Line Segments - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about this fundamental geometry concept with easy explanations and practice activities
What is a Line Segment?
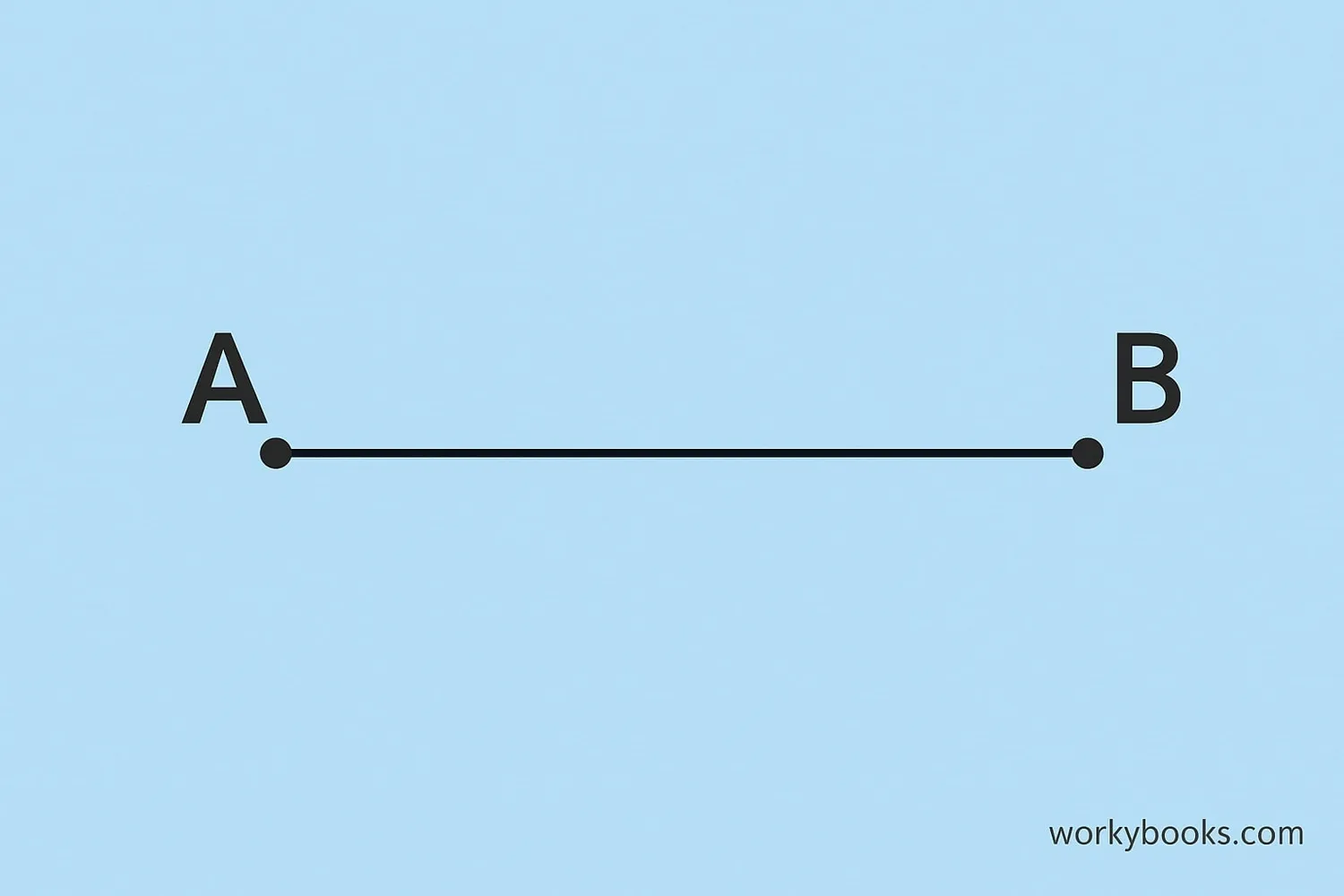
A line segment is a straight path between two points. It has two endpoints and a specific length. Think of it like a piece of string stretched between two points - it doesn't go on forever in either direction.
Here's how line segments are different from other geometry concepts:
- Line: Goes on forever in both directions (no endpoints)
- Ray: Starts at a point and goes on forever in one direction (one endpoint)
- Line Segment: Has two endpoints and a fixed length
We represent a line segment by writing its two endpoints with a line over them, like AB (for a segment between points A and B).
Key Concept
A line segment is the shortest path between two points. It has two endpoints and a definite length.
Properties of Line Segments
Line segments have several important properties that make them special in geometry:
1. Two Endpoints: Every line segment has two endpoints that mark where it begins and ends.
2. Definite Length: Unlike lines and rays, line segments have a specific, measurable length.
3. Straight Path: Line segments are always straight - they don't curve or bend.
4. Part of a Line: A line segment is a portion of a line between two points on that line.
5. Can Be Measured: We can measure the length of a line segment using tools like rulers or measuring tapes.
6. Can Be Named: We name line segments by their endpoints (like segment AB or segment CD).
Remember
When you see two points connected by a straight path, you're looking at a line segment!
