Constants - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about unchanging values in math with easy explanations, examples, and practice activities
What is a Constant?
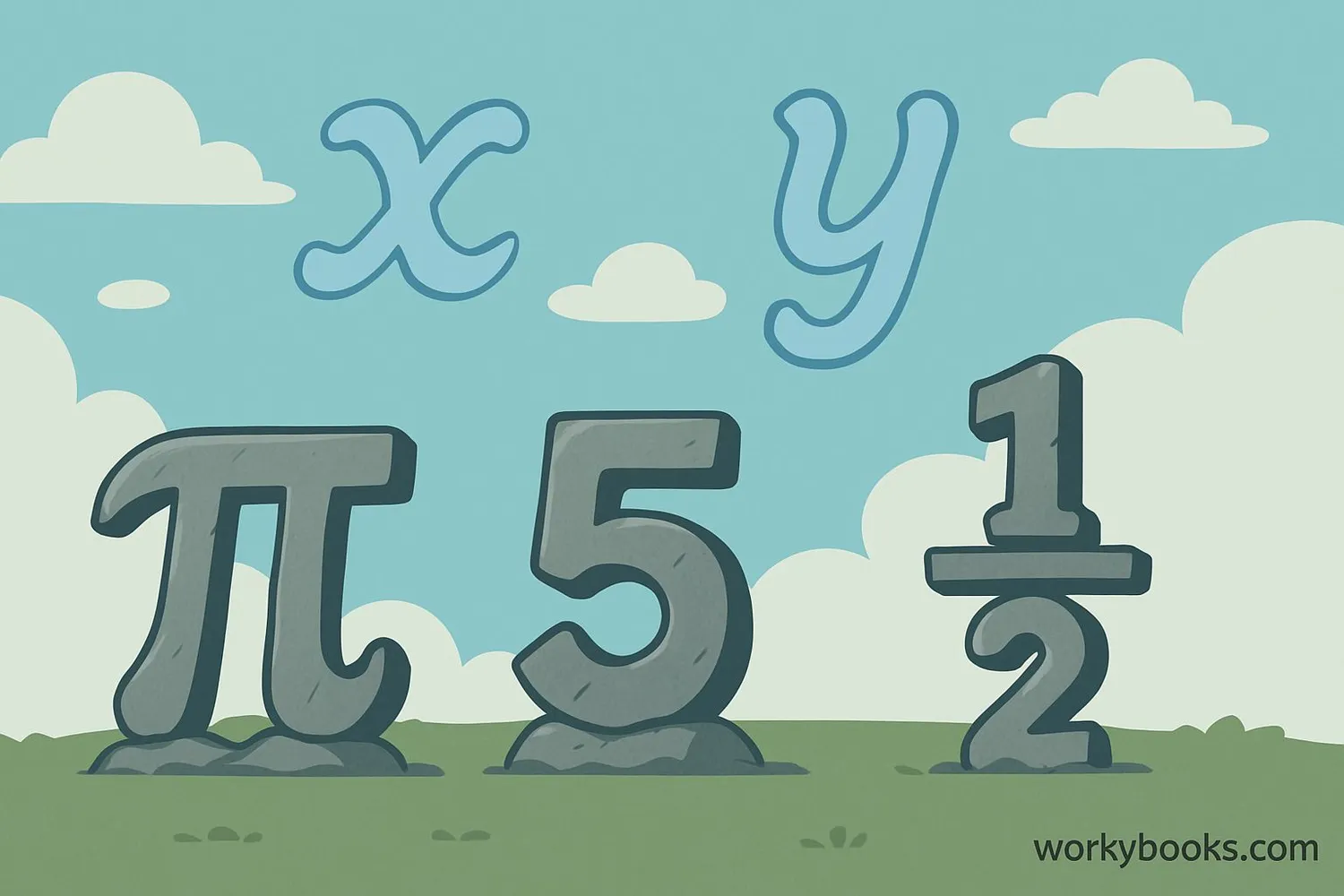
A constant is a fixed value in mathematics that never changes. Unlike variables that can represent different numbers, constants always stay the same. They are like anchors in math problems that provide stability and consistency.
