Base of an Exponent - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn how exponents work with clear explanations, examples, and practice activities
What is the Base of an Exponent?
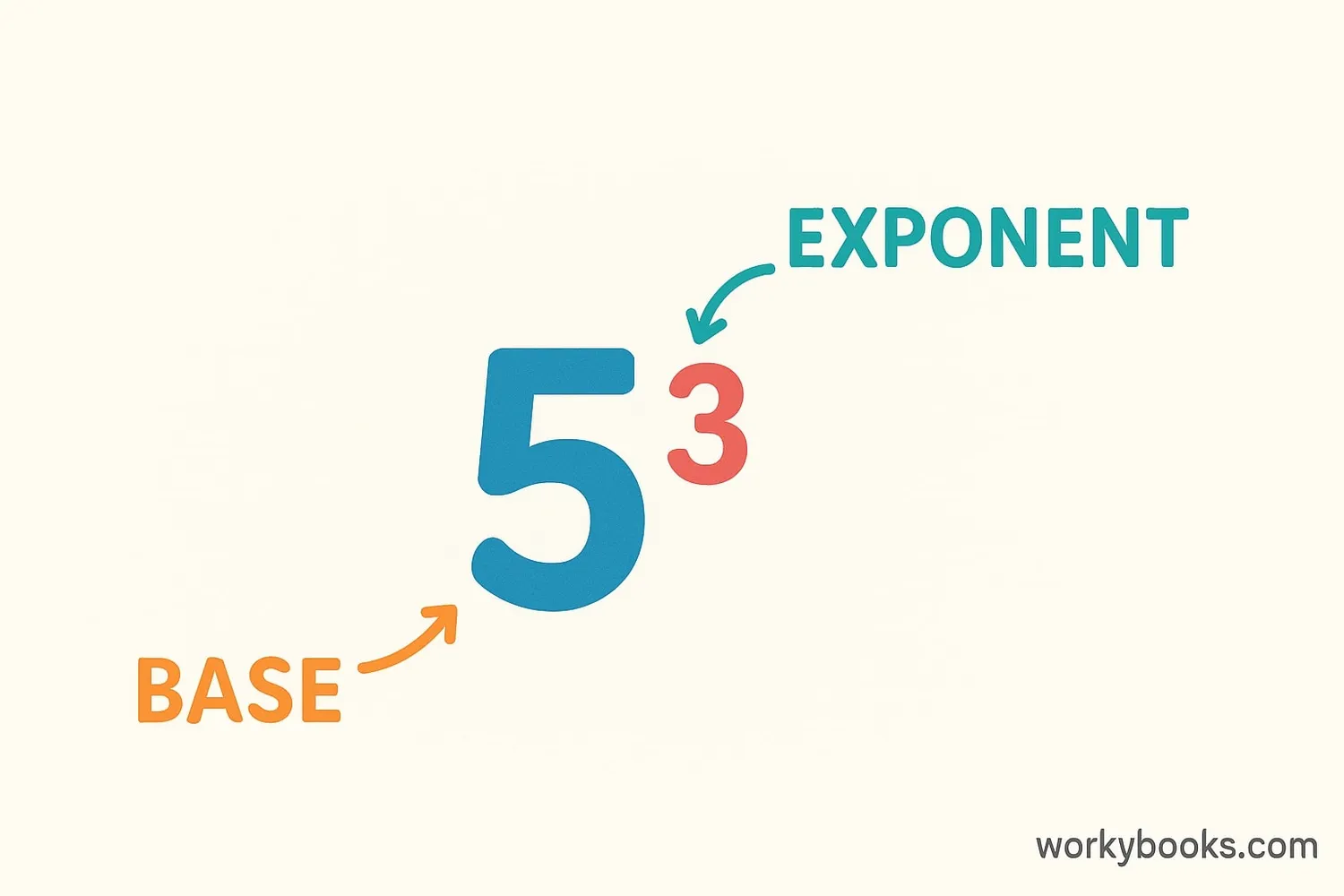
The base of an exponent is the number that gets multiplied by itself. The exponent (the small number above and to the right) tells us how many times to multiply the base by itself.
Think of the base as the main character in a multiplication story. It's the number that gets repeated in the multiplication. For example, in the expression 53 (read as "five to the third power" or "five cubed"), 5 is the base and 3 is the exponent.
Why is this important? Understanding the base helps us work with exponents and solve math problems more efficiently. It's like knowing the main ingredient in a recipe!
