Division - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn division with easy explanations, visual examples, and interactive activities
What is Division?
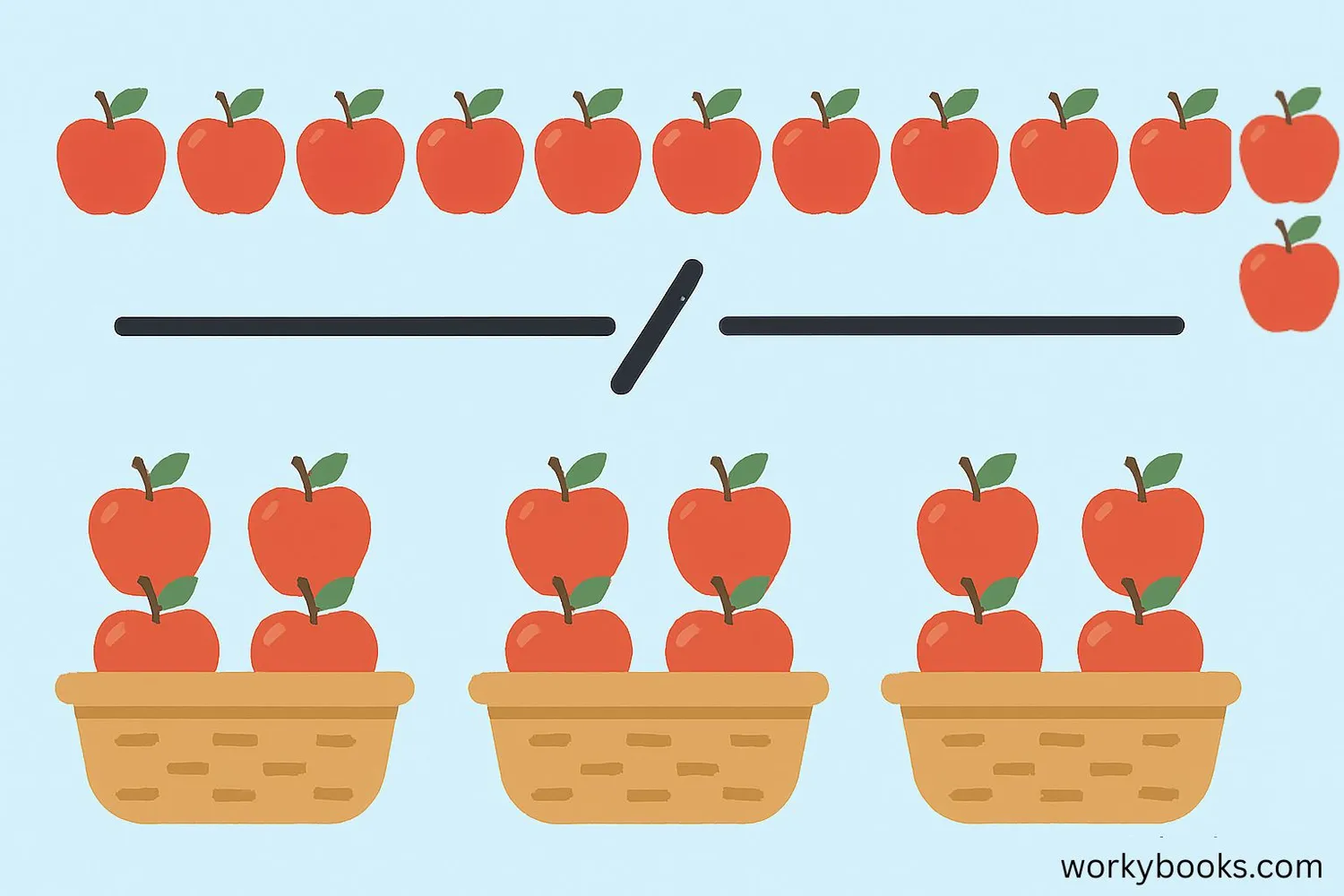
Division is a mathematical operation that helps us share or group things equally. When we divide, we're splitting a larger number into equal smaller parts.
