Geomagnetic Storms - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how space weather affects our planet!
What Are Geomagnetic Storms?
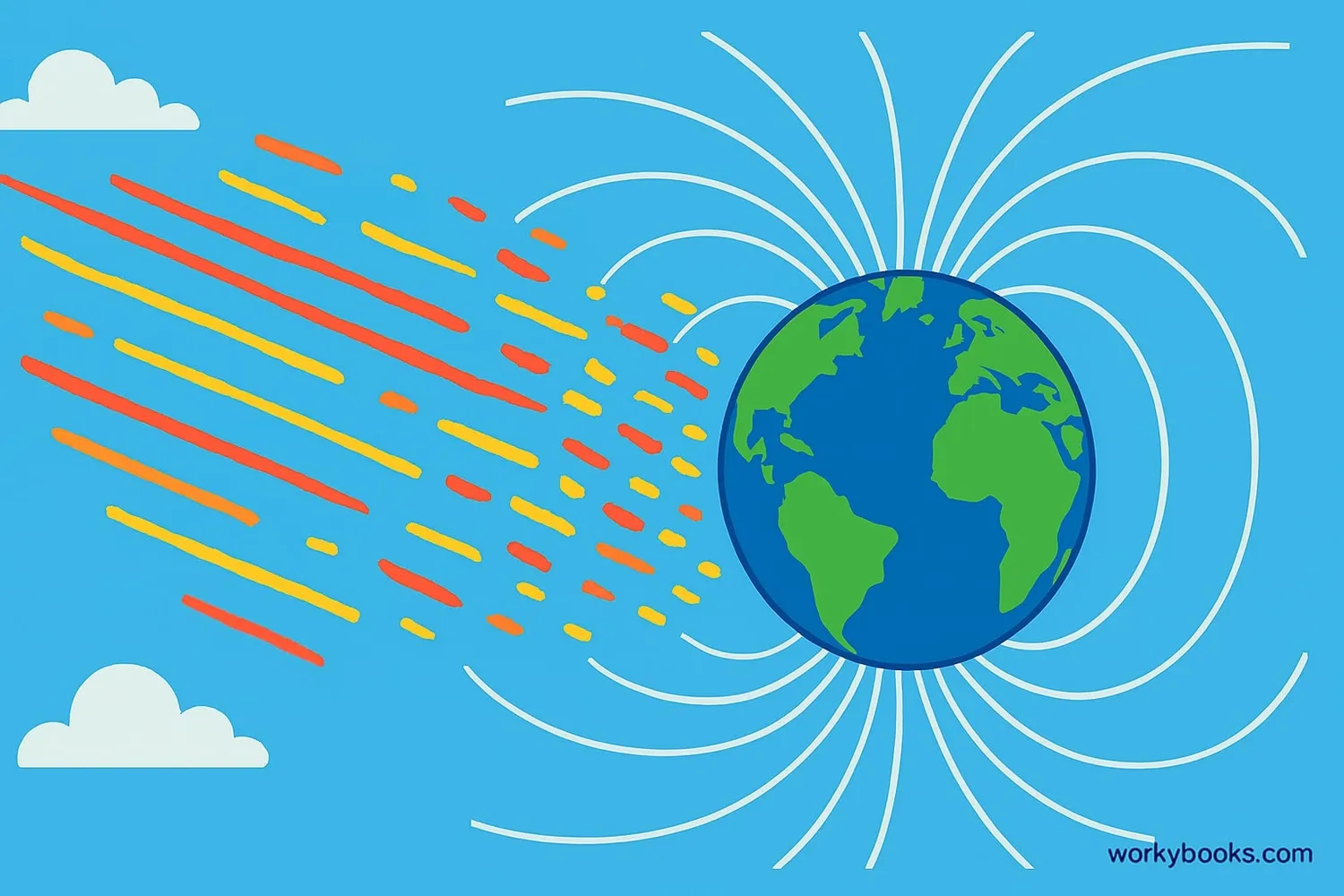

A geomagnetic storm is a disturbance in Earth's magnetic field caused by energy from the Sun. It's like space weather that affects our planet!
These storms happen when the Sun sends out huge bursts of energy called solar flares or giant clouds of particles called coronal mass ejections (CMEs). When these reach Earth, they interact with our magnetic field, causing it to shake and vibrate.
Space Weather Fact!
The most powerful geomagnetic storm ever recorded happened in 1859 and was called the Carrington Event. It caused telegraph systems to fail all over the world!