Key Concept
Base × Base × ... (as many times as the exponent) = Result
How Exponents Work
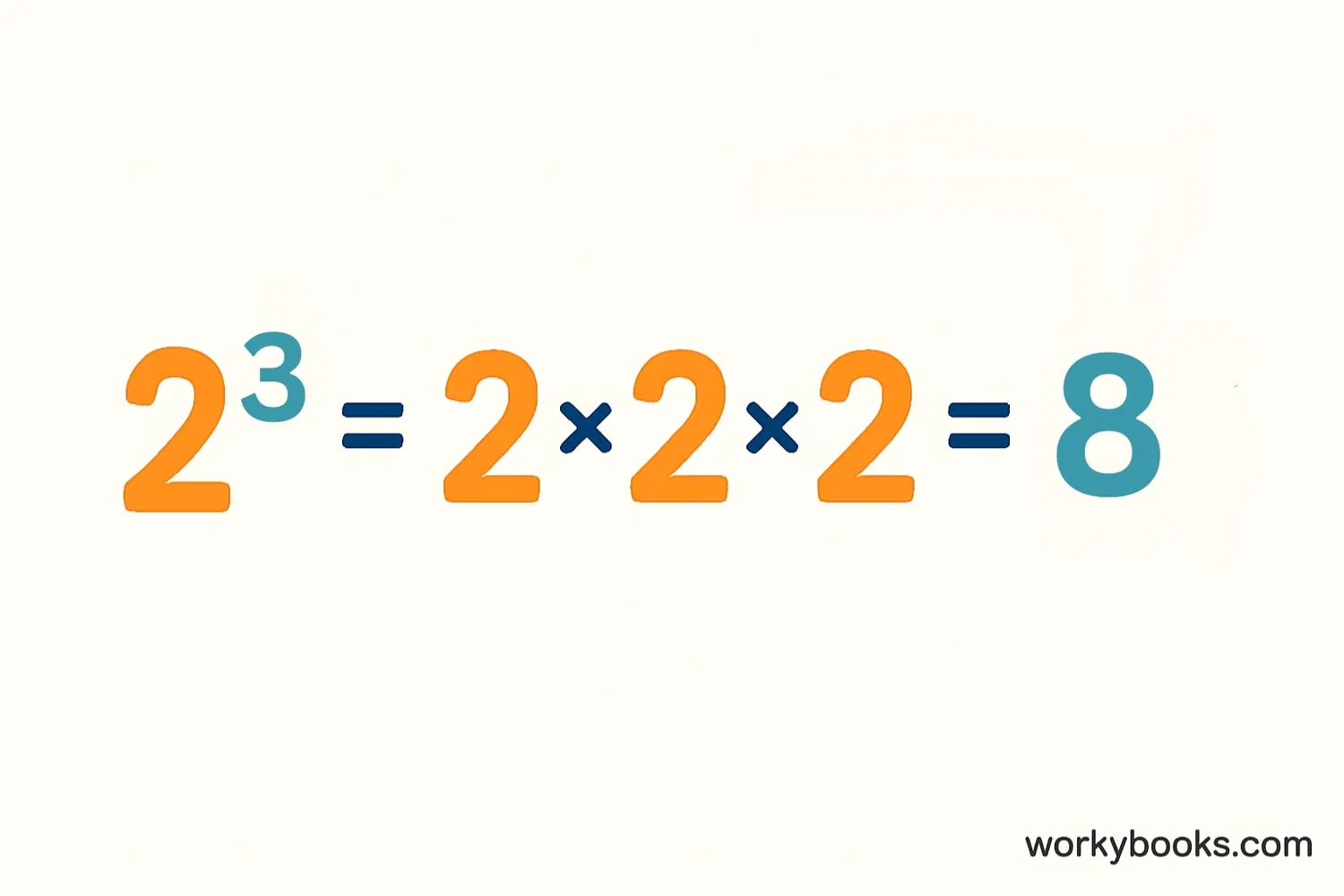
Exponents are a shortcut for repeated multiplication. Instead of writing the same number many times, we use exponents to show how many times the base is multiplied by itself.
Exponent Structure
The base is the number being multiplied, and the exponent tells you how many times to multiply it.
Example: 42 (read as "four squared")
Step 1: Identify the base → 4
Step 2: Identify the exponent → 2
Step 3: Multiply the base by itself exponent times → 4 × 4
Step 4: Calculate the result → 16
So 42 = 16. See how much simpler exponents make multiplication!
