Brackets - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about parentheses, curly braces, and square brackets in math expressions
What are Brackets in Math?
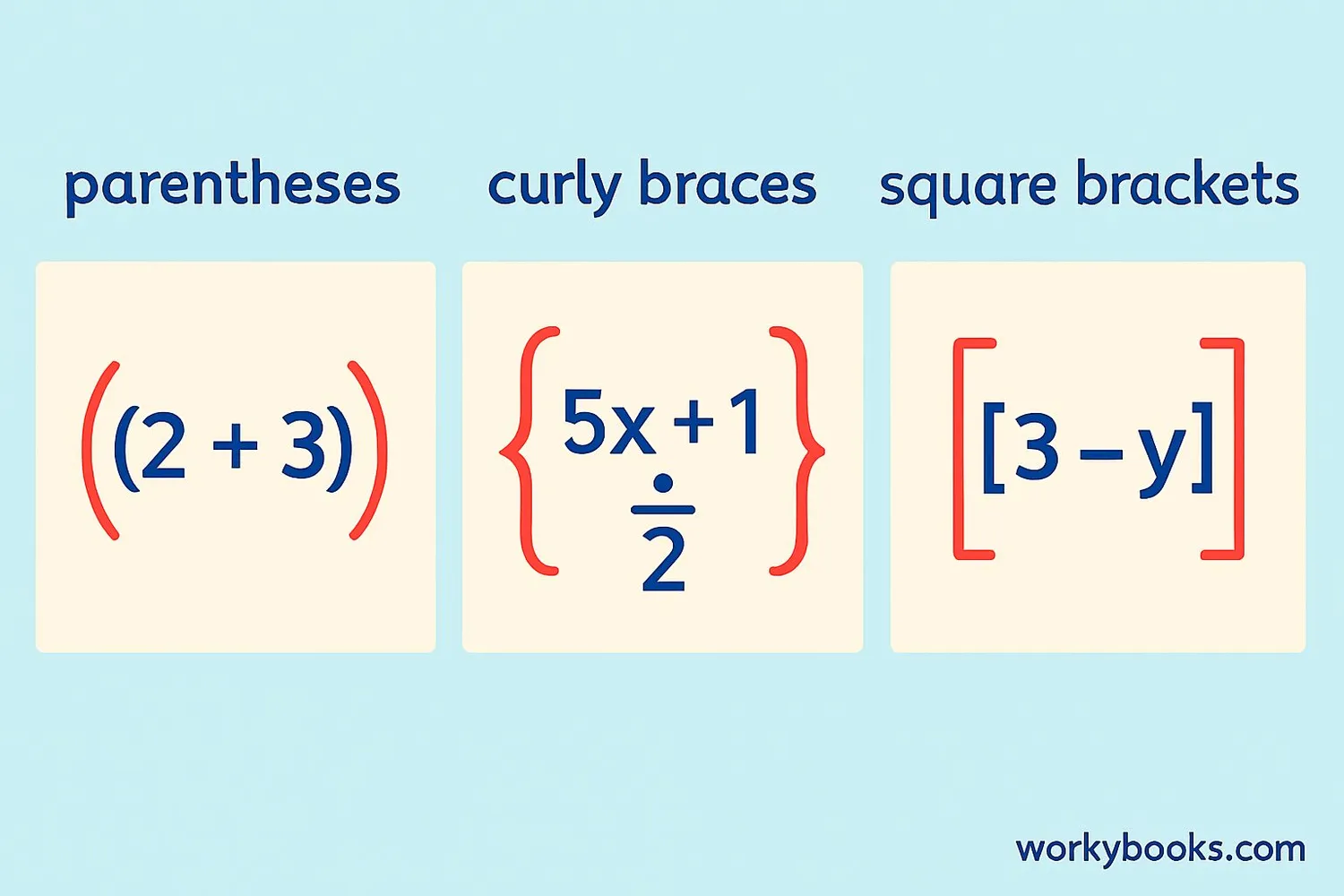
Brackets are special symbols in mathematics that help us organize and group parts of math expressions. They tell us which operations to do first, especially when we have more than one operation in an expression.