Constants can be:
- Whole numbers like 5, 12, or 100
- Decimals like 3.14 or 0.5
- Fractions like ½ or ¾
- Special symbols like π (pi) or e
Constants help us solve problems by giving us reliable, unchanging values to work with. They appear everywhere in math - from simple addition problems to complex scientific formulas.
Key Concept
Constants are fixed values that remain unchanged throughout a mathematical problem or equation.
Variables vs. Constants
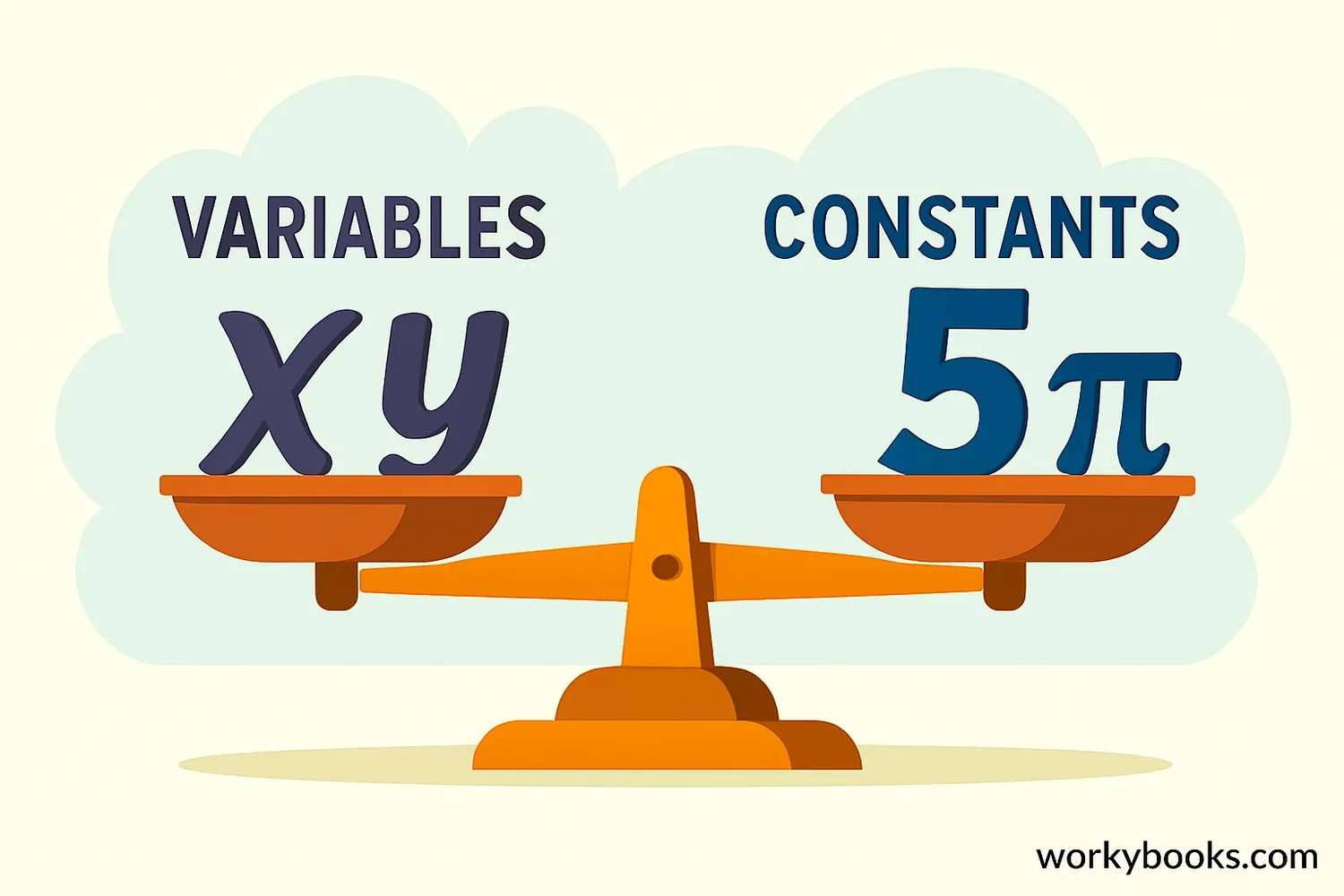
In mathematics, we work with two main types of values: variables and constants. Understanding the difference between them is important:
Variables: Symbols (usually letters) that represent unknown or changing values. They can be different numbers in different situations.
