Cube and Cuboid - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about these special 3D shapes, their properties, differences, and how to calculate their volume
What are Cubes and Cuboids?
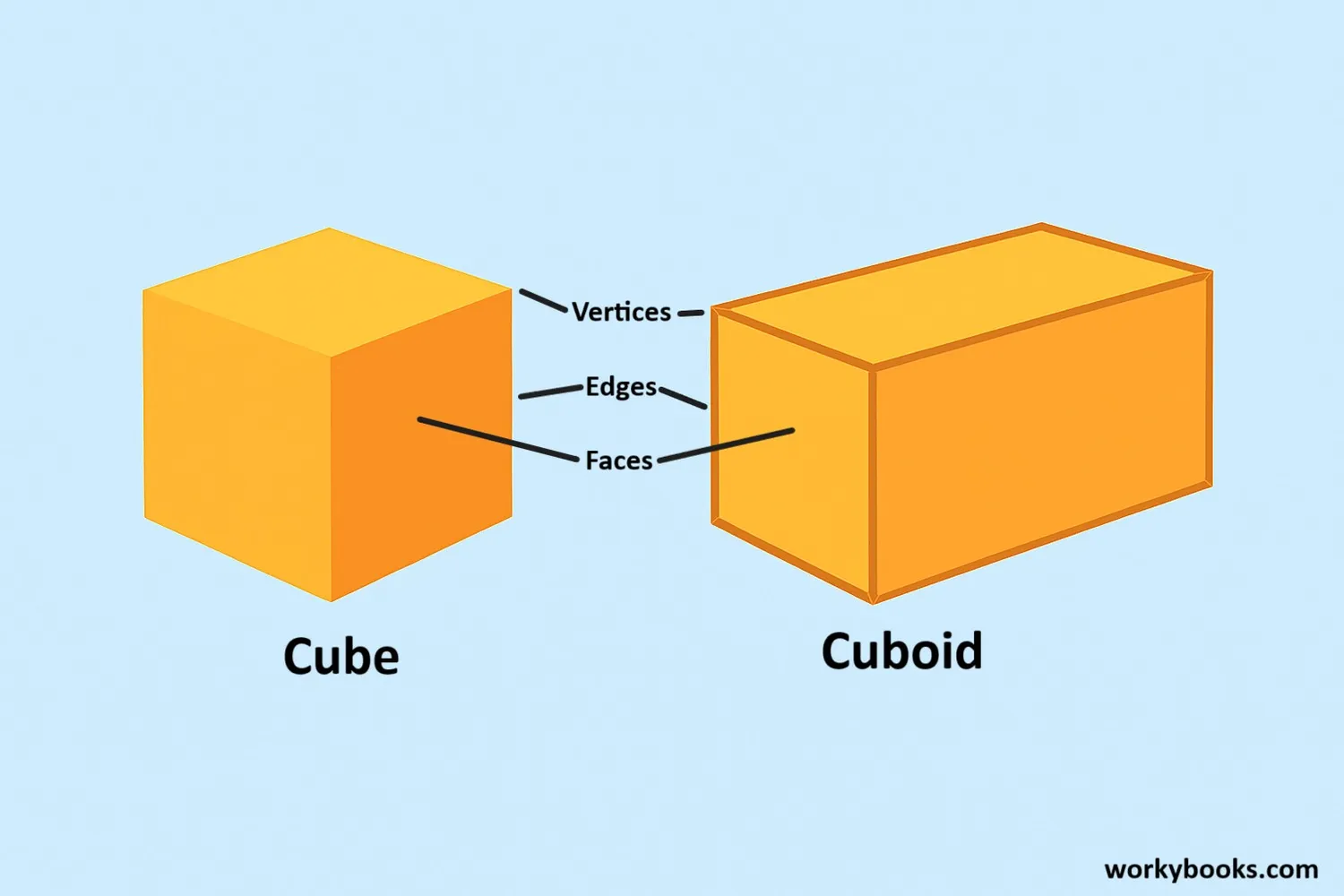
Cubes and cuboids are both three-dimensional shapes that have six faces, eight vertices (corners), and twelve edges. They belong to the family of rectangular prisms.
A cube is a special type of cuboid where all six faces are identical squares. Think of dice or Rubik's cubes - they have equal sides in all directions.
A cuboid (also called rectangular prism) has six rectangular faces. Opposite faces are equal. Most boxes, books, and buildings are cuboid-shaped.
Both shapes are important in geometry because they help us understand how three-dimensional objects work in our world.
Key Concept
All cubes are cuboids, but not all cuboids are cubes. A cube is a special cuboid with equal sides.
Properties of Cubes and Cuboids
Cube Properties
- All six faces are squares of equal size
- All twelve edges are of equal length
- All angles are right angles (90 degrees)
- Has 8 vertices (corners)
- All faces meet at right angles
- It is a regular polyhedron
Cuboid Properties
- Six rectangular faces (not necessarily squares)
- Opposite faces are equal and parallel
- All angles are right angles (90 degrees)
- Has 8 vertices (corners)
- Has 12 edges of three different lengths
- It is an irregular polyhedron
Differences Between Cubes and Cuboids
| Feature | Cube | Cuboid |
|---|---|---|
| Faces | 6 equal squares | 6 rectangles (opposites equal) |
| Edges | All 12 edges equal | 3 sets of 4 edges each (different lengths) |
| Vertices | 8 vertices | 8 vertices |
| Diagonals | Equal space diagonals | Three different space diagonals |
| Symmetry | High symmetry (multiple axes) | Lower symmetry |
| Special Case | Special cuboid with equal sides | General rectangular prism |
Remember
The key difference is that a cube has all sides equal, while a cuboid has sides of different lengths (length, width, height).
Volume Calculation
Volume of a Cube
Where s is the length of any side of the cube
Volume of a Cuboid
Where l is length, w is width, and h is height
Example 1: A cube has sides of 4 cm. What is its volume?
Solution: V = 4 × 4 × 4 = 64 cm³
Example 2: A cuboid is 5 cm long, 3 cm wide, and 2 cm high. What is its volume?
Solution: V = 5 × 3 × 2 = 30 cm³
Volume tells us how much space a 3D shape occupies. It's measured in cubic units like cm³ or m³.
Real-World Examples

Cube Examples
- Dice used in board games
- Rubik's cube puzzle
- Sugar cubes
- Building blocks
- Ice cubes
Cuboid Examples
- Books and notebooks
- Bricks and building blocks
- Shipping boxes
- Refrigerators
- Smartphones and tablets
Shape Knowledge Quiz
Test your knowledge about cubes and cuboids with this 5-question quiz.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about cubes and cuboids:
Shape Trivia
Discover interesting facts about cubes and cuboids:
Ancient Measurements
Ancient Egyptians used cubit rods (cuboid-shaped) as measurement tools. One royal cubit was approximately 52.4 cm long and was subdivided into smaller units.
Salt Crystals
Table salt crystals naturally form perfect cubes because of how sodium and chloride atoms arrange themselves in a repeating cubic pattern.
Space Stations
Many space station modules are cuboid-shaped because this shape efficiently uses space and is easier to construct than other shapes.
Largest Rubik's Cube
The world's largest Rubik's Cube is a cuboid measuring 1.57m × 1.57m × 1.57m and weighing over 100kg. It was built by Tony Fisher of England.





