Orangutans: The Rainforest Gardeners - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the amazing red apes of Borneo and Sumatra and why they need our help
What are Orangutans?

Orangutans are one of our closest relatives in the animal kingdom! These amazing great apes are known for their intelligence, gentle nature, and distinctive reddish-brown fur. The name "orangutan" comes from Malay words meaning "person of the forest" - a perfect description for these tree-dwelling primates.
There are three species of orangutans: Bornean, Sumatran, and the recently discovered Tapanuli. They are the largest tree-dwelling animals on Earth, with adult males weighing up to 200 pounds! Orangutans are famous for their long arms, which can stretch up to 7 feet - perfect for swinging through the rainforest canopy.
Intelligent Animals
Orangutans are incredibly smart! They use tools in the wild, like sticks to get honey from beehives or leaves as umbrellas during rain. They can solve complex problems and even learn sign language in captivity.
Where Orangutans Live
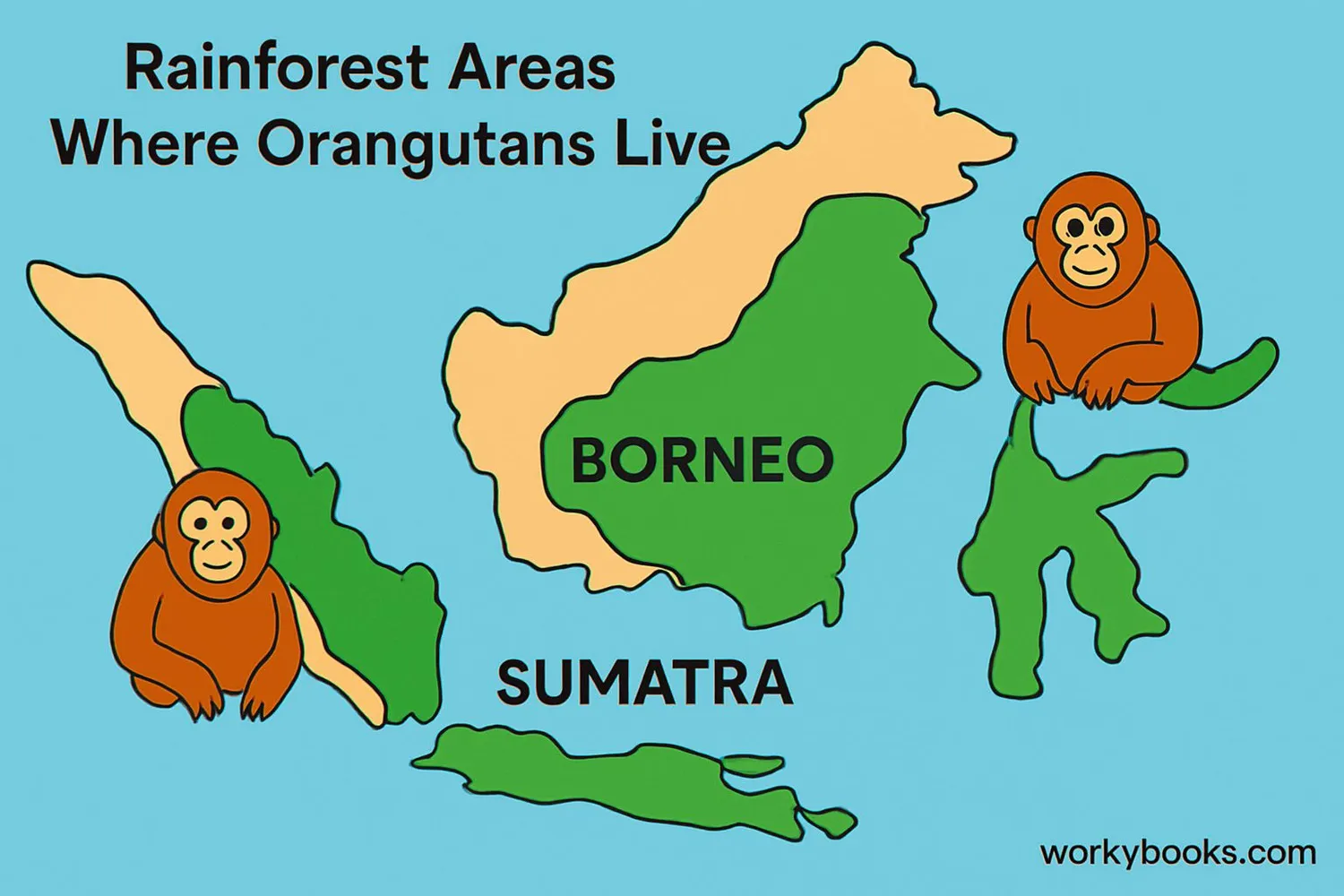
Orangutans are found only on the islands of Borneo and Sumatra in Southeast Asia. These rainforest animals live exclusively in tropical rainforests, spending most of their lives high up in the trees. They are arboreal apes, meaning they live in trees and rarely come down to the forest floor.
