Line of Symmetry: Definition, Shapes, and Examples for Kids
Understanding symmetry is an exciting part of learning geometry for young students. Symmetry is all around us—in nature, in art, and in the objects we use every day. In this blog, we’ll explore the line of symmetry, understand its definition, discover the types of symmetry, and look at fun examples and practice problems.
What is a Line of Symmetry?
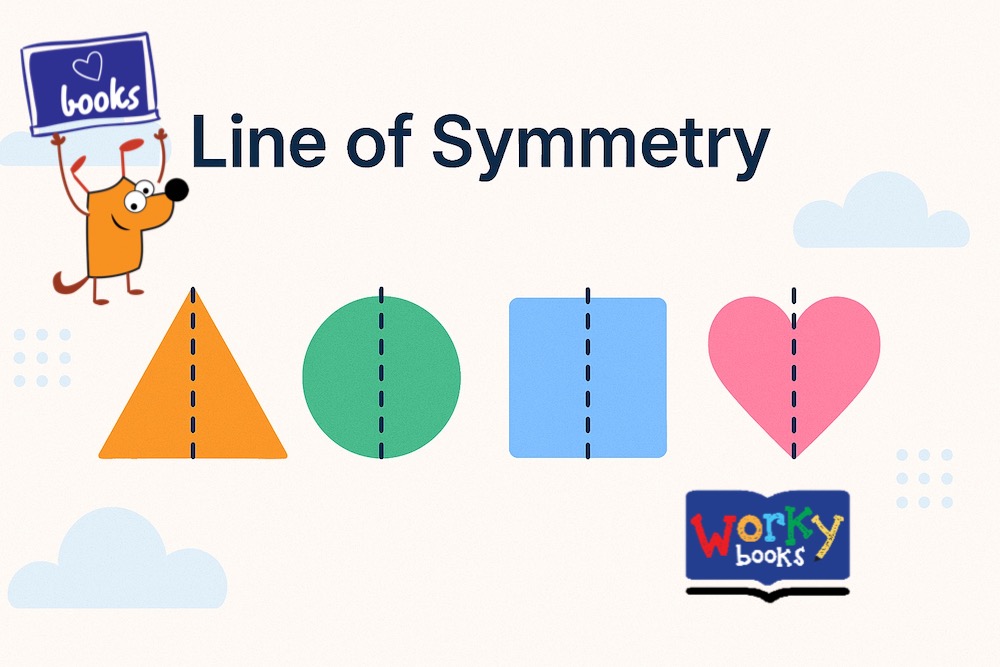
A line of symmetry is a line that divides a shape into two identical halves. If you fold the shape along this line, both sides match exactly. This concept is also known as mirror symmetry.
Imagine folding a heart shape in half—it looks the same on both sides. That folding line is a symmetry line. It helps children recognize patterns and balance in shapes, which is a key part of understanding geometry.
In classroom teaching aligned with Shapes 4.G.A.2, students are expected to identify lines of symmetry in two-dimensional figures and explore how these lines function across various shapes.
Definition of Line of Symmetry
The definition of symmetry in simple terms is a balance or similarity between two halves of an object. The line of symmetry is the imaginary line that makes the two halves identical when folded or reflected.
In mathematical terms, a shape is symmetrical if one half is a mirror image of the other. These shapes are called symmetrical shapes. The lines of symmetry definition applies not just to geometric shapes, but also to alphabets, objects, and even nature.

