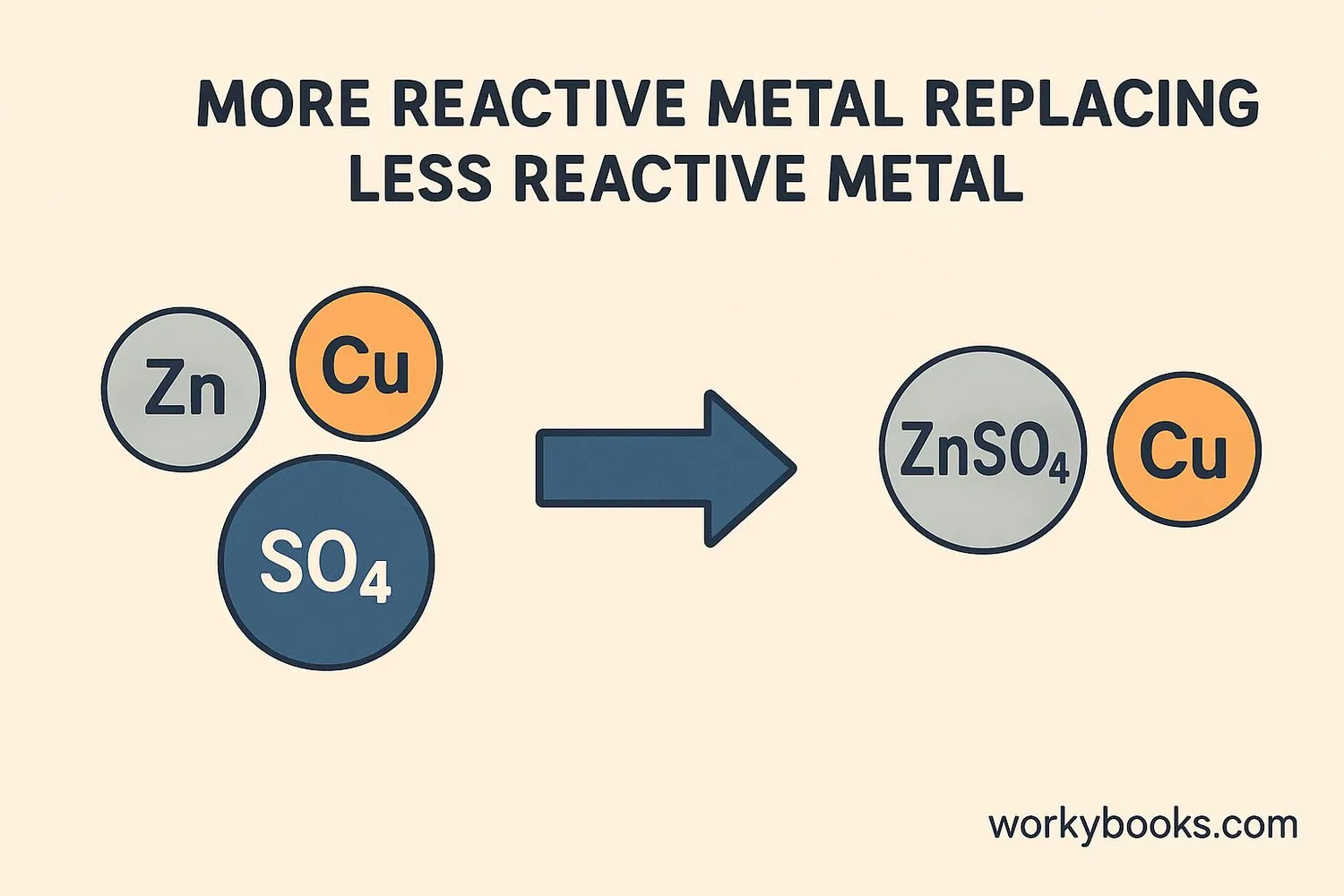
Single replacement reactions follow specific rules based on the reactivity of elements. Here's what happens step by step:
Element Approaches
A free element approaches a compound
Reactivity Check
The free element must be more reactive than the element it wants to replace
Replacement
The more reactive element replaces the less reactive one in the compound
New Products
A new compound and a free element are formed
For example, when zinc metal is placed in copper sulfate solution:
Examples of Single Replacement Reactions
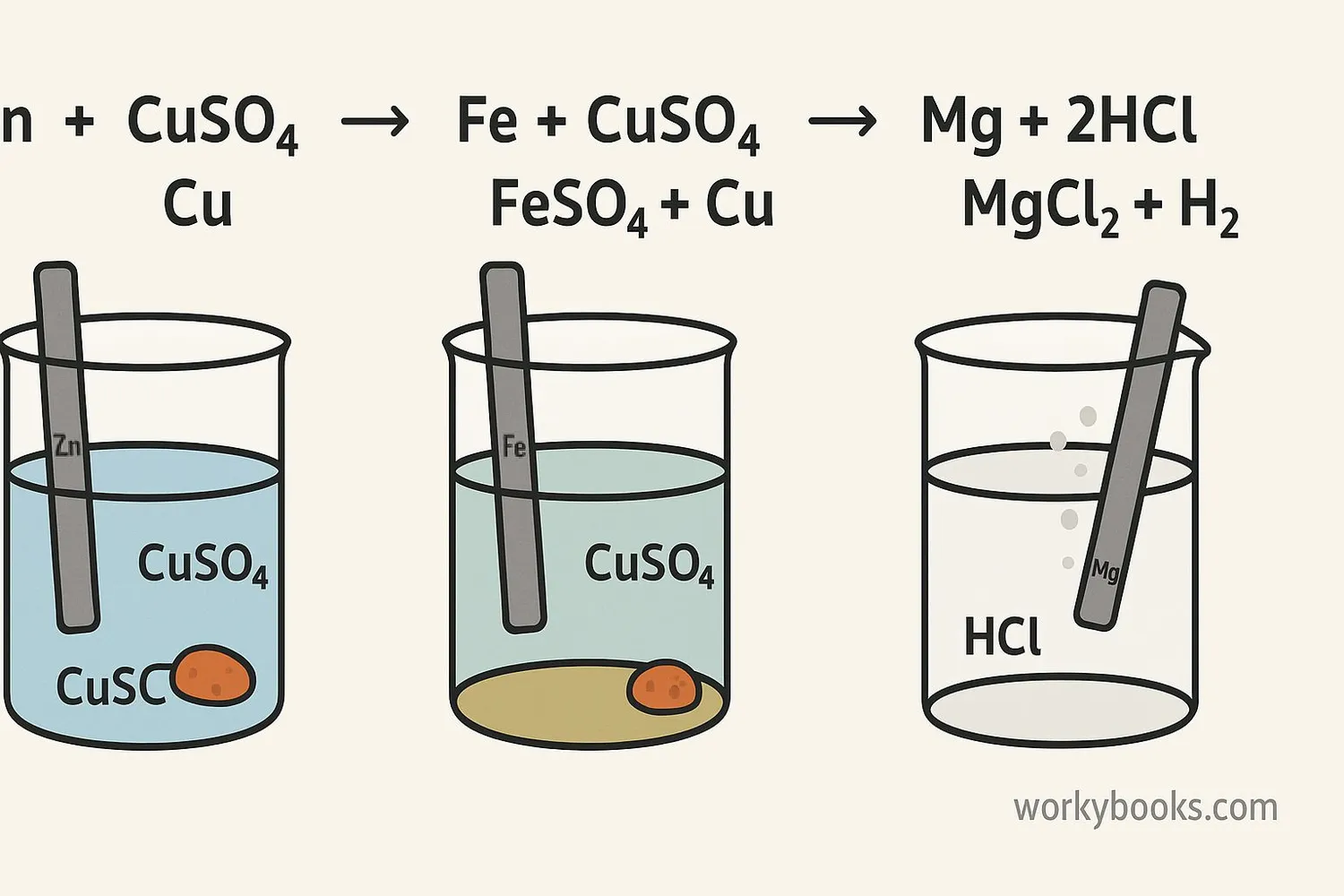
Single replacement reactions occur all around us. Here are some common examples:
Zinc and Copper Sulfate
Zn + CuSO₄ → ZnSO₄ + Cu
Zinc replaces copper, forming zinc sulfate and copper metal
Magnesium and Hydrochloric Acid
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl₂ + H₂
Magnesium replaces hydrogen, forming magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas
Aluminum and Iron Oxide
2Al + Fe₂O₃ → Al₂O₃ + 2Fe
Aluminum replaces iron, forming aluminum oxide and iron metal (thermite reaction)
Real-world Application
Single replacement reactions are used in metal extraction. For example, aluminum can be used to extract less reactive metals like iron from their ores.
