Mass and Volume - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about measurement concepts with simple explanations, examples, and quizzes
What is Mass?
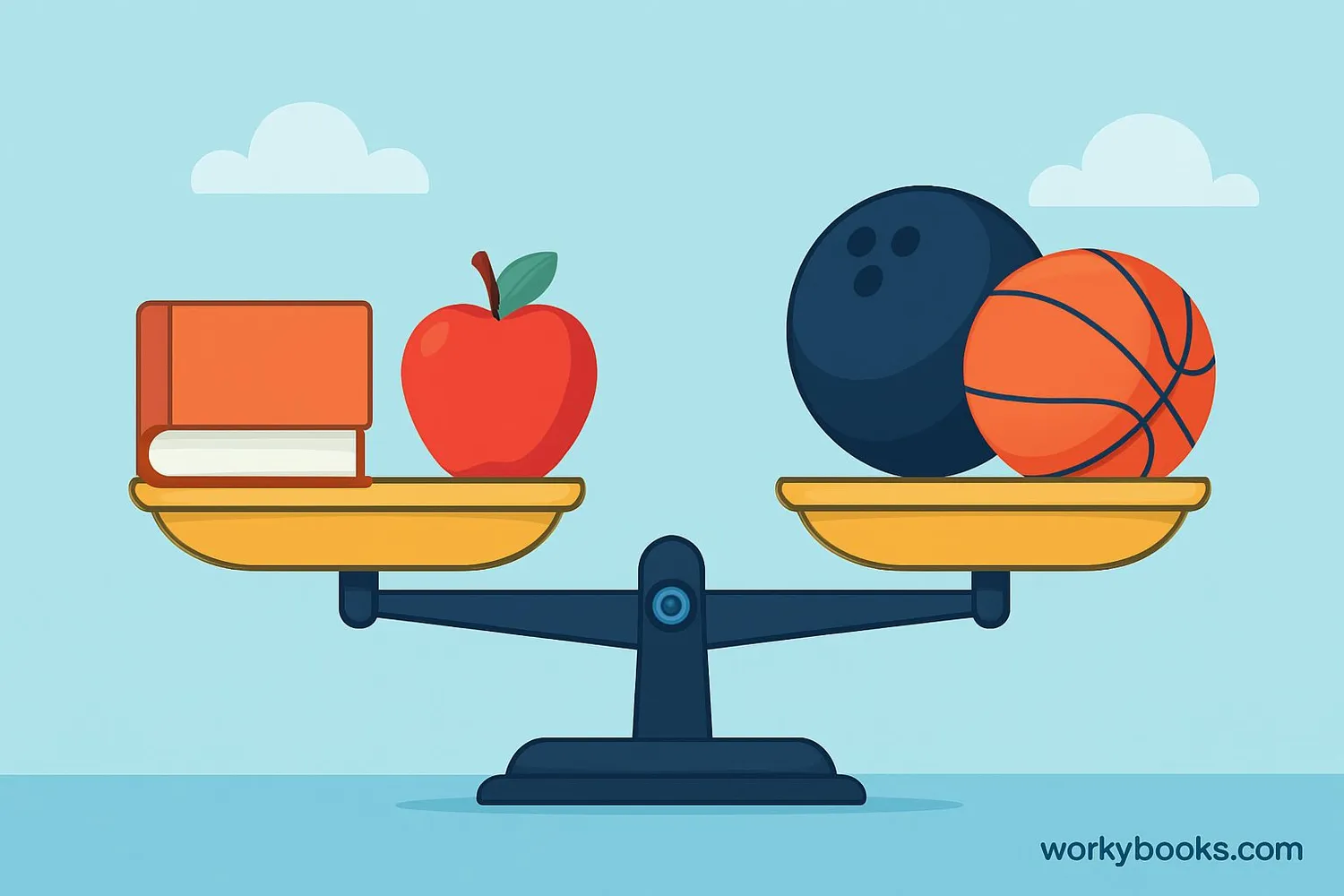

Mass is the amount of matter in an object. It tells us how much "stuff" something is made of. Mass stays the same no matter where the object is - on Earth, on the Moon, or in space!
We measure mass using units like:
- Grams (g) - for small objects like paperclips
- Kilograms (kg) - for larger objects like books or people
Mass Facts
1 kilogram = 1,000 grams
The SI unit (international standard) for mass is the kilogram
Key Concept
Mass is different from weight. Weight measures the force of gravity on an object, while mass measures the amount of matter.
What is Volume?