Orangutans build new nests every night by bending branches into comfortable sleeping platforms. A mother orangutan will share her nest with her baby for several years. Their rainforest homes are incredibly important - not just for orangutans, but for thousands of other species too!
Borneo Wildlife
Home to about 100,000 Bornean orangutans in dense rainforest habitats
Sumatra Animals
Only about 14,000 Sumatran orangutans remain in fragmented forests
Habitat Loss
Over 80% of orangutan habitat has disappeared in the last 20 years
Why Orangutans are Endangered
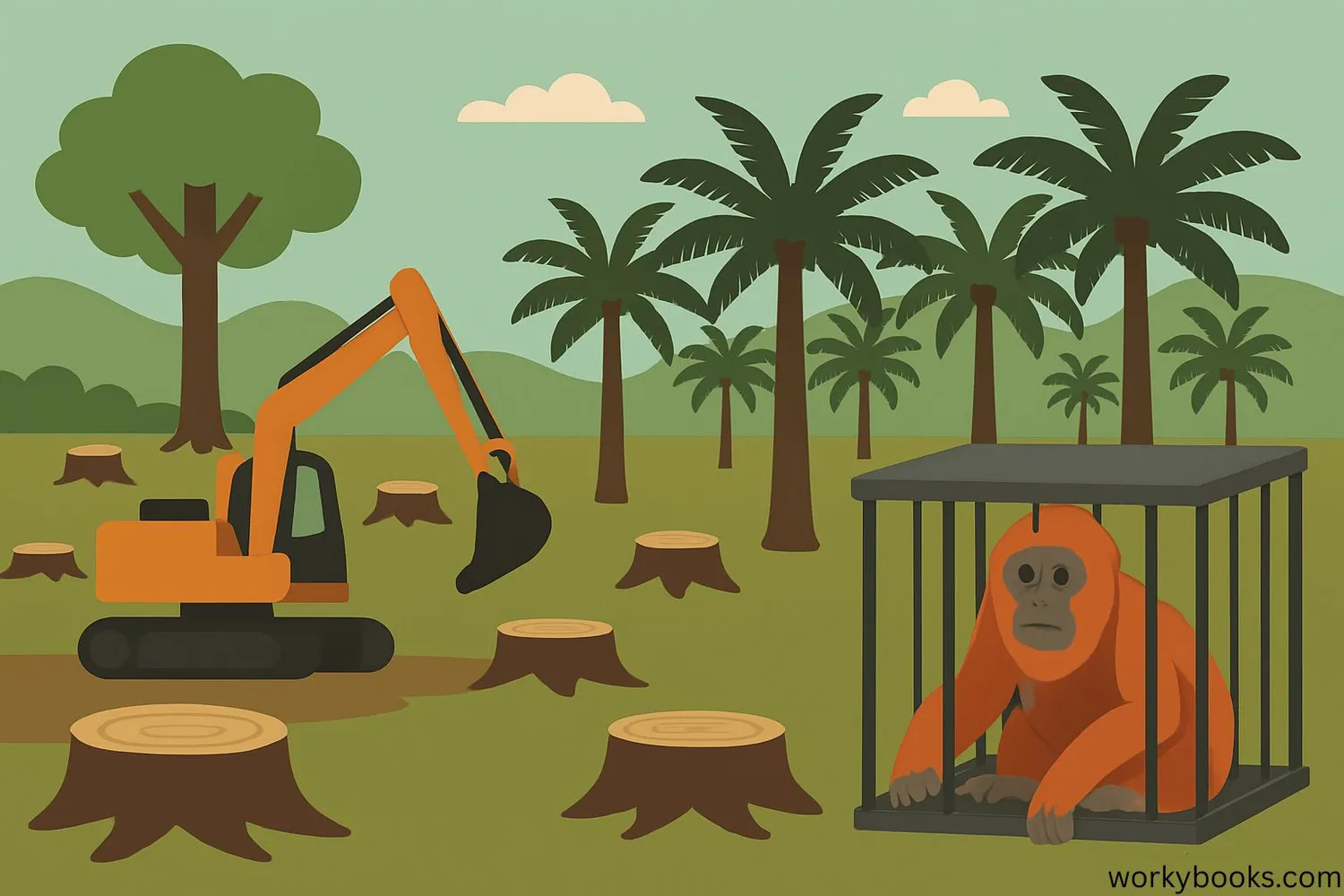

All three species of orangutans are critically endangered, meaning they face an extremely high risk of extinction in the wild. These threatened species face several major challenges:
Habitat Loss
Rainforests are cleared for palm oil plantations, logging, and agriculture
Illegal Pet Trade
Baby orangutans are captured after mothers are killed
Forest Fires
Intentional burning destroys habitats and kills orangutans
Climate Change
Alters rainfall patterns and forest ecosystems
Human Conflict
Orangutans are killed when they wander onto plantations
