Long Division - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn step-by-step division with clear explanations and practice activities
What is Long Division?
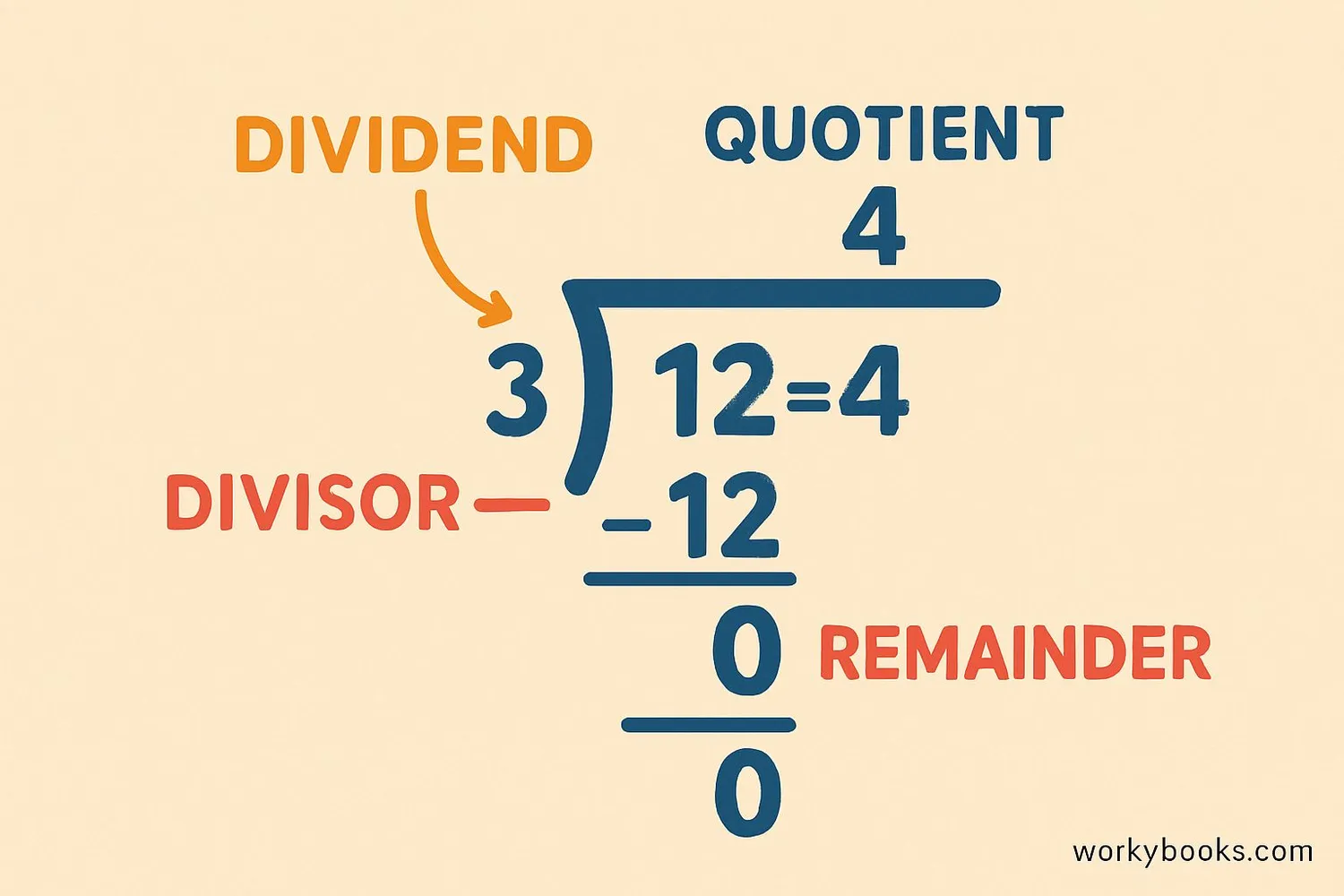
Long division is a method for dividing large numbers that breaks the problem into smaller, more manageable steps. It's called "long" division because we write out all the steps. This method helps us divide numbers that are too big to solve in our heads.