How Geomagnetic Storms Work
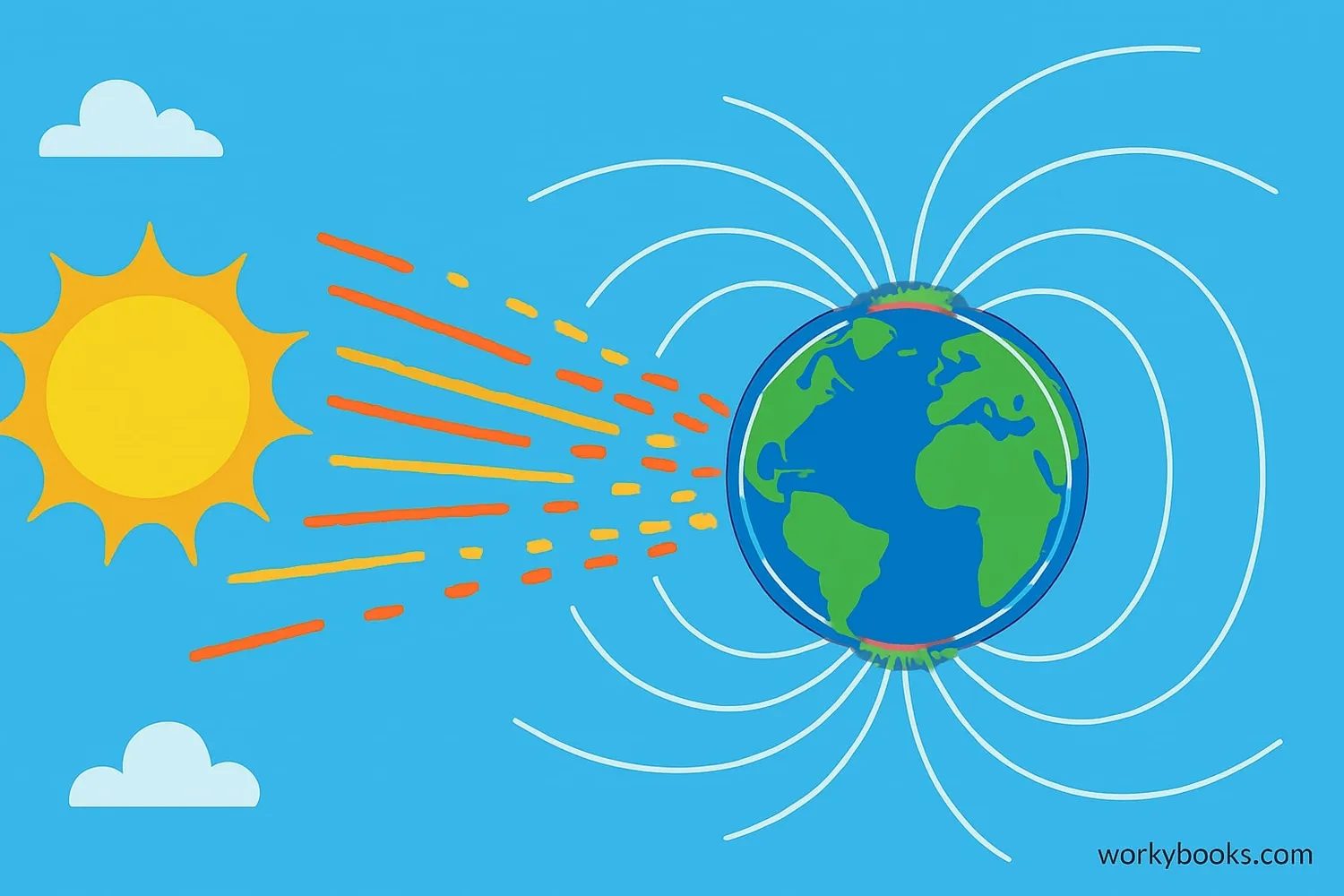
Geomagnetic storms are like cosmic dances between the Sun and Earth. Here's how they work step by step:
Solar Activity
The Sun releases solar flares or coronal mass ejections (CMEs)
Travel Through Space
Charged particles travel toward Earth at high speed
Magnetosphere Interaction
Particles collide with Earth's magnetic shield
Energy Transfer
Energy is transferred to Earth's magnetic field
Auroras Form
Particles enter atmosphere near poles, creating lights
During strong storms, the magnetic field changes can create electrical currents in the ground that affect power lines and other technology. Scientists measure storm strength using the Kp index and Dst index scales.
Magnetic Shield!
Earth's magnetosphere extends about 65,000 kilometers (40,000 miles) toward the Sun and much farther in the opposite direction, protecting us from solar radiation.