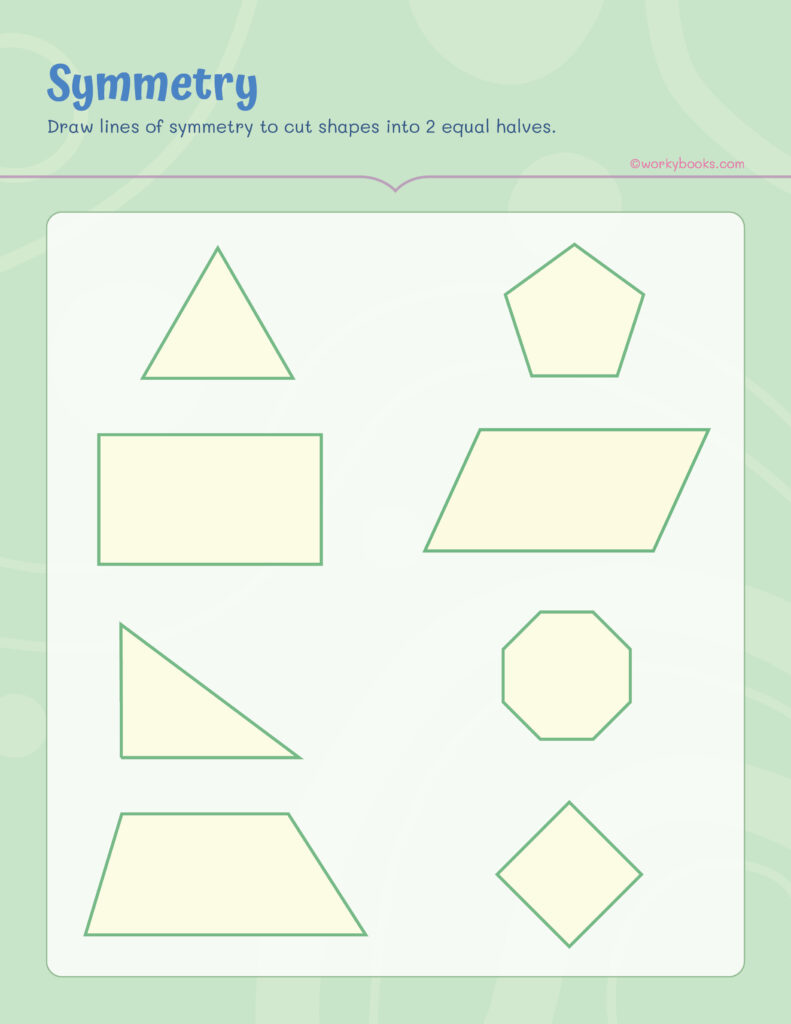
Number of Lines of Symmetry in a Shape
Different shapes have different numbers of symmetry lines:
- Square – 4 lines of symmetry
- Rectangle – 2 lines of symmetry
- Equilateral Triangle – 3 lines
- Isosceles Triangle – 3 line
- Hexagon) – 6 lines
- Alphabet Letters – Some like A, M, and T have vertical symmetry lines
A printable worksheet on CCSS 4.G.A.3 – Geometry Shapes is a great way for students to explore these symmetry lines in detail through drawing and folding activities.
Real-Life Examples of Symmetry
Symmetry is not just found in math books—it’s everywhere! Recognizing it in the real world helps children better understand its purpose and beauty.
1. Nature:
- Butterflies have mirror symmetry; their left and right wings are nearly identical.
- Leaves, flowers, and even spider webs show stunning symmetrical patterns.
2. Architecture:
- Famous buildings like the Taj Mahal or parliament houses use symmetry to create balance and beauty.
- Doors and windows are often placed symmetrically to improve design and structure.
3. Sports and Equipment:
- A tennis court, snowboard, or soccer ball often shows reflection or rotational symmetry to maintain balance and function.
4. Letters and Words:
- Letters like A, H, M, T, and U show vertical symmetry.
- Words like “WOW” or “MOM” are examples of symmetrical words.

When Do Children Learn About Lines of Symmetry in Primary School?
In most educational curriculums, children begin learning about line symmetry around Grade 2 or Grade 3. This is when students start exploring geometric shapes worksheets and understanding spatial awareness.
Teachers introduce symmetry using drawing activities, cut-out shapes, or folding exercises. By Grade 4 or 5, students begin identifying multiple symmetry lines in complex figures and learn terms like rotational and reflection symmetry.
The CCSS 4.G.A.2 and 4.G.A.3 standards provide a structured way for teachers to present these ideas and assess students’ understanding using both hands-on and visual methods.
Examples and Practice Problems on Line of Symmetry
Here are some fun ways to practice symmetry:
Examples:
- Fold a paper heart and see both sides match.
- Draw a vertical line through a square and note that both halves are the same.
- Reflect your name vertically—see which letters are symmetrical!