In long division, we have four important parts:
Dividend - The number being divided (inside the division bracket)
Divisor - The number we're dividing by (outside the bracket)
Quotient - The answer (on top of the bracket)
Remainder - What's left over when division isn't exact
For example: In 15 ÷ 4 = 3 R3, 15 is the dividend, 4 is the divisor, 3 is the quotient, and 3 is the remainder.
Key Concept
Division is the opposite of multiplication. If 4 × 3 = 12, then 12 ÷ 3 = 4.
Step-by-Step Long Division
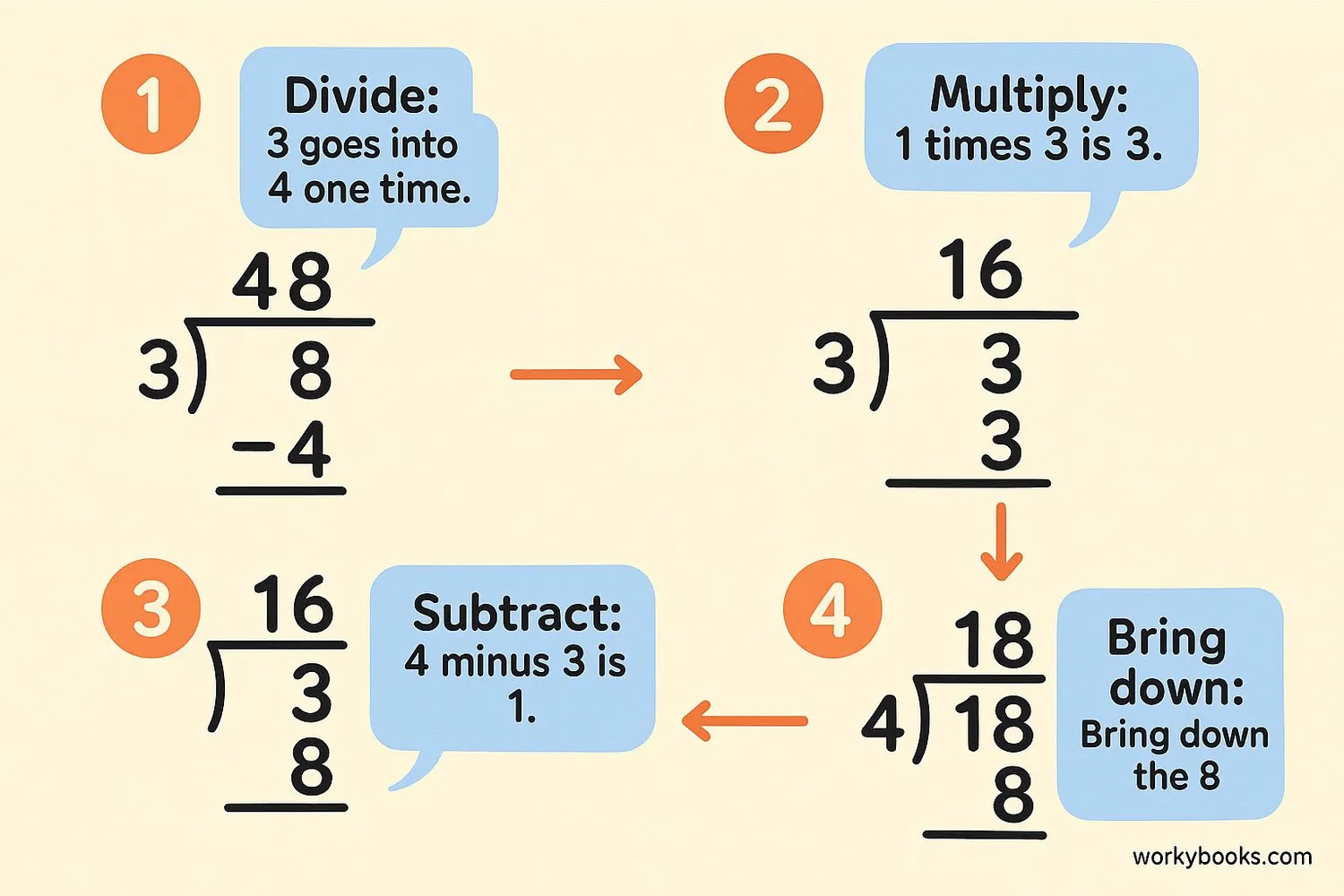
Let's learn the DMSB method - an easy way to remember the steps of long division:
Divide, Multiply, Subtract, Bring down
Step 1: Divide
Look at the first digit of the dividend. Can the divisor go into it? If not, look at the first two digits. Divide and write the answer above the dividend.