Think of brackets like containers that hold certain parts of a math problem together. Just like how we use containers to organize our things, brackets help us organize math operations so we know what to calculate first.
The most common types of brackets are:
- Parentheses ( ) - These are the most frequently used brackets
- Curly Braces { } - Often used in sets and special groupings
- Square Brackets [ ] - Used when we need to group things that already have parentheses
Key Concept
Brackets help us follow the order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS) by grouping parts of an expression that should be calculated first.
Types of Mathematical Brackets
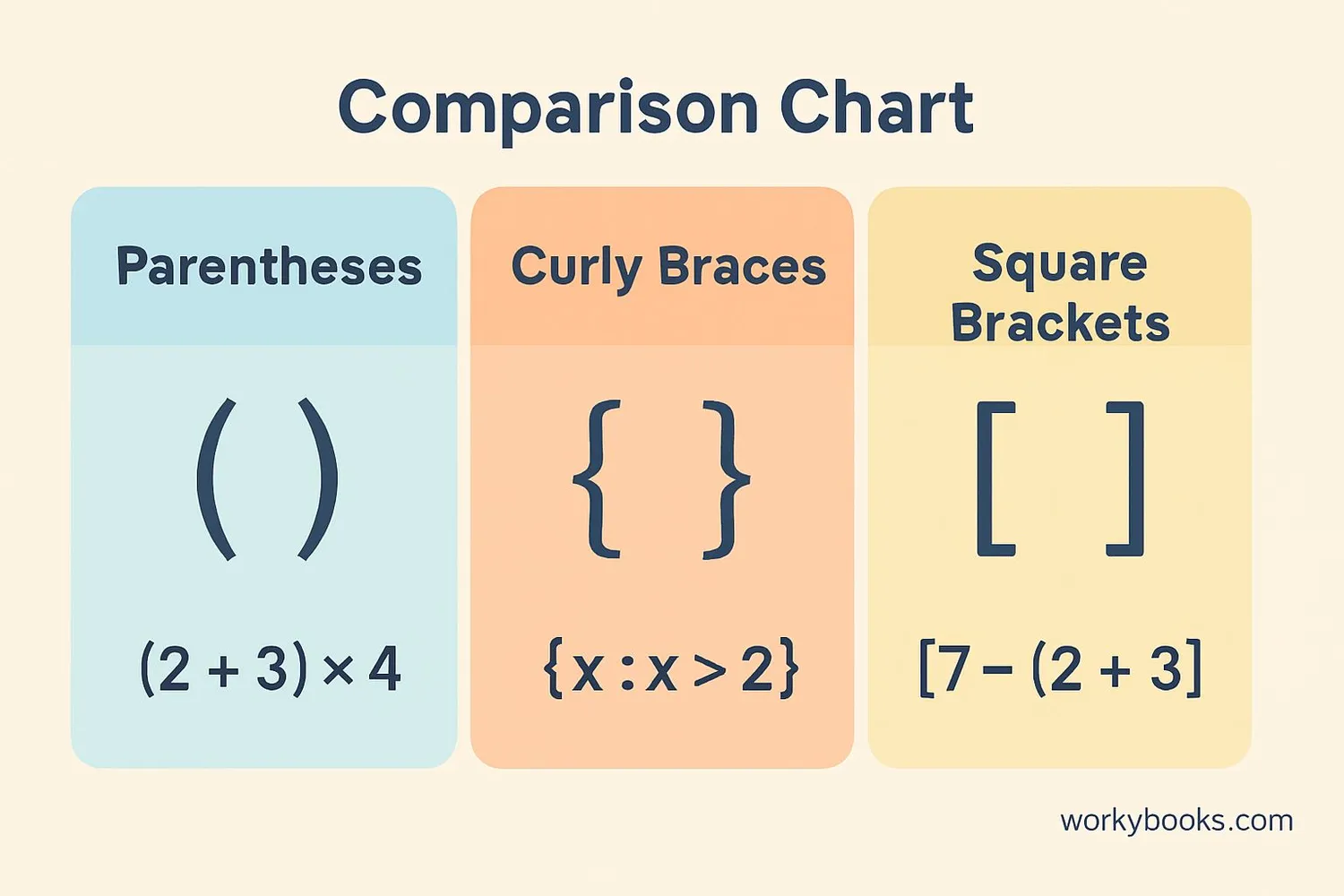
There are three main types of brackets used in mathematics. Each has a special purpose:
Parentheses
These are the most common brackets. They group operations that should be done first.