Length and Midpoint of a Line Segment
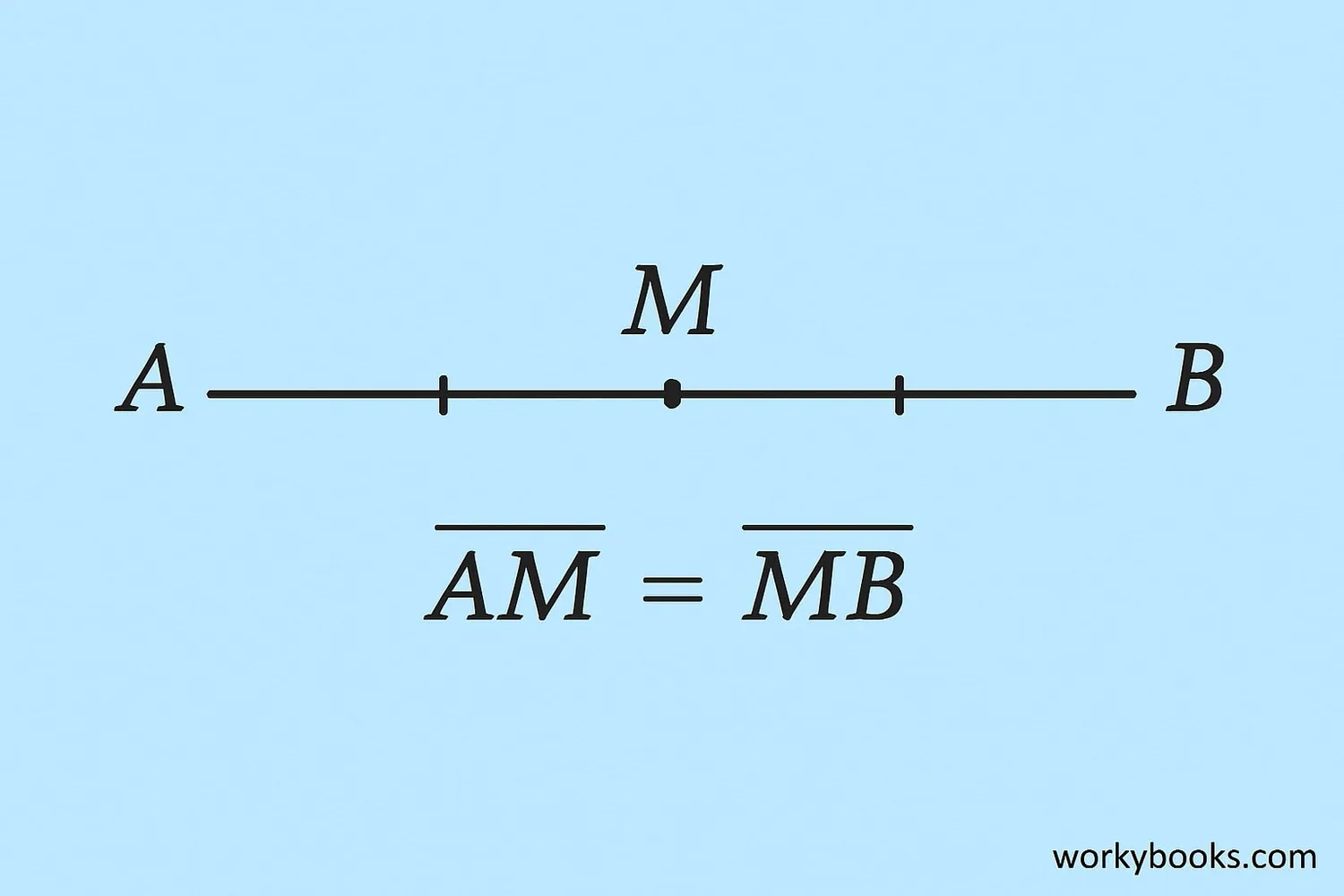
Length: The length of a line segment is the distance between its two endpoints. We can measure this with a ruler or calculate it using coordinates.
Distance Formula: If we know the coordinates of both endpoints (A = (x₁, y₁) and B = (x₂, y₂)), we can calculate the length using:
Distance Formula
This formula calculates the straight-line distance between two points.
Midpoint Formula: If we know the coordinates of both endpoints (A = (x₁, y₁) and B = (x₂, y₂)), we can find the midpoint M using:
Midpoint Formula
This formula calculates the exact middle point between two endpoints.
Solution: Midpoint M = [(2+6)/2, (3+7)/2] = (4, 5)
Calculation Tip
For simple measurements, you can fold a paper with two points so they touch - the fold line will show the midpoint!
Real-World Examples
Line segments are all around us! Here are some examples you can find in everyday life:
1. Edges of Objects: The sides of a book, a table, or a picture frame are line segments.
2. Pencils and Pens: When you look at a pencil on your desk, you're seeing a line segment.
3. Streets and Paths: A straight path in a park or a section of road between two intersections.
4. Bridges: The straight supports between two bridge pillars form line segments.
5. Sports Fields: The lines marking boundaries on a soccer field or basketball court are made of line segments.
6. Building Structures: Steel beams in construction are real-world line segments.
7. Art and Design: Many drawings and designs use line segments to create shapes and patterns.
Can you find five line segments in the room you're in right now?
Observation Tip
Look for straight edges with two endpoints - these are all line segments in our world!
Line Segment Quiz
Test your knowledge with this 5-question quiz about line segments. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about line segments:
Geometry Trivia
Discover interesting facts about geometry and line segments:
Ancient Geometry
The concept of line segments dates back to ancient Egypt, where surveyors (called "rope-stretchers") used ropes to create straight lines and right angles for building pyramids and dividing farmland.
Longest Straight Line
The longest possible straight line on Earth you can sail without hitting land is from Pakistan to Russia - approximately 32,090 km (about 20,000 miles)! This is essentially a line segment on our spherical planet.
In Nature
While perfect line segments are rare in nature, some crystals form with straight edges. Spider silk is also arranged in straight lines at the molecular level, giving it incredible strength.
Computer Graphics
All 3D models in computer graphics are made up of thousands of line segments and polygons. Video games and animated movies rely on these geometric building blocks to create realistic scenes.