3 ⟌ 48
Step 2: Multiply
Multiply the divisor by the number you just wrote above the dividend. Write the result below the first digits of the dividend.
3 ⟌ 48
3
-
Step 3: Subtract
Subtract the result from the digits above. Write the difference below.
3 ⟌ 48
3
-
1
Step 4: Bring down
Bring down the next digit of the dividend next to the subtraction result.
3 ⟌ 48
3
-
18
Repeat the steps
Start again with the Divide step for the new number. Continue until there are no more digits to bring down.
3 ⟌ 48
3
-
18
18
--
0
Remember
Always start with the largest place value and work from left to right. Take it one step at a time!
Division with Remainders

Sometimes numbers don't divide evenly. The remainder is what's left over after dividing. We write it with an "R" followed by the remainder.
Example: 17 ÷ 3
1. 3 goes into 17 five times (5 × 3 = 15)
2. Subtract 15 from 17 = 2
3. There are no more digits to bring down
4. Answer: 5 R2 (5 with remainder 2)
We can check our answer by multiplying the divisor by the quotient and adding the remainder: (3 × 5) + 2 = 15 + 2 = 17
3 ⟌ 17
15
--
2
Real World Remainders
If you have 17 cookies to share equally with 3 friends, each gets 5 cookies and there are 2 left over.
Dividing by 2-Digit Numbers
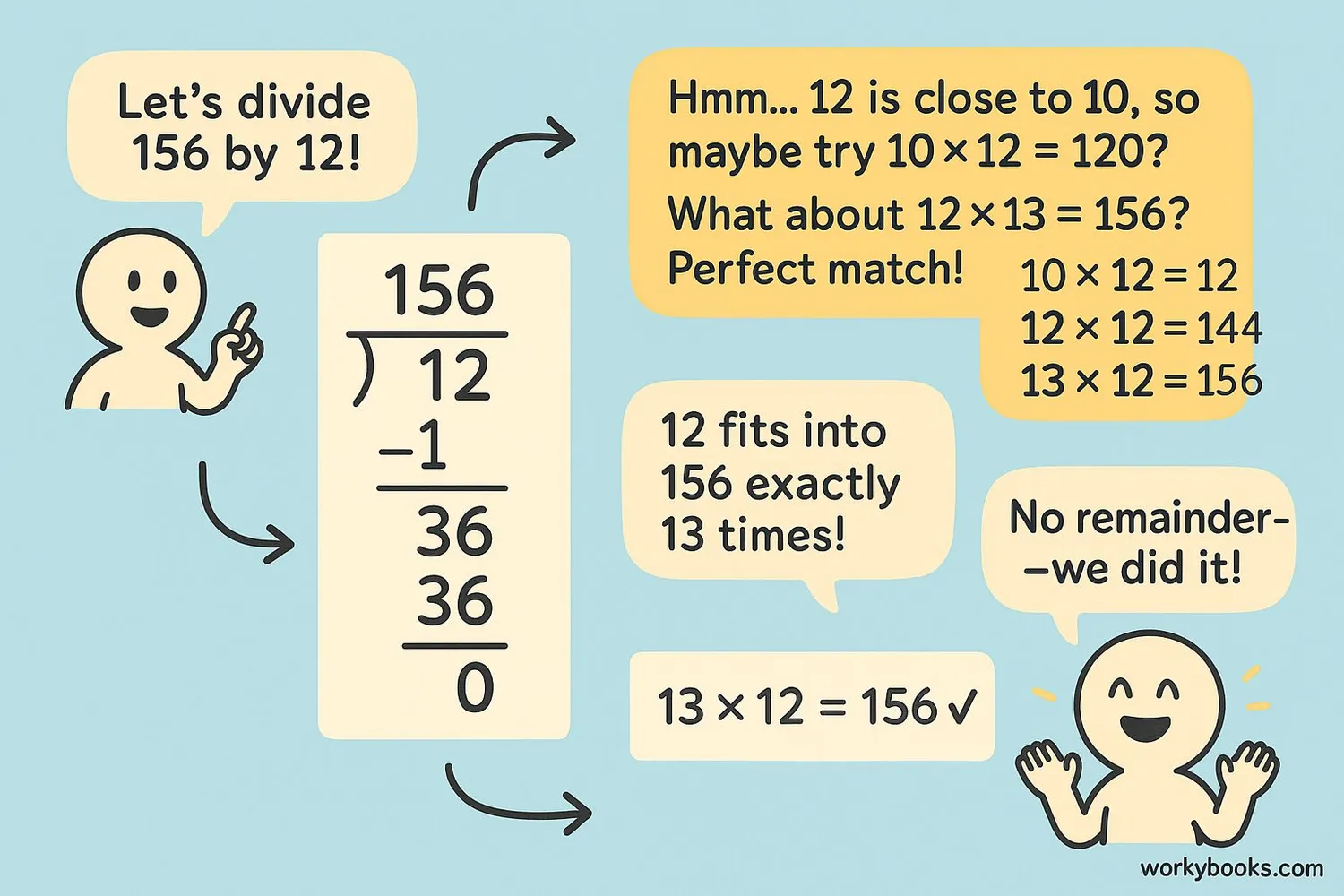
Dividing by 2-digit numbers follows the same steps, but we need to estimate more carefully.
Example: 156 ÷ 12
1. Look at the first two digits of the dividend (15). 12 goes into 15 once. Write 1 above.
2. Multiply 1 × 12 = 12. Write below 15.
3. Subtract: 15 - 12 = 3.
4. Bring down the next digit (6) to make 36.
5. How many times does 12 go into 36? 3 times (12 × 3 = 36).
6. Write 3 above. Subtract 36 - 36 = 0.
Answer: 13
12 ⟌ 156
12
--
36
36
--
0
Estimation Tip
Round the divisor to the nearest ten to help with estimation. For 12, think "how many times does 10 go into 36?"