Remember
Any number to the power of 1 is itself: 71 = 7
Any number to the power of 0 is 1: 90 = 1
Exponent Rules
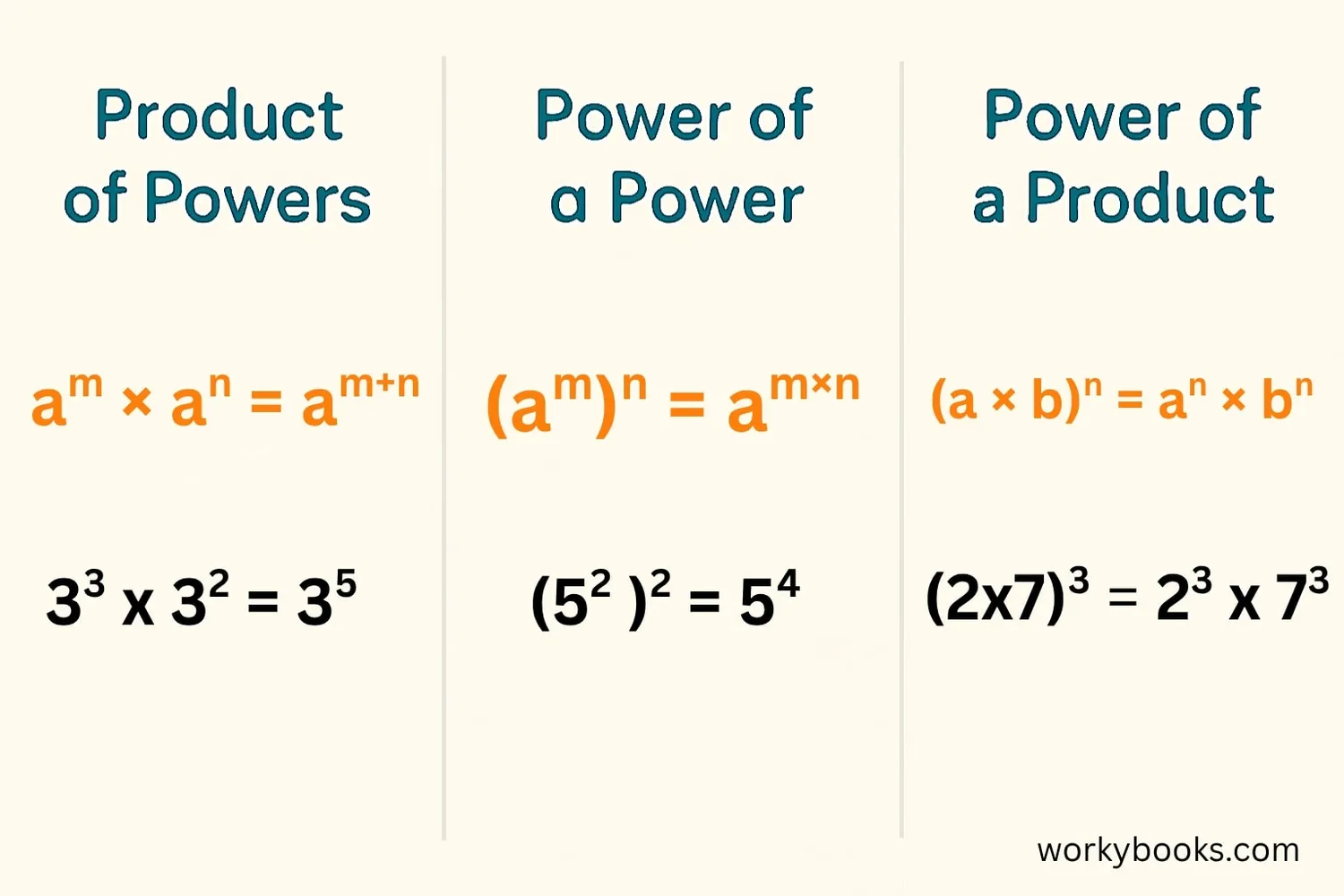
Once you understand the base, you can learn some important exponent rules that make calculations easier:
Product of Powers
When multiplying powers with the same base, add the exponents:
Example: 32 × 33 = 32+3 = 35 = 243
Power of a Power
When raising a power to another power, multiply the exponents:
Example: (23)2 = 23×2 = 26 = 64
Power of a Product
When raising a product to a power, raise each factor to the power:
Example: (3 × 4)2 = 32 × 42 = 9 × 16 = 144
Rule Tip
These rules only work when the bases are the same! Pay attention to the base when applying these rules.