Think of division as the opposite of multiplication. If multiplication is about putting equal groups together, division is about splitting a larger group into equal smaller groups.
For example, if you have 12 cookies and want to share them equally with 3 friends, you would divide 12 by 3 to find that each person gets 4 cookies.
Key Concept
Division is about fair sharing. It answers questions like "How many in each group?" or "How many groups can we make?"
Division Vocabulary

Learning division vocabulary helps us understand and talk about division problems clearly. Here are the important terms:
Dividend
The number that is being divided. In 12 ÷ 3 = 4, 12 is the dividend.
Divisor
The number by which the dividend is divided. In 12 ÷ 3 = 4, 3 is the divisor.
Quotient
The result of the division. In 12 ÷ 3 = 4, 4 is the quotient.
Remainder
The amount left over when division is not exact. For example, 14 ÷ 3 = 4 with a remainder of 2.
Remember
Division can be thought of as repeated subtraction. For example, 12 ÷ 3 means how many times we can subtract 3 from 12 until we reach 0.
Division Symbols
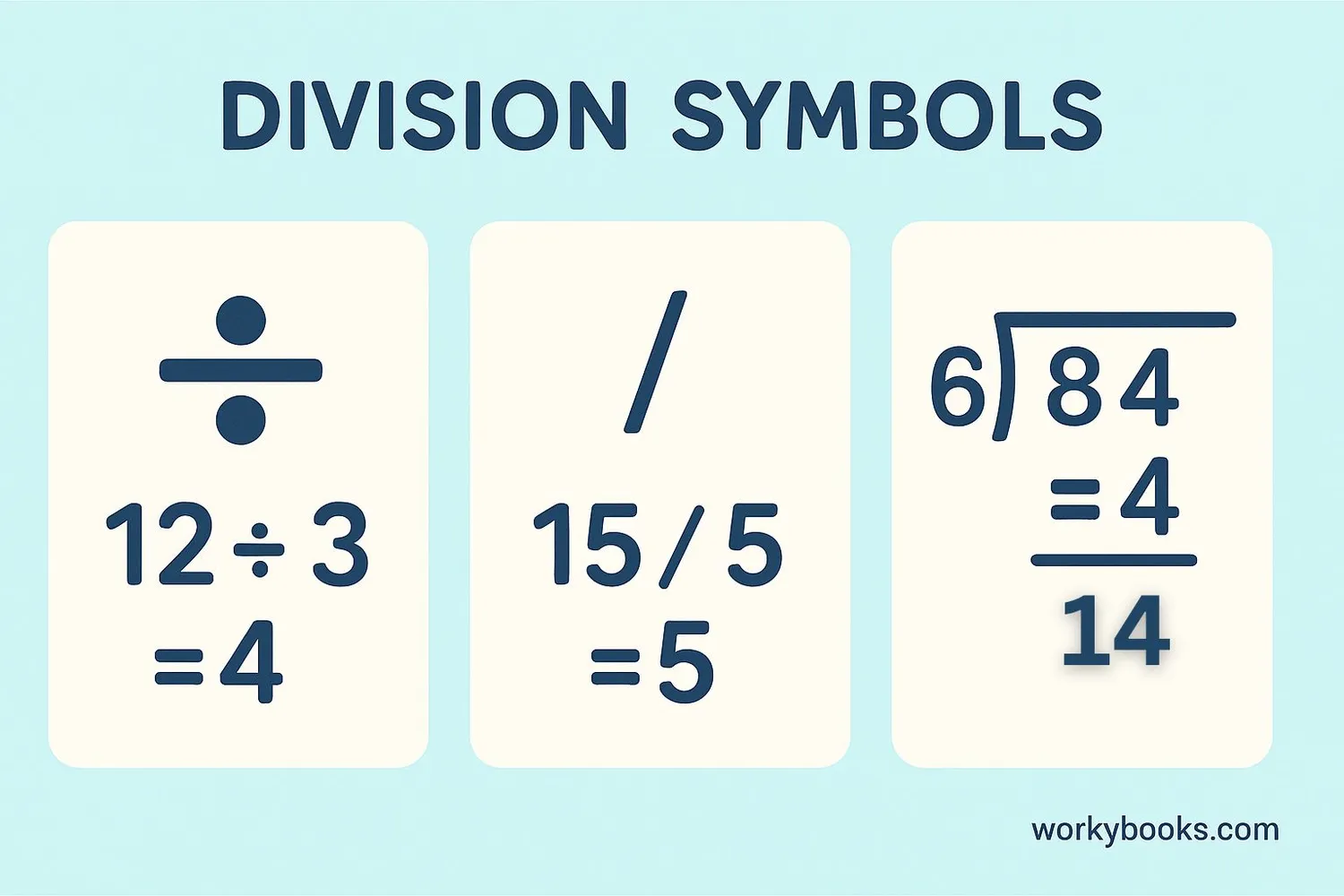
Division can be written in several different ways. It's important to recognize all of them:
Division Symbols
3)12
All of these mean "12 divided by 3 equals 4"