Constants: Fixed values that never change. They remain the same no matter what.
Look at this algebraic expression:
- 3 is a constant coefficient
- x is a variable
- 7 is a constant term
The constants (3 and 7) stay the same, while the variable (x) can change. This combination allows us to create flexible formulas that work for different situations.
Remember
Constants are the reliable, unchanging parts of math equations, while variables represent values that can change.
Types of Constants

There are several types of constants in mathematics:
Numerical Constants: Fixed numbers like 5, 12, or 100. These are the simplest constants.
Fractional Constants: Fractions that represent fixed values, like ½ or ¾.
Decimal Constants: Fixed decimal values like 0.5 or 3.14.
Mathematical Constants: Special values that appear throughout mathematics:
These special constants are so important that they have their own symbols! Mathematicians use these constants to solve problems in geometry, physics, engineering, and many other fields.
Fun Fact
The constant π has been calculated to over 50 trillion digits, but we usually just use 3.14 or 22/7!
Constants in Algebra
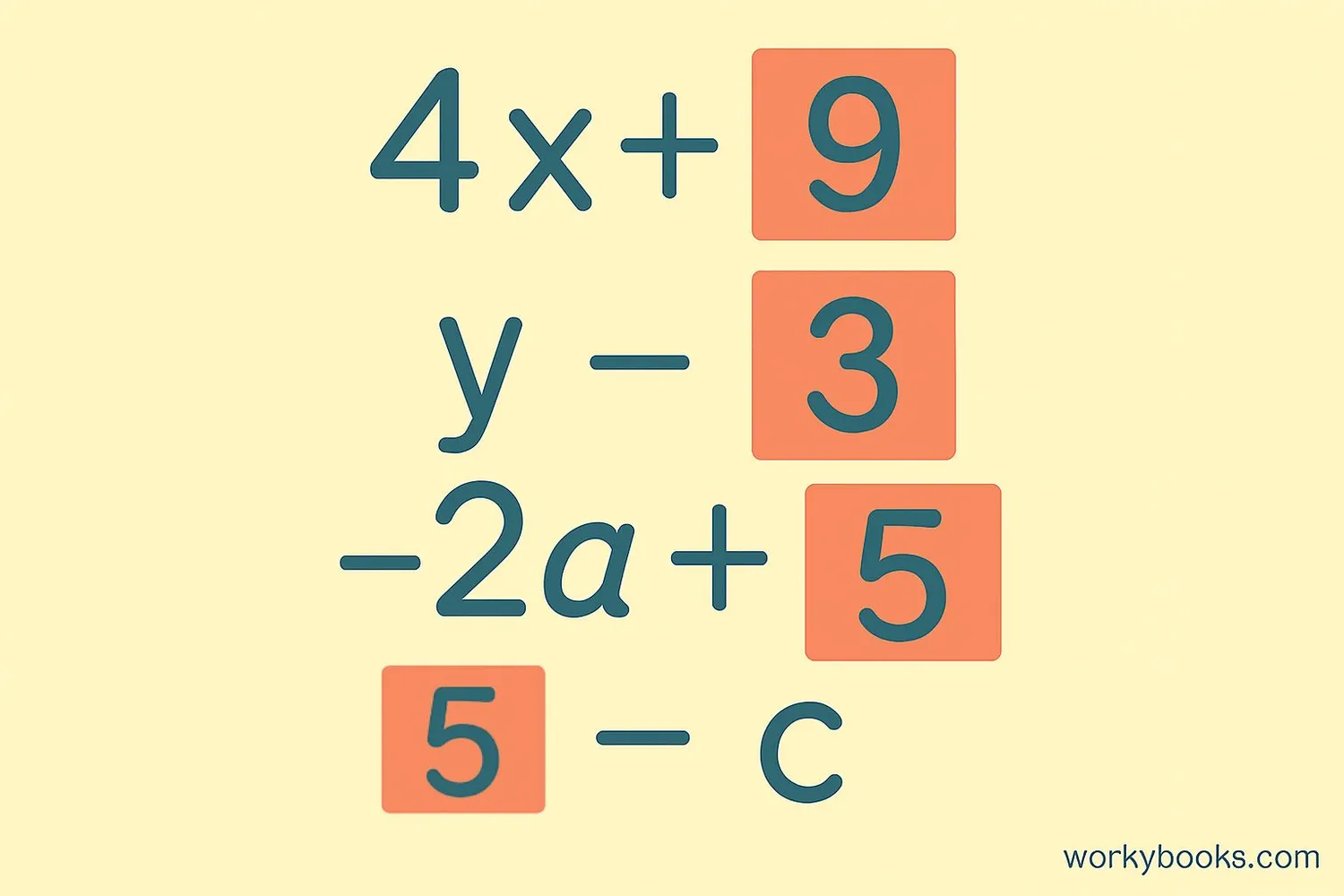
In algebra, constants play several important roles:
Constant Term: A number by itself in an expression, like the 5 in "3x + 5".
Coefficient: A constant that multiplies a variable, like the 4 in "4x".
Constant vs. Coefficient:
- A coefficient is a constant multiplied by a variable
- A constant term stands alone without any variables
Consider the quadratic equation:
- a and b are coefficients (constants multiplying variables)
- c is a constant term
Constants help determine the shape and position of graphs. For example, in the equation y = mx + b, the constant b determines where the line crosses the y-axis.
Remember
In algebra, a constant term is a number without any variables attached to it.