Real-World Examples
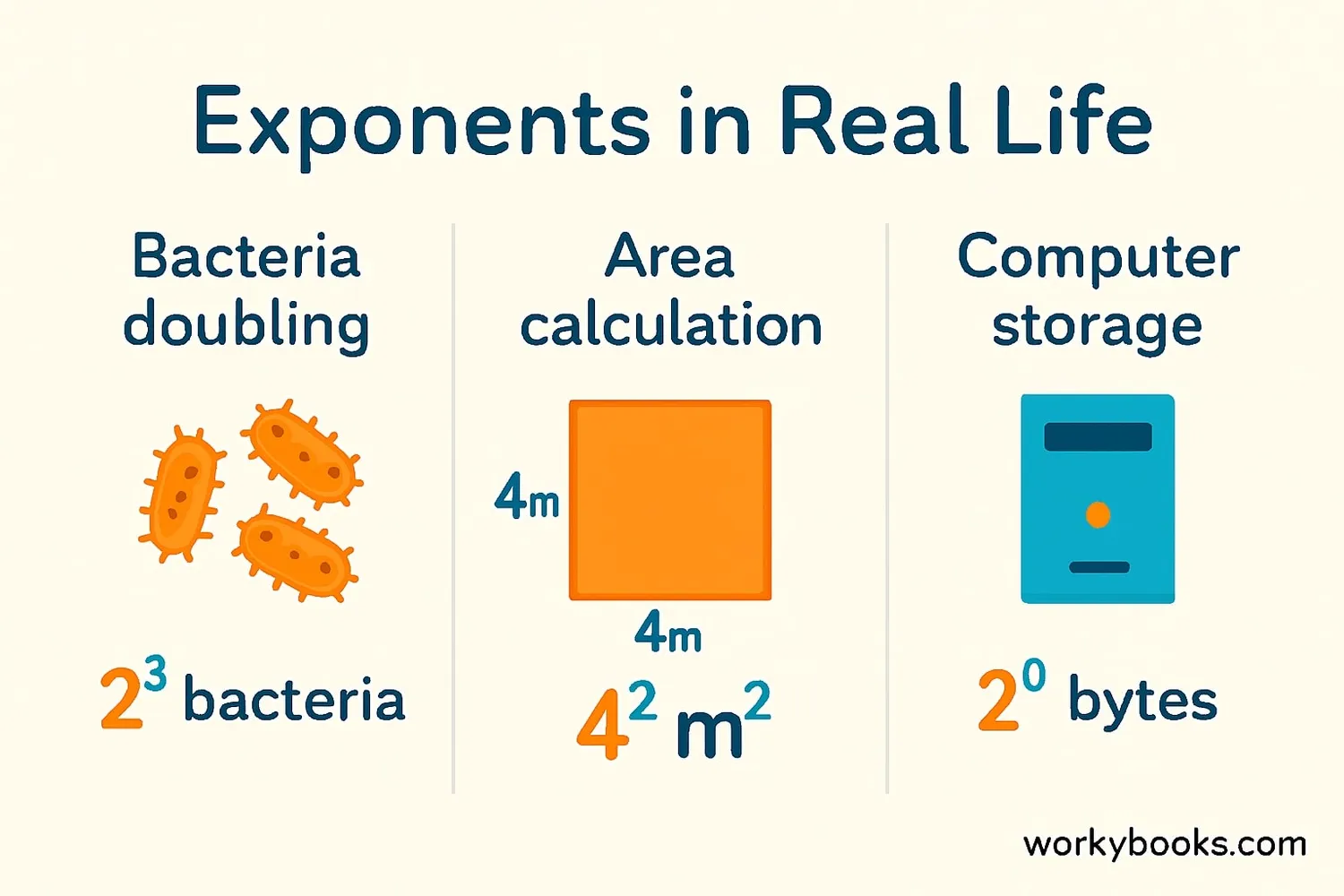
Let's practice with some real-world examples of exponents:
Example 1: Area Calculation
The area of a square is calculated using exponents. A square with sides of 5 meters has an area of:
Example 2: Bacteria Growth
If bacteria double every hour, how many will you have after 4 hours starting with 1 bacterium?
Example 3: Computer Storage
Computer storage uses exponents. A kilobyte is 210 bytes:
Math Tip
When working with exponents, always identify the base first. This helps you understand what number is being multiplied.
Exponent Practice Quiz
Test your knowledge with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about exponents and their bases:
Math Trivia
Discover interesting facts about exponents and their history:
Ancient Exponents
The concept of exponents dates back to ancient Egypt and Babylon. The Egyptians used a form of exponentiation in their calculations for building pyramids around 1800 BCE.
Scientific Notation
Exponents are essential in scientific notation, which helps scientists write very large or very small numbers. For example, the speed of light is 3 × 108 m/s.
Computer Science
Exponents are fundamental in computer science. Computer memory uses powers of 2 - a kilobyte is 210 bytes (1024 bytes), and a megabyte is 220 bytes (1,048,576 bytes).
Large Numbers
The largest named number is the googolplex, which is 10googol, where a googol is 10100. This number is so large that there isn't enough space in the universe to write it out!