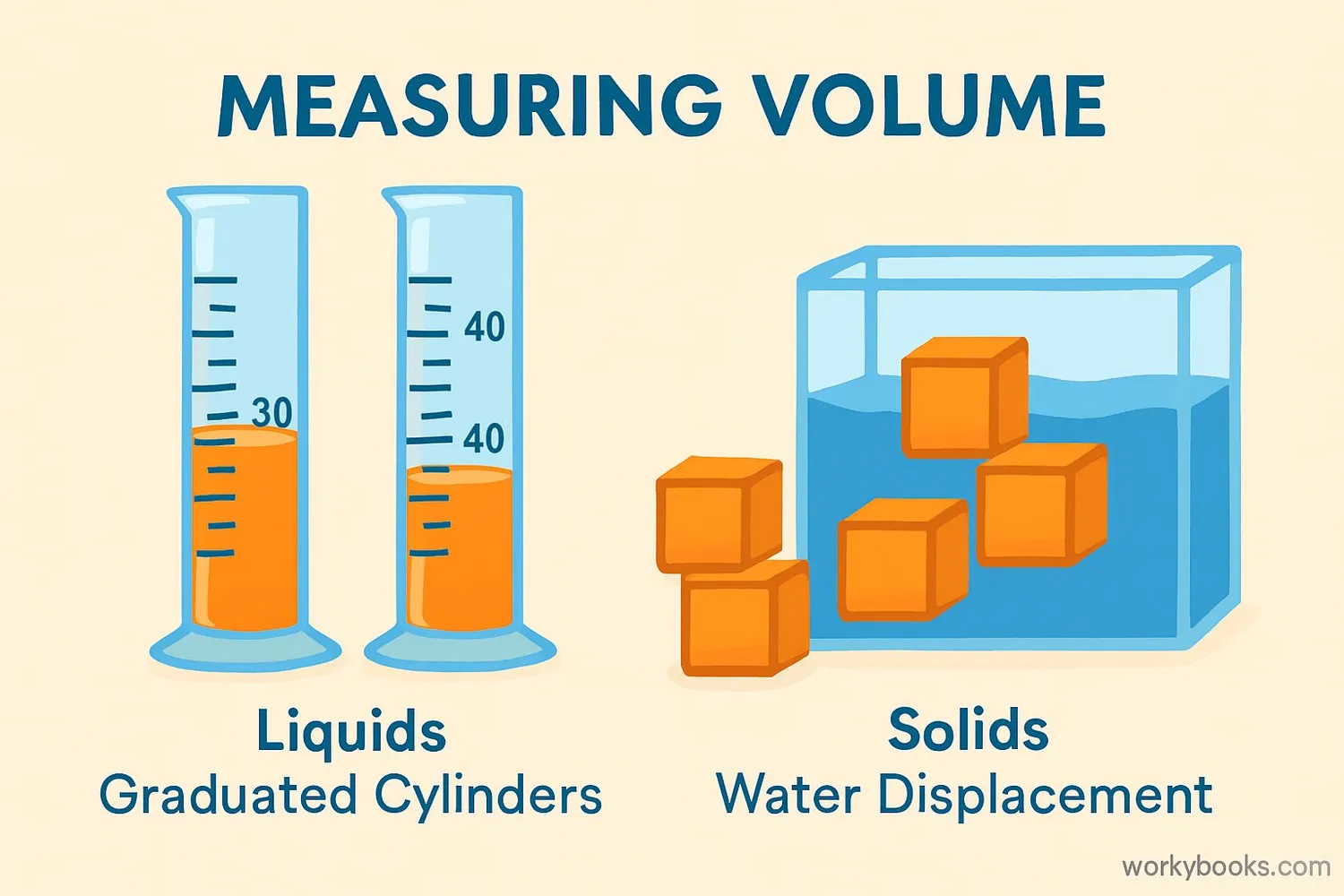
Volume is the amount of space an object takes up. It tells us how much room something needs. Everything has volume - solids, liquids, and gases!
We measure volume using units like:
- Milliliters (mL) - for small amounts like medicine
- Liters (L) - for larger amounts like juice bottles
- Cubic centimeters (cm³) - for solid objects
Volume Facts
1 liter = 1,000 milliliters
1 milliliter = 1 cubic centimeter (for water)
Remember
Liquids take the shape of their container, but their volume stays the same no matter what container they're in.