Long Division with Decimals

Dividing with decimals is similar to whole number division. The key is to place the decimal point correctly.
Step 1: If the divisor is a decimal, move the decimal point to the right to make it a whole number.
Step 2: Move the decimal point in the dividend the same number of places.
Step 3: Divide as with whole numbers.
Step 4: Place the decimal point in the quotient directly above where it is in the dividend.
Example: 5.6 ÷ 4
1. 4 is already a whole number.
2. Place the decimal point in the quotient above the dividend's decimal point.
3. 4 goes into 5 once. Write 1 above, then decimal point.
4. Multiply 1 × 4 = 4. Subtract: 5 - 4 = 1.
5. Bring down 6 to make 16.
6. 4 goes into 16 four times. Write 4 above.
7. Answer: 1.4
4 ⟌ 5.6
4
-
1.6
1.6
---
0
Remember
You can add zeros to the dividend after the decimal point if needed: 5.6 is the same as 5.600
Long Division Quiz
Test your division skills with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about long division:
Division Trivia
Discover interesting facts about division and mathematics:
Ancient Division
The oldest known division algorithm dates back to 2000 BC in ancient Egypt. Egyptians used a method of doubling and halving to solve division problems.
Dividing by Zero
Division by zero is undefined. If you try to divide any number by zero, calculators will show an error because it's mathematically impossible.
Division in Nature
Cell division is how living things grow and repair themselves. One cell divides into two, then those two divide into four, and so on - just like mathematical division!
Largest Division Problem
The largest division problem ever solved on paper had a dividend with 100,000 digits! It took mathematicians several weeks to complete the calculation.