The obelus symbol (÷) is most common in elementary math. The slash (/) is often used with fractions and in computer programming. The division bracket is used for long division problems.
Symbol Tip
When you see a fraction like ¾, it means 3 divided by 4. Fractions are another way to show division!
Division Algorithm
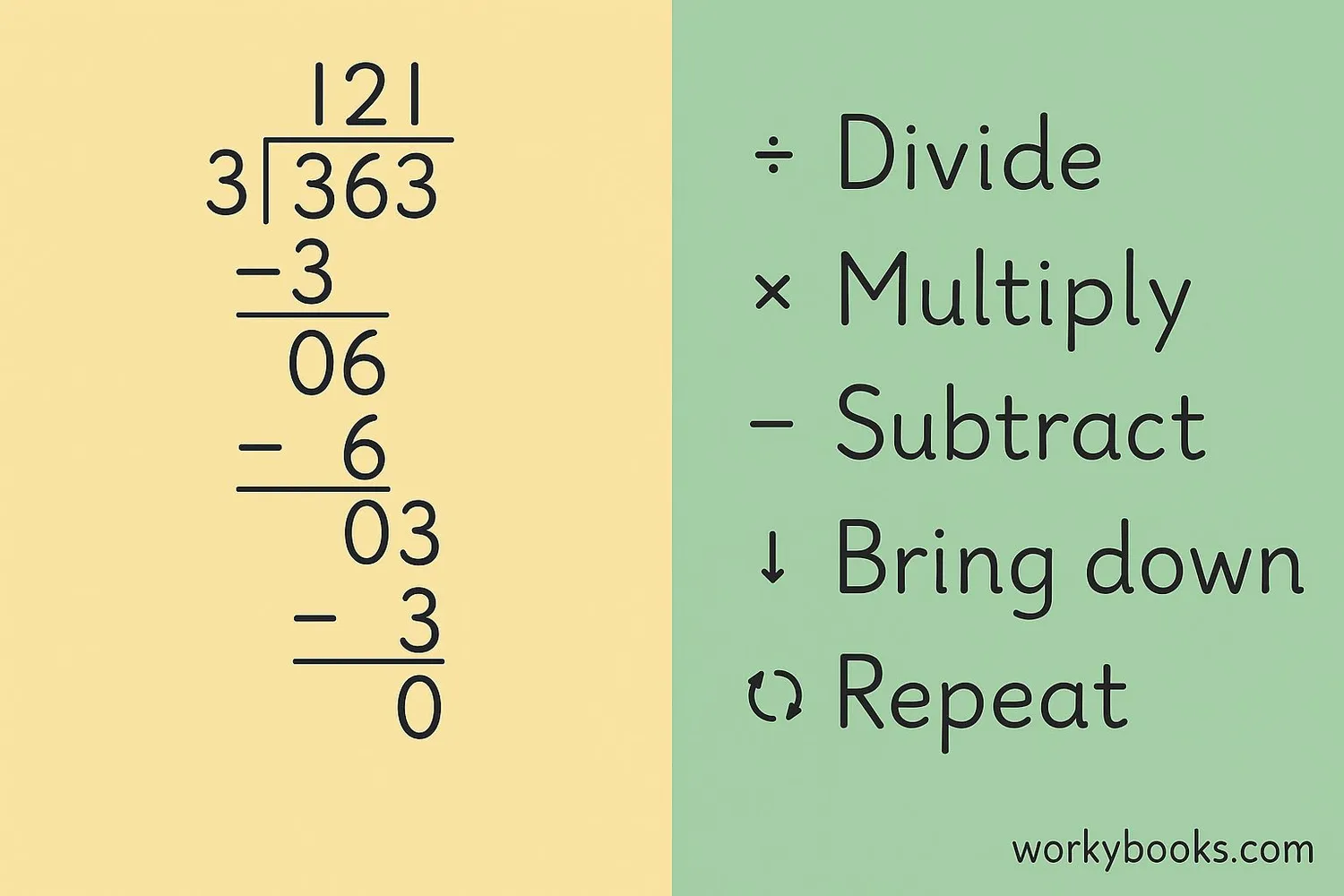
The division algorithm is a step-by-step process for solving division problems, especially helpful for larger numbers. Here's how it works:
Division Steps
Remember: Divide, Multiply, Subtract, Bring down
3)126
-12
06
-6
0
Let's break down the steps:
1. Divide: How many times does 3 go into 12? (4 times)
2. Multiply: 4 × 3 = 12
3. Subtract: 12 - 12 = 0
4. Bring down: Bring down the next digit (6)
5. Repeat: How many times does 3 go into 6? (2 times)
6. Multiply: 2 × 3 = 6
7. Subtract: 6 - 6 = 0
The answer is 42 with no remainder.
Algorithm Tip
Practice the steps with smaller numbers first before moving to larger division problems.
Division Examples
Let's look at some examples of division in action:
Example 1: Maria has 20 stickers. She wants to share them equally with 4 friends. How many stickers will each person get?
Solution: 20 ÷ 5 = 4 (Maria + 4 friends = 5 people)
Example 2: A farmer has 36 eggs. He puts them in cartons that hold 12 eggs each. How many cartons does he need?
Solution: 36 ÷ 12 = 3 cartons
Example 3: There are 45 students going on a field trip. Each van can carry 7 students. How many vans are needed?
Solution: 45 ÷ 7 = 6 with remainder 3, so 7 vans are needed
Example 4: A rope is 28 feet long. If it's cut into 4 equal pieces, how long is each piece?
Solution: 28 ÷ 4 = 7 feet
Example Tip
Word problems often contain clues about whether to divide. Look for words like "share," "equal groups," "each," or "per."
Division Practice Quiz
Test your division knowledge with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about division:
Math Trivia
Discover interesting facts about division and mathematics:
Ancient Division
The earliest evidence of division comes from ancient Egypt around 2000 BC. Egyptians used a method called "doubling" to perform division calculations.
Division by Zero
Division by zero is undefined in mathematics. This is because there's no number that can be multiplied by 0 to get a non-zero number. Computers will often show an error if you try to divide by zero.
Division Symbol Origin
The division symbol (÷) is called an obelus. It was first used by Swiss mathematician Johann Rahn in 1659 in his book "Teutsche Algebra."
Division Record
The largest number ever divided in a recorded mental calculation was 13,195,000 divided by 856. This was accomplished by Willem Klein in 1981.