Mass vs Volume
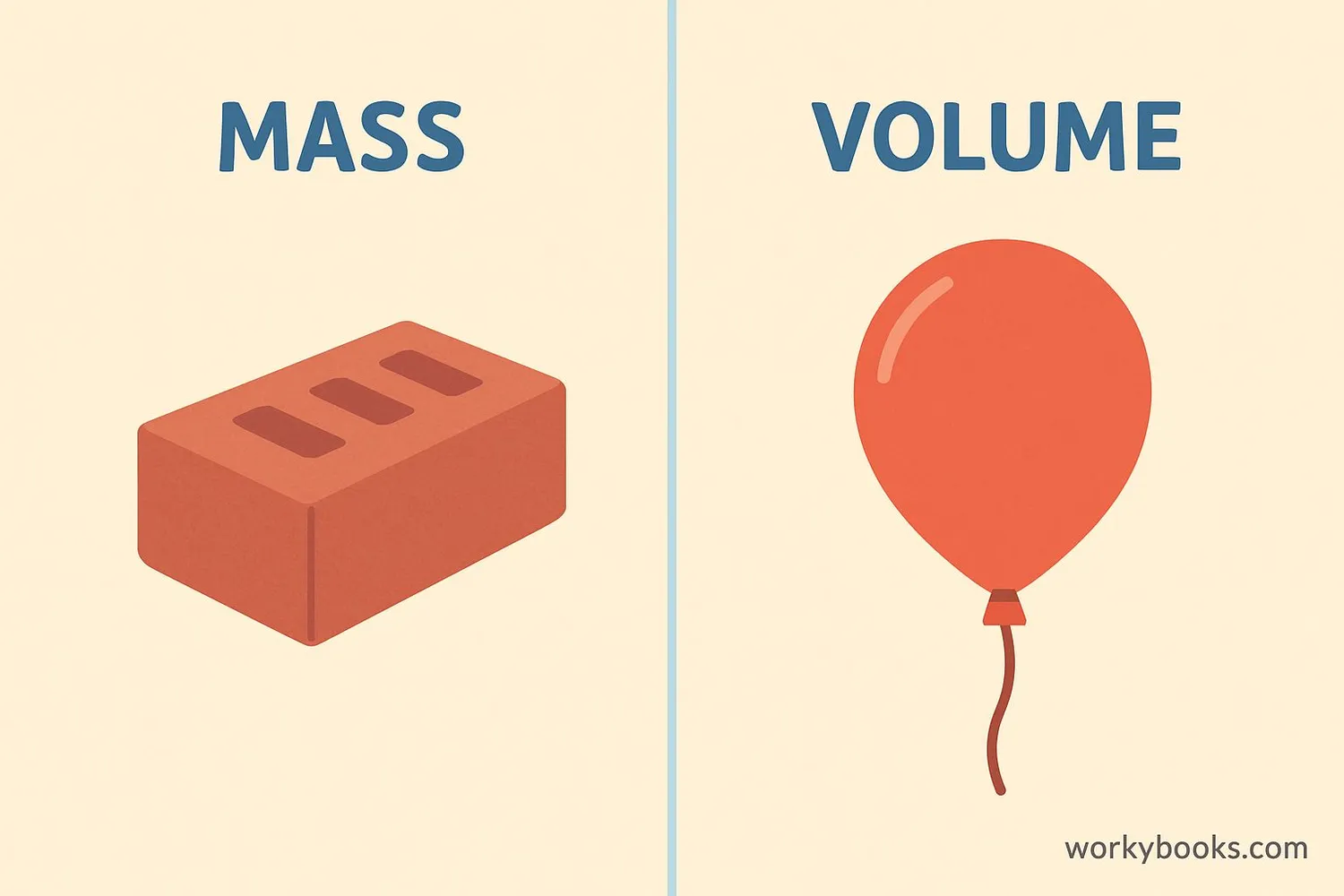
While mass and volume are both measurements, they tell us different things about objects:
| Mass | Volume |
|---|---|
| Measures amount of matter | Measures space occupied |
| Measured in grams/kilograms | Measured in liters/milliliters |
| Doesn't change with shape | Changes with shape (for gases) |
| Measured with balances | Measured with rulers or cylinders |
| Same everywhere | Can change with temperature |
Real World Example
A balloon has large volume but small mass, while a brick has small volume but large mass.