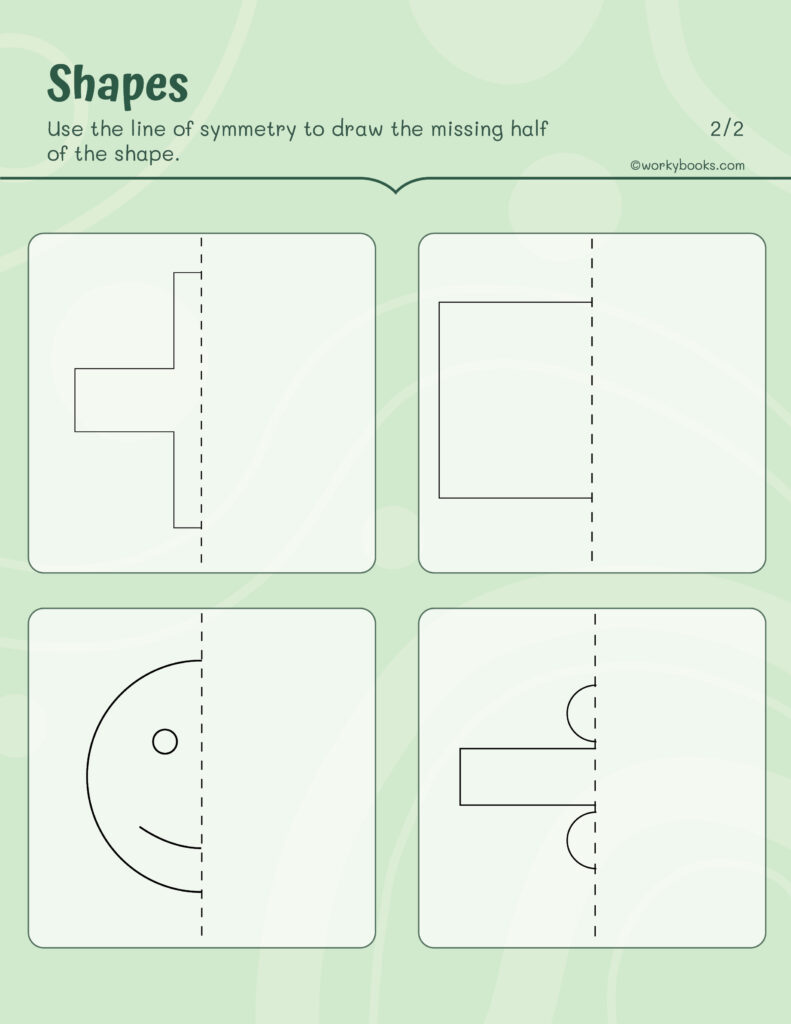
Practice Problems:
- How many lines of symmetry does a rectangle have?
- Draw a line of symmetry through an equilateral triangle.
- Which alphabet letters have reflection symmetry?
- Does the shape below (show triangle, square, etc.) have rotational symmetry?
These exercises help kids visualize and reinforce the concept of symmetry while practicing symmetrical shapes.
Conclusion
Understanding the line of symmetry opens up a world of pattern recognition, balance, and spatial thinking. From nature to letters and shapes, symmetry surrounds us and forms a key part of a child’s geometry learning journey.
To make learning symmetry even more fun and interactive, explore the line of symmetry worksheets offered by Workybooks. These educational resources are designed to match Common Core standards like CCSS 4.G.A.2 and 4.G.A.3, and include a wide variety of printable activities for kids.
Workybooks’ tools and worksheets provide a hands-on approach to teaching symmetry lines, line symmetry, and symmetrical shapes in geometry, helping children visualize, understand, and enjoy geometry!
Frequently Asked Questions on Line of Symmetry
1. What does symmetry mean?
Symmetry means that one part of a shape or object is the exact mirror image of the other part.
2. What is a line of symmetry in math?
A line of symmetry is an imaginary line that divides a shape into two matching halves.
3. Can a shape have more than one line of symmetry?
Yes! Some shapes like circles and squares have multiple lines of symmetry.
4. What are symmetrical shapes?
Symmetrical shapes are shapes that can be divided into identical parts by a line of symmetry.
5. What is the difference between rotational and reflection symmetry?
Reflection symmetry flips a shape over a line, while rotational symmetry turns the shape around a point.