Why Geomagnetic Storms Matter
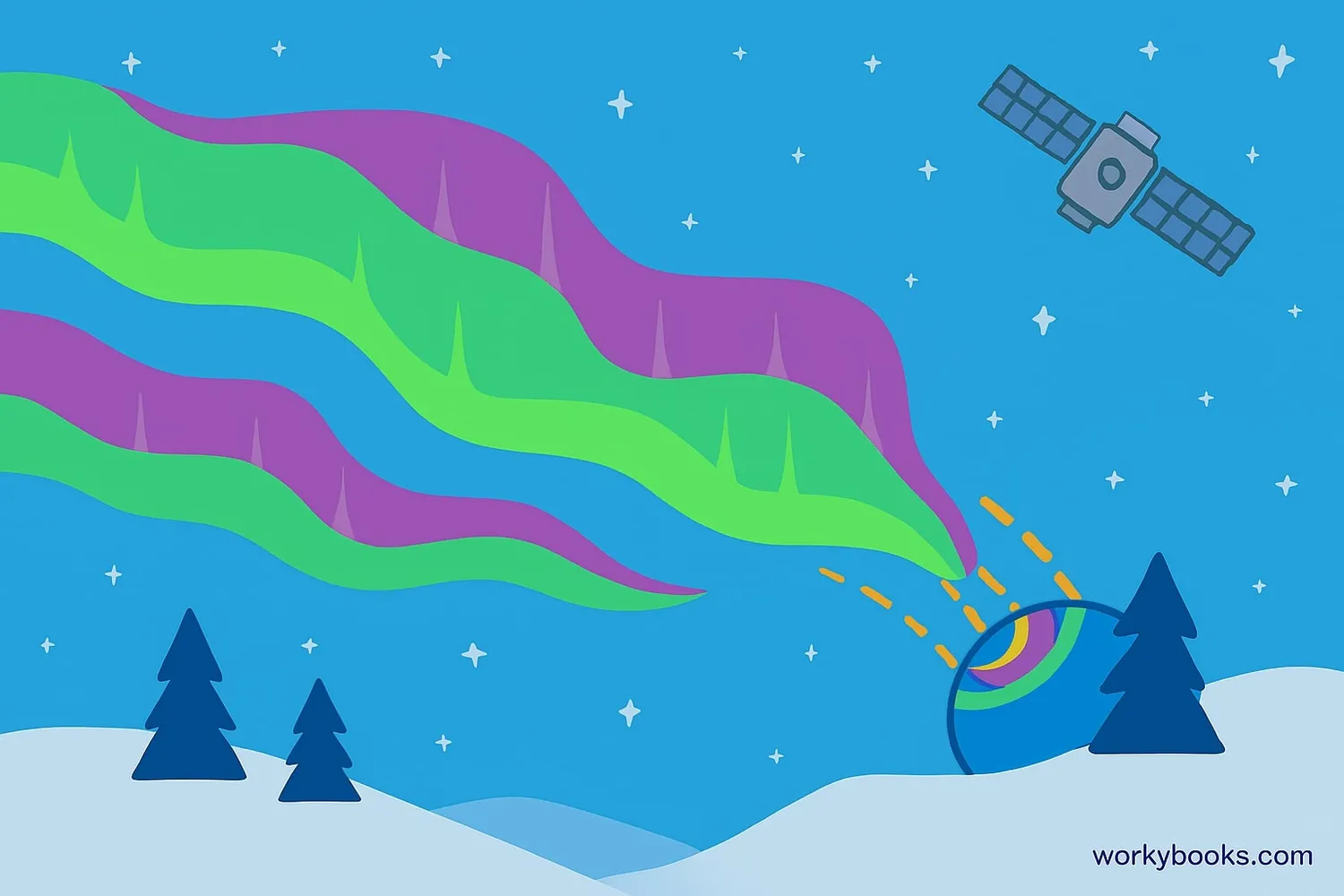

Geomagnetic storms affect our planet in both beautiful and challenging ways:
Auroras
Create stunning Northern and Southern Lights (Aurora Borealis and Aurora Australis)
Satellite Disruption
Can interfere with satellite communications and GPS systems
Power Grids
May cause power outages by overloading electrical systems
Other effects include:
• Disruption to radio communications
• Radiation hazards for astronauts
• Navigation challenges for animals
• Pipeline corrosion
Scientists monitor the Sun constantly to predict geomagnetic storms and give warnings to power companies, airlines, and satellite operators.
Space Weather Quiz
Test your knowledge about geomagnetic storms with this quiz!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about geomagnetic storms:
Space Weather Trivia
Discover amazing facts about geomagnetic storms and space weather!
Colorful Auroras
Auroras aren't just green! Depending on the atmospheric gases and altitude, they can appear red, blue, purple, or even pink. The most common color is pale green, created by oxygen at about 100 km above Earth.
Solar Cycles
The Sun has an 11-year activity cycle. During "solar maximum," the Sun has more sunspots and produces more solar flares and CMEs. The next solar maximum is predicted around 2025.
Animal Navigation
Geomagnetic storms can confuse animals that use Earth's magnetic field for navigation. Birds, whales, and even some insects might get lost during strong space weather events!
Historical Event
The Carrington Event of 1859 was so powerful that auroras were seen as far south as Cuba and Hawaii! Telegraph operators received shocks from their equipment, and some systems caught fire.