Real-World Examples

Constants are all around us in daily life:
Example 1: There are always 60 minutes in an hour. This is a constant value.
Example 2: The number of days in a week is always 7. This never changes.
Example 3: The freezing point of water is 0°C or 32°F. These are constant temperatures.
Example 4: In the formula for the area of a circle (A = πr²), π is a constant (approximately 3.14) that never changes.
Example 5: The speed of light in a vacuum is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second - a physical constant.
These examples show how constants provide stability and predictability in our understanding of the world.
Did You Know?
The constant e (Euler's number) is used in calculating compound interest, population growth, and even in the shape of a hanging chain!
Constant Knowledge Quiz
Test your understanding of constants with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about constants in math:
Math Constants Trivia
Discover fascinating facts about mathematical constants:
Calculating Pi
The constant π has been known for nearly 4,000 years! Ancient Babylonians calculated it as 3.125, while Egyptians used 3.1605. Today, supercomputers have calculated π to over 50 trillion digits.
Euler's Number
The constant e (approximately 2.71828) appears in many areas of mathematics. It's used in calculating compound interest, population growth, radioactive decay, and even in the design of arches and bridges.
Golden Ratio
The golden ratio (φ ≈ 1.618) appears throughout nature. It can be seen in the arrangement of leaves on a stem, the spiral of a seashell, the proportions of the human body, and even in famous artworks like the Mona Lisa.
Speed of Light
The speed of light in a vacuum is a physical constant (299,792,458 m/s). Albert Einstein's famous equation E = mc² uses the constant c to represent this unchanging speed.