Understanding Density
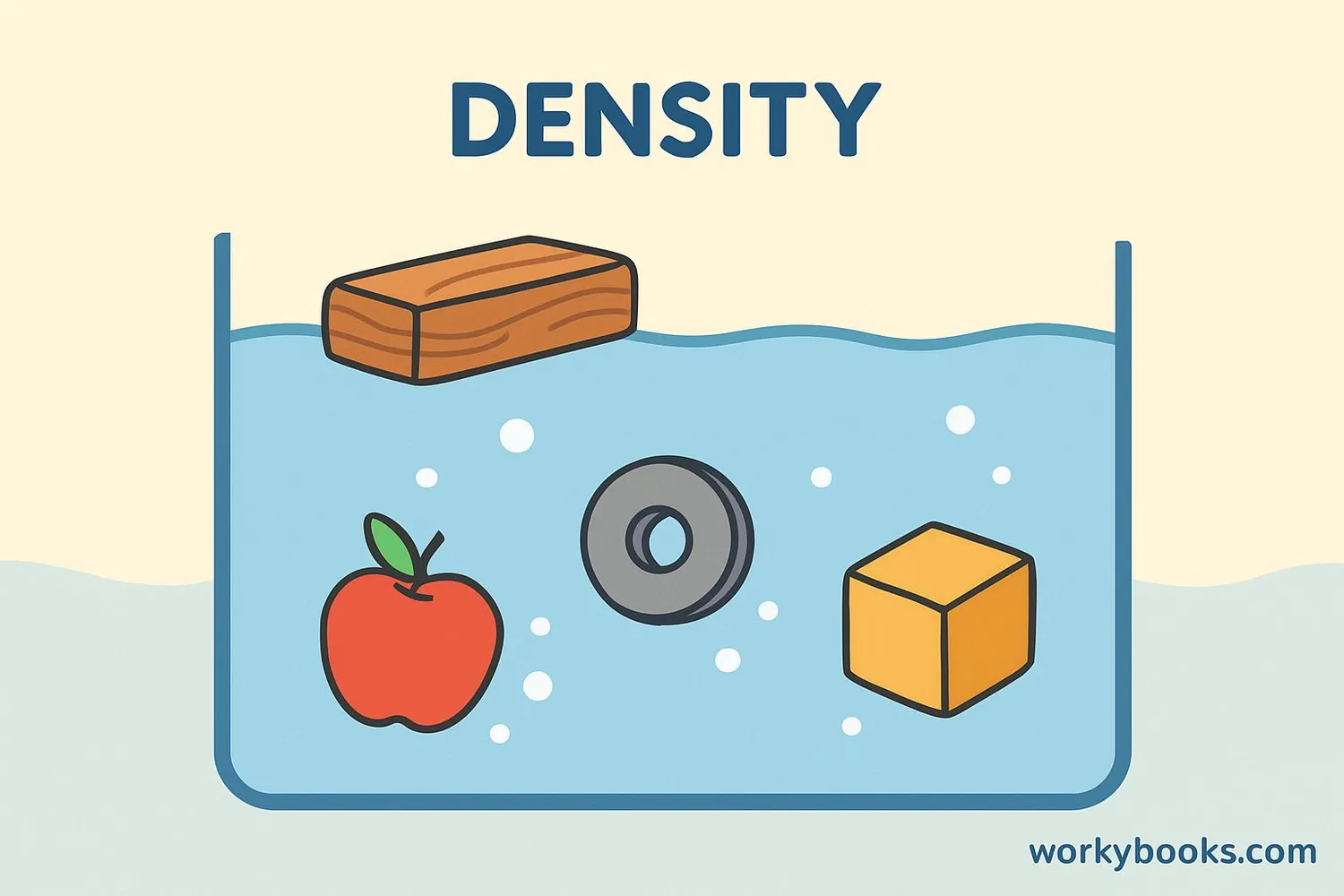
Density is a special measurement that combines mass and volume. It tells us how tightly packed the matter in an object is.
Density Formula
Units: grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or grams per milliliter (g/mL)
Example: If a block has a mass of 50 grams and volume of 10 cm³, its density is:
50 g ÷ 10 cm³ = 5 g/cm³
Science Fact
Water has a density of 1 g/cm³. Objects with density less than 1 float, while those with density more than 1 sink.
Real-World Examples

Let's look at some examples of mass and volume in everyday life:
Mass Examples:
- A paperclip has a mass of about 1 gram
- A liter of water has a mass of 1 kilogram
- An average apple has a mass of about 150 grams
- A soda can holds 355 mL of liquid
- A swimming pool might hold 50,000 liters of water
- A cereal box has a volume of about 2,000 cm³
- Wood floats because its density is less than water (about 0.7 g/cm³)
- Steel sinks because its density is more than water (about 7.8 g/cm³)
- Ice floats on water because it's less dense than liquid water
Try This
Find three objects at home. Guess their masses, then check using a kitchen scale. Compare your guesses to the actual measurements!
Practice Quiz
Test your understanding with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about mass and volume:
Measurement Trivia
Discover interesting facts about mass and volume:
The Kilogram Standard
The kilogram was originally defined by a physical platinum-iridium cylinder kept in France. In 2019, it was redefined using fundamental physics constants for more accuracy.
Lightest Solid
Aerogel is the lightest solid material, with density as low as 0.001 g/cm³. It's often called "frozen smoke" because it's 99.8% air!
Space Measurements
Astronauts use special space scales that measure mass by oscillating objects, since regular scales that depend on gravity don't work in orbit.
Largest Volume
The Pacific Ocean has the largest volume of any body of water on Earth - about 710 million cubic kilometers! That's 710,000,000,000,000,000,000 liters!