The Activity Series
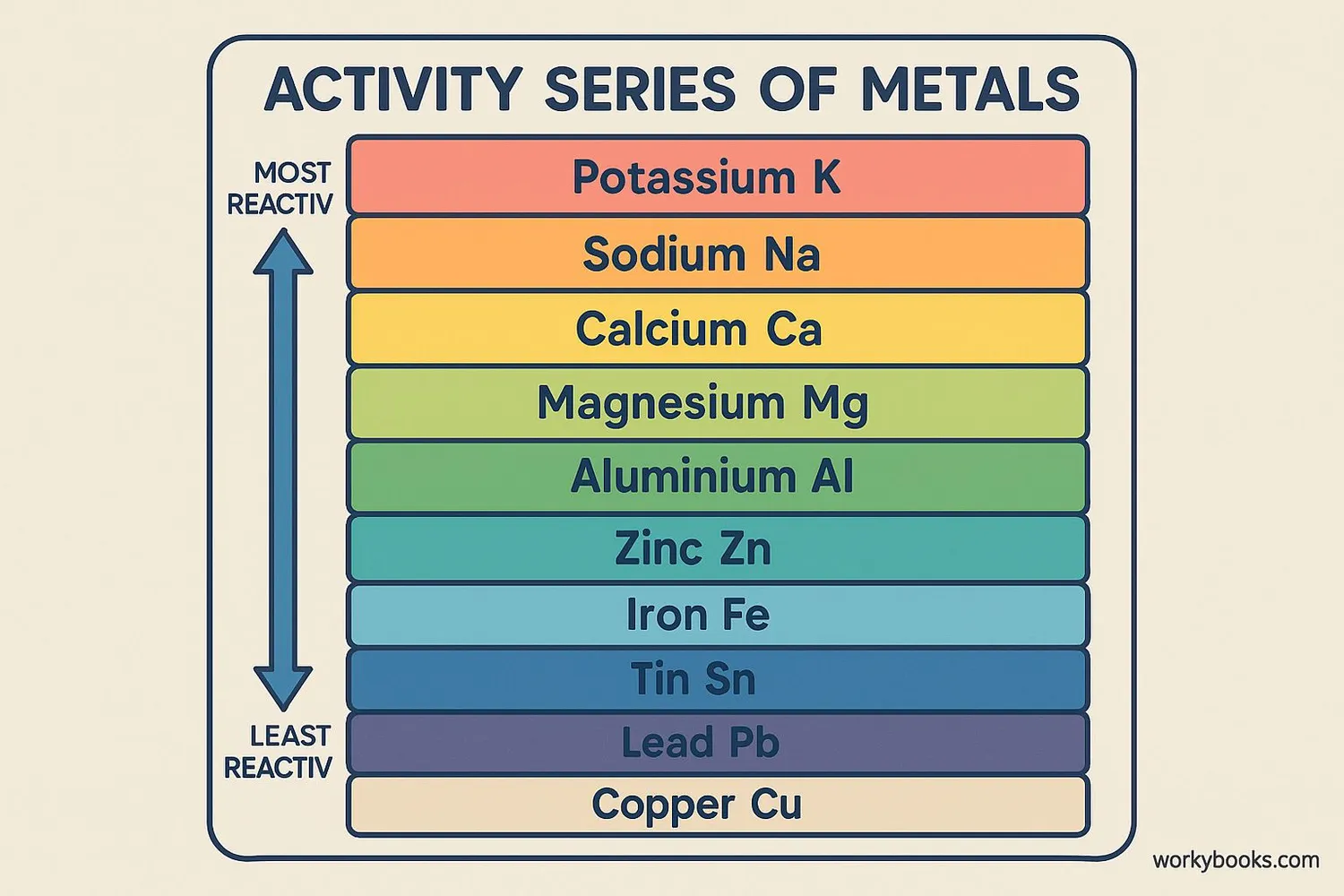
The activity series is a list of elements organized by their reactivity. It helps us predict whether a single replacement reaction will occur:
| Metal | Reactivity | Can Replace |
|---|---|---|
| Potassium (K) | Most Reactive | All metals below it |
| Sodium (Na) | Very Reactive | All metals below it |
| Calcium (Ca) | Reactive | All metals below it |
| Magnesium (Mg) | Reactive | All metals below it |
| Aluminum (Al) | Reactive | All metals below it |
| Zinc (Zn) | Moderately Reactive | All metals below it |
| Iron (Fe) | Moderately Reactive | All metals below it |
| Lead (Pb) | Low Reactive | All metals below it |
| Hydrogen (H) | Reference Point | — |
| Copper (Cu) | Low Reactive | Silver and gold only |
| Silver (Ag) | Very Low Reactive | Gold only |
| Gold (Au) | Least Reactive | None |
Rule: An element can only replace another element in a compound if it is higher in the activity series.
For example, zinc can replace copper in copper sulfate because zinc is higher than copper in the activity series. But copper cannot replace zinc in zinc sulfate because copper is lower than zinc.
Single Replacement Reaction Quiz
Test your knowledge with this quiz on single replacement reactions! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about single replacement reactions:
Interesting Facts
Discover some fascinating facts about single replacement reactions!
Historical Discovery
The concept of single replacement reactions was first systematically studied by Antoine Lavoisier in the late 18th century, who is often called the "father of modern chemistry".
Industrial Application
The thermite reaction, a type of single replacement reaction between aluminum and iron oxide, is used to weld railroad tracks together and in some military applications.
Biological Connections
Single replacement reactions play a role in biological systems too! The replacement of magnesium by other metals in chlorophyll molecules can affect photosynthesis in plants.
Environmental Impact
Single replacement reactions are used in environmental cleanup. For example, iron metal can be used to remove toxic metals like lead and cadmium from contaminated water through displacement.




