Importance of Köppen Climate Classification System
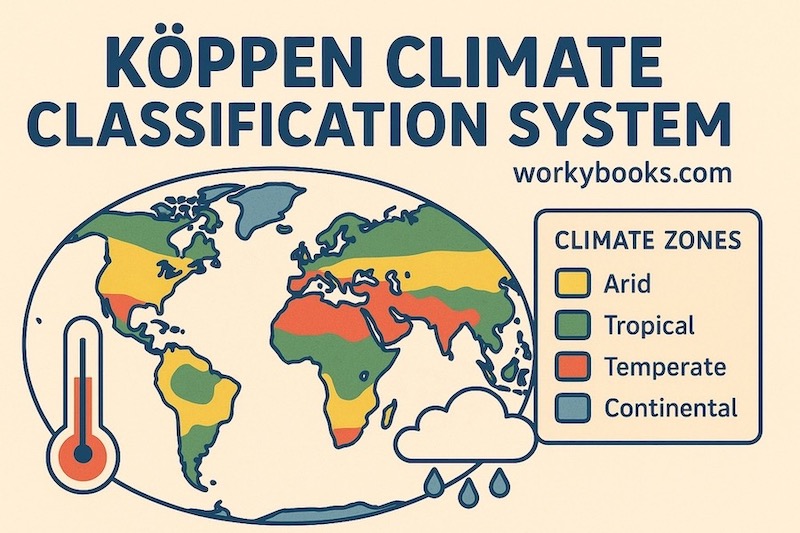
The Köppen climate classification system is one of the most widely used methods for categorizing the world’s climates. Developed by German climatologist Vladimir Köppen in 1884, this system provides a clear framework for understanding global climate patterns. It has become an essential tool in geography education and climate science.
What is the Köppen Climate Classification System?
The Köppen Climate Classification System is the most widely used method to categorize the world’s climates. Developed by German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1884, it divides climates into types of climate based on temperature, precipitation, and seasonal patterns. This system helps geographers, scientists, and teachers analyze the climate system and its impact on ecosystems, agriculture, and human activities.
What Two Factors Are Used to Classify Climate in the Köppen System?
According to the Köppen Climate Classification System, two primary factors determine climate categories:
- Temperature: Average monthly and annual temperatures.
- Precipitation: Amount, type (rain, snow), and seasonal distribution.
These measurements, taken as monthly averages over many years, help scientists determine which climate zone a particular location belongs to.
. These factors help identify patterns like tropical rainforests, arid deserts, or polar tundras.
What are the 5 Köppen’s climate categories?
The Köppen climate classification system is a method that divides the world’s climates into distinct climate categories. The climates are labeled using letter combinations. The first letter represents the main climate group, while additional letters provide more specific details about temperature and precipitation patterns. This creates a comprehensive climate system that can describe any location on Earth.
The Köppen system recognizes five main climate categories:
- A (Tropical): Hot climates with average temperatures above 18°C (64°F) year-round
- B (Dry): Arid and semi-arid regions where evaporation exceeds precipitation
- C (Temperate): Mild climates with moderate temperatures and distinct seasons
- D (Continental): Cold climates with significant temperature variations between seasons
- E (Polar): Extremely cold climates with average temperatures below 10°C (50°F) in the warmest month
Each of these main categories is further divided into subcategories. For example, the temperate climate group includes Mediterranean climates (Csa) and humid subtropical climates (Cfa).

Understanding the US Köppen Climate Map
The United States displays remarkable climate diversity according to the Köppen climate zones. The US Köppen climate map reveals:
- Humid subtropical climates (Cfa) dominate the southeastern states
- Mediterranean climates (Csa/Csb) occur along parts of California’s coast
- Cold continental climates (Dfa/Dfb) cover the northern Great Plains and Upper Midwest
- Desert climates (BWh/BWk) characterize the Southwest
- Humid continental climates (Dwa/Dwb) appear in the northeastern states
This variety makes the United States an excellent case study for teaching climate classification in geography.