We do the addition inside the parentheses first: 3 + 2 = 5, then multiply by 4 to get 20.
Curly Braces
Used for sets and special groupings, especially in algebra and advanced math.
This represents a set of numbers. Also used in functions: f(x) = {x + 1 if x > 0}
Square Brackets
Used when we need to group expressions that already have parentheses.
We do the operation in parentheses first: 3×2=6, then 6+5=11, then 11×2=22.
Remember
When you see multiple types of brackets, start with the innermost brackets and work your way out.
Why Brackets Matter in Math
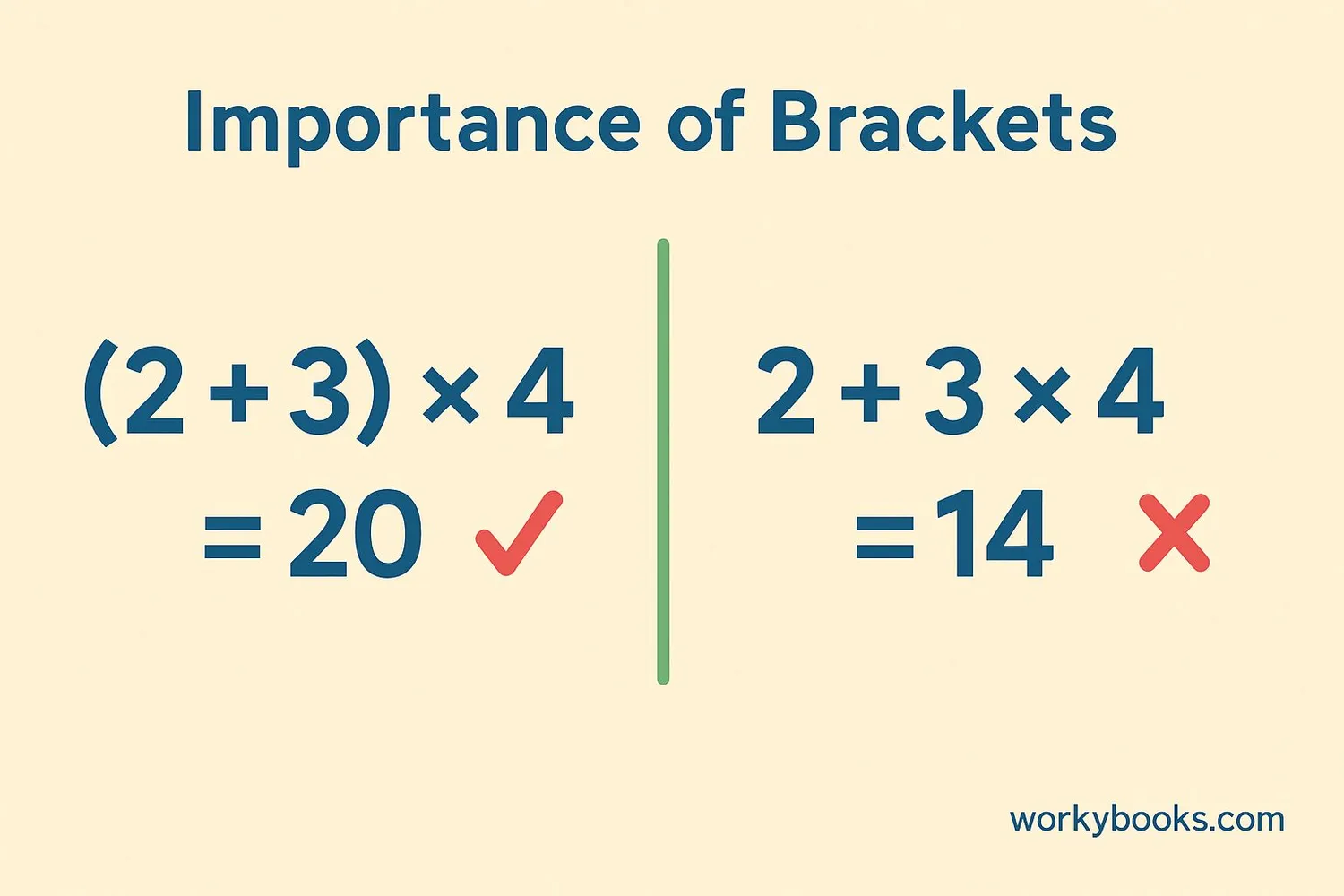
Brackets are extremely important in mathematics because they change the meaning and result of expressions. Without brackets, different people might interpret an expression differently and get different answers!
Consider this example:
Order of Operations
Remember PEMDAS: Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division (from left to right), Addition and Subtraction (from left to right)
Without brackets: First we do multiplication (3×2=6), then addition (5+6=11)
Example 2: (5 + 3) × 2
With brackets: First we do addition (5+3=8), then multiplication (8×2=16)
See how the brackets completely changed the answer? That's why they're so important!
Bracket Rules
1. Always solve expressions inside brackets first
2. If there are brackets inside brackets, solve the innermost ones first
3. Brackets can change the order of operations
Using Brackets: Examples
Let's practice using brackets with some examples:
Example 1: 4 × (2 + 3)
Solution: First do the addition inside the parentheses: 2 + 3 = 5, then multiply: 4 × 5 = 20