Orangutans reproduce very slowly. A female has only 3-4 babies in her lifetime, with each baby staying with its mother for 6-8 years. This slow reproduction rate makes it difficult for populations to recover from losses.
Critical Situation
Sumatran orangutan numbers have dropped by 80% in the last 75 years. Without immediate action, these amazing primates could disappear from the wild within our lifetime.
Orangutan Conservation Efforts
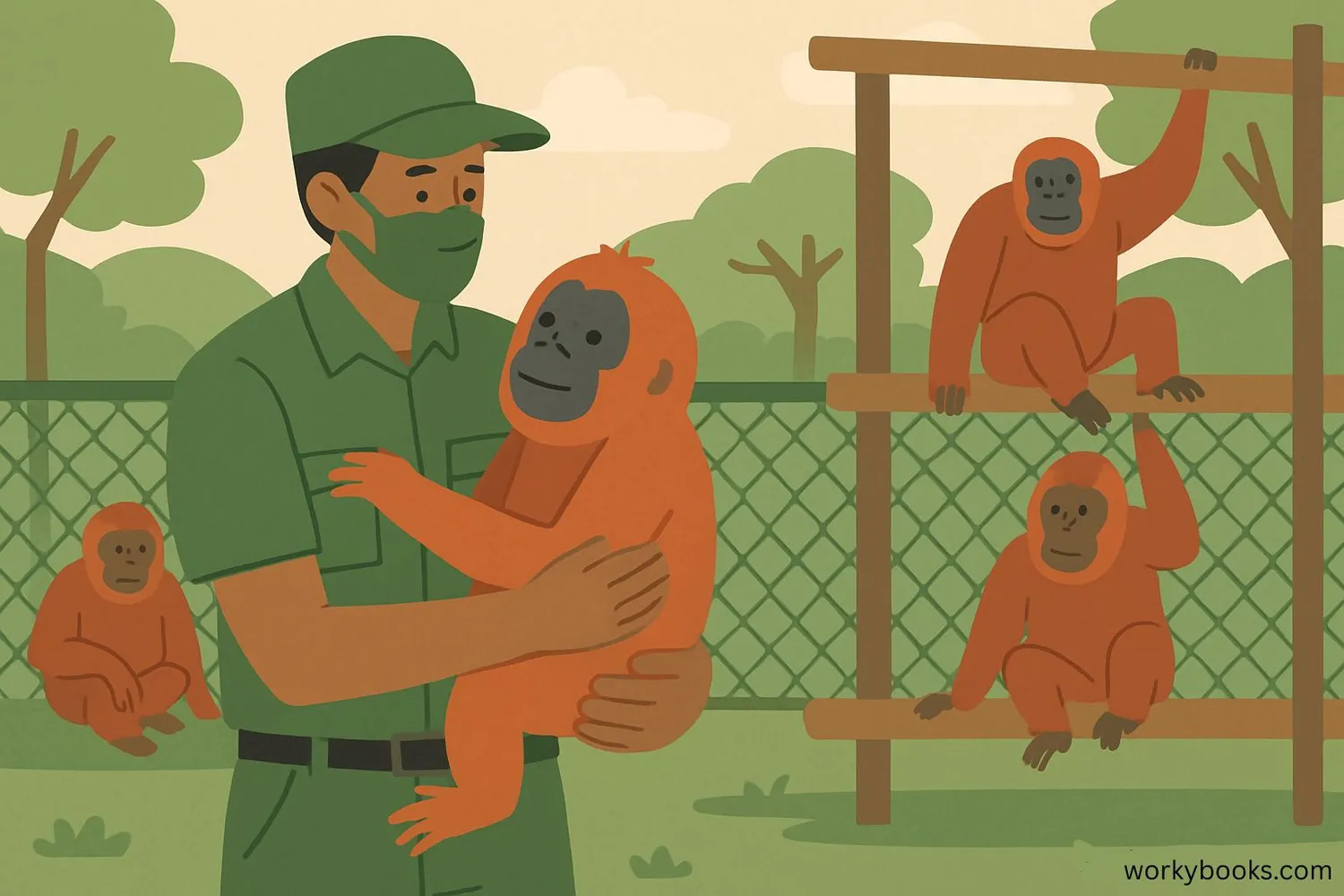

Many organizations and governments are working hard on primate conservation to save orangutans. Wildlife protection efforts include:
Habitat Protection
Creating protected areas and wildlife corridors
Rescue Centers
Caring for orphaned orangutans and preparing them for return to the wild
Palm Oil Alternatives
Promoting sustainable palm oil and consumer awareness
Education
Teaching local communities about orangutan conservation
Anti-Poaching
Strengthening laws against illegal wildlife trade
You can help too! By choosing products with sustainable palm oil, supporting conservation organizations, and spreading awareness about these amazing jungle animals, you're helping protect orangutans for future generations.
How You Can Help
Look for the RSPO (Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil) logo on products. Reduce paper use. Support reputable orangutan conservation organizations. Spread awareness about these incredible animals!
Orangutan Knowledge Quiz
Test what you've learned about orangutans with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you know.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about orangutans:
Amazing Orangutan Trivia
Discover some incredible facts about these red apes:
Close Relatives
Orangutans share 97% of their DNA with humans! They are one of our closest relatives in the animal kingdom, along with chimpanzees and gorillas.
Incredible Strength
An adult male orangutan is seven times stronger than a human! Their powerful arms help them swing through trees and build nests high in the canopy.
Clever Tool Users
Orangutans use tools in the wild - they make umbrellas from large leaves, use sticks to extract insects, and create sponges from chewed leaves to drink water.
Water Avoidance
Unlike many primates, orangutans dislike water and can't swim! Their heavy bodies and lack of buoyancy make them avoid deep water at all costs.