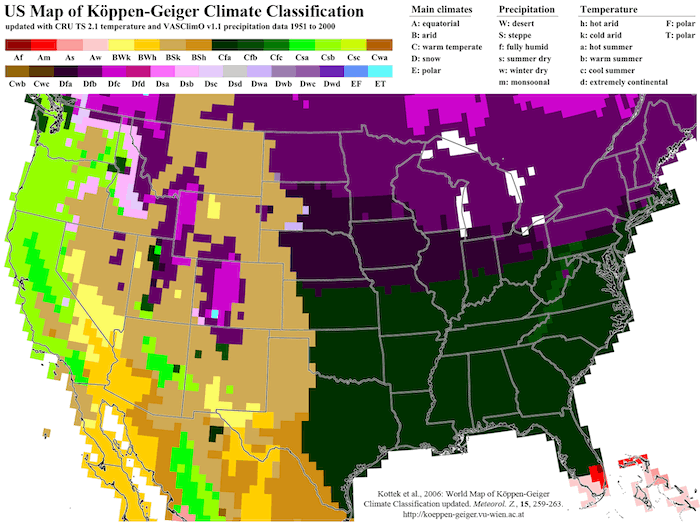
source:WORLD MAP OF THE KÖPPEN-GEIGER CLIMATE CLASSIFICATION UPDATED
MAP FOR THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA from https://koeppen-geiger.vu-wien.ac.at/usa.htm
How to Read a Köppen Climate Chart
A climate chart for any location typically shows:
- Monthly temperature averages (usually as a line graph)
- Monthly precipitation totals (often as bar graphs)
- The Köppen classification code for that location
Teachers can use these charts to help students identify climate patterns. Students learn to recognize the relationship between temperature and precipitation that defines each climate type.
Commonly Asked Questions About Köppen Climate Classification
Q1: What are the 2 main factors in the Köppen system?
A: Temperature and precipitation.
Q2: What climate type is a tropical rainforest?
A: Af (Tropical rainforest climate).
Q3: Why is the Köppen system important?
A: It simplifies global climate patterns for research and education.
Q4: Is the Köppen system updated?
A: Yes, modern versions include minor adjustments for urbanization.
Q5: Where can I find the US Köppen map?
A: Check resources like the USDA or climate.gov.
Q6: Why is the Köppen system still used today?
A: The Köppen system remains popular because it’s simple, effective, and based on observable data. It provides a standardized way to discuss climate globally.
Q7: How many Köppen climate types exist in total?
A: There are approximately 30 climate subtypes when including all letter combinations, though the exact number varies slightly depending on the specific version used.
Q8: Can Köppen classifications change over time?
A: Yes, climate classifications can shift due to climate change. Some regions have experienced transitions between Köppen zones as temperatures and precipitation patterns change.
Q9: What’s the difference between climate and weather in this system?
A: Weather refers to daily conditions, while climate represents long-term averages. Köppen classification uses climate data averaged over at least 30 years.
Q10: How accurate is the Köppen system for local climates?
A: While excellent for regional classification, the Köppen system may not capture microclimates or small-scale variations within a zone.
Teaching Resources for the Köppen Climate System
To enhance classroom learning about Köppen climate zones:
- Interactive Maps: Use online Köppen climate maps that allow students to explore different regions
- Climate Data Websites: Access real climate data from weather stations worldwide
- Case Studies: Examine how climate affects agriculture, architecture, and lifestyle in different zones
- Field Trips: Visit local weather stations or geography departments
- Educational Video on Köppen system
Interactive Learning Resources from workybooks:
This NGSS-aligned science reading passage explains the Köppen Climate Classification System, a scientific method used to categorize Earth’s climates based on temperature and precipitation.
Koppen climate classification – Interactive educational page with activities, quizzes, visual content, and FAQ section designed for young learners
EXPLORE NOW to check out our NGSS-aligned reading passages on Earth Science. Enhance your classroom with standards-based materials that make complex concepts accessible and engaging!