Example 2: [10 - (2 × 3)] ÷ 2
Solution: First do the multiplication inside the parentheses: 2 × 3 = 6, then subtraction: 10 - 6 = 4, then division: 4 ÷ 2 = 2
Example 3: {2 × [3 + (4 - 1)]} ÷ 2
Solution: Start with the innermost parentheses: 4 - 1 = 3, then brackets: 3 + 3 = 6, then curly braces: 2 × 6 = 12, then division: 12 ÷ 2 = 6
Word Problem: Sarah bought 3 apples for $2 each and 2 oranges for $1.50 each. What was her total cost?
Expression: (3 × 2) + (2 × 1.50)
Solution: 3×2=6, 2×1.50=3, then 6+3=9. Total cost is $9.
Remember
In word problems, brackets help group related quantities together, making the expression easier to understand and solve.
Brackets Practice Quiz
Test your understanding of brackets with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about brackets in mathematics:
Math Trivia
Discover interesting facts about mathematical brackets:
Historical Origins
The use of parentheses in mathematics dates back to the 16th century. Italian mathematician Rafael Bombelli was one of the first to use them systematically in his 1572 book "Algebra".
Different Names
What Americans call "parentheses" are known as "brackets" in the UK, while what Americans call "brackets" are called "square brackets" in the UK. This can cause some confusion!
Most Brackets Used
The most complex mathematical expression ever published contained over 2,000 sets of nested brackets. It would take more than 10 pages to write it out completely!
Beyond Mathematics
Brackets are essential in computer programming too! Different programming languages use various bracket types to organize code, define functions, and create data structures.





