Rigid Transformations - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn how shapes can move without changing size or shape
What are Rigid Transformations?
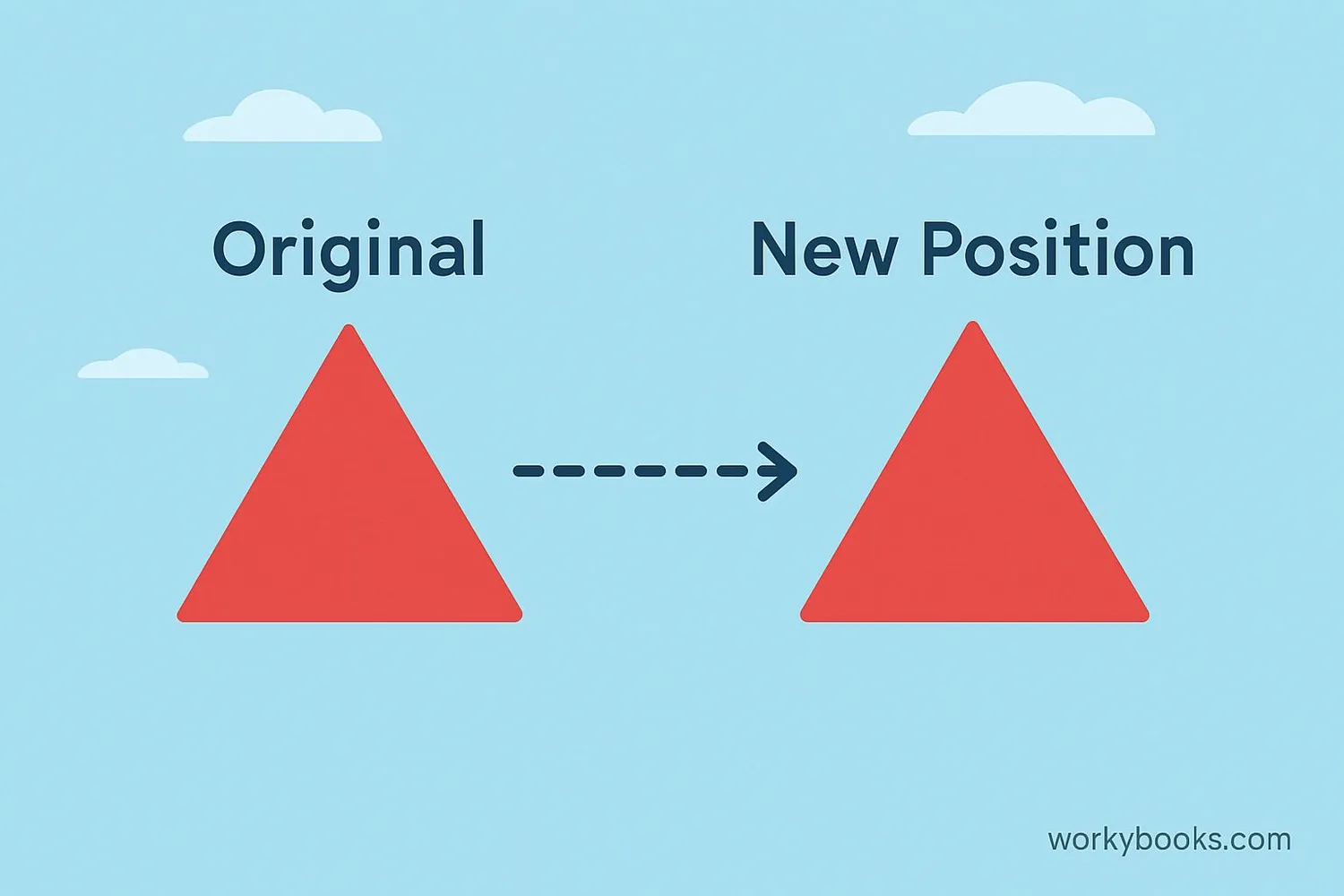
Rigid transformations (also called isometries or Euclidean transformations) are ways to move a shape without changing its size or shape. Think of it like sliding, flipping, or turning a puzzle piece - the piece stays exactly the same, just in a new position.
The three main types of rigid transformations are:
- Translation (sliding)
- Rotation (turning)
- Reflection (flipping)
Rigid transformations are important because they help us understand how shapes can move in space while keeping their properties the same. This is useful in art, architecture, and even video games!
Key Concept
In rigid transformations, the shape's size, angles, and side lengths never change - only its position or orientation.
Types of Rigid Transformations
Translation
Sliding a shape in any direction without rotating or flipping it. Every point moves the same distance in the same direction.
Rotation
Turning a shape around a fixed point called the center of rotation. The shape rotates at a specific angle.
Reflection
Flipping a shape over a line to create a mirror image. The reflection line is called the line of symmetry.
Remember
Any rigid transformation can be created by combining translations, rotations, and reflections. Together, these form what mathematicians call the Euclidean group.
Properties of Rigid Transformations
Rigid transformations have special properties that always stay the same:
1. Distance Preservation: The distance between any two points stays exactly the same after the transformation.
2. Angle Preservation: All angles in the shape remain the same size.
3. Parallelism: Lines that were parallel before the transformation stay parallel.
4. Collinearity: Points that were in a straight line stay in a straight line.
5. Size and Shape: The overall size and shape of the figure doesn't change.
Transformations that preserve these properties are called isometries. Some rigid transformations like reflections change the "handedness" of a shape (like how your left hand becomes a right hand in the mirror), while translations and rotations (which form the special Euclidean group) preserve orientation.
Real-World Examples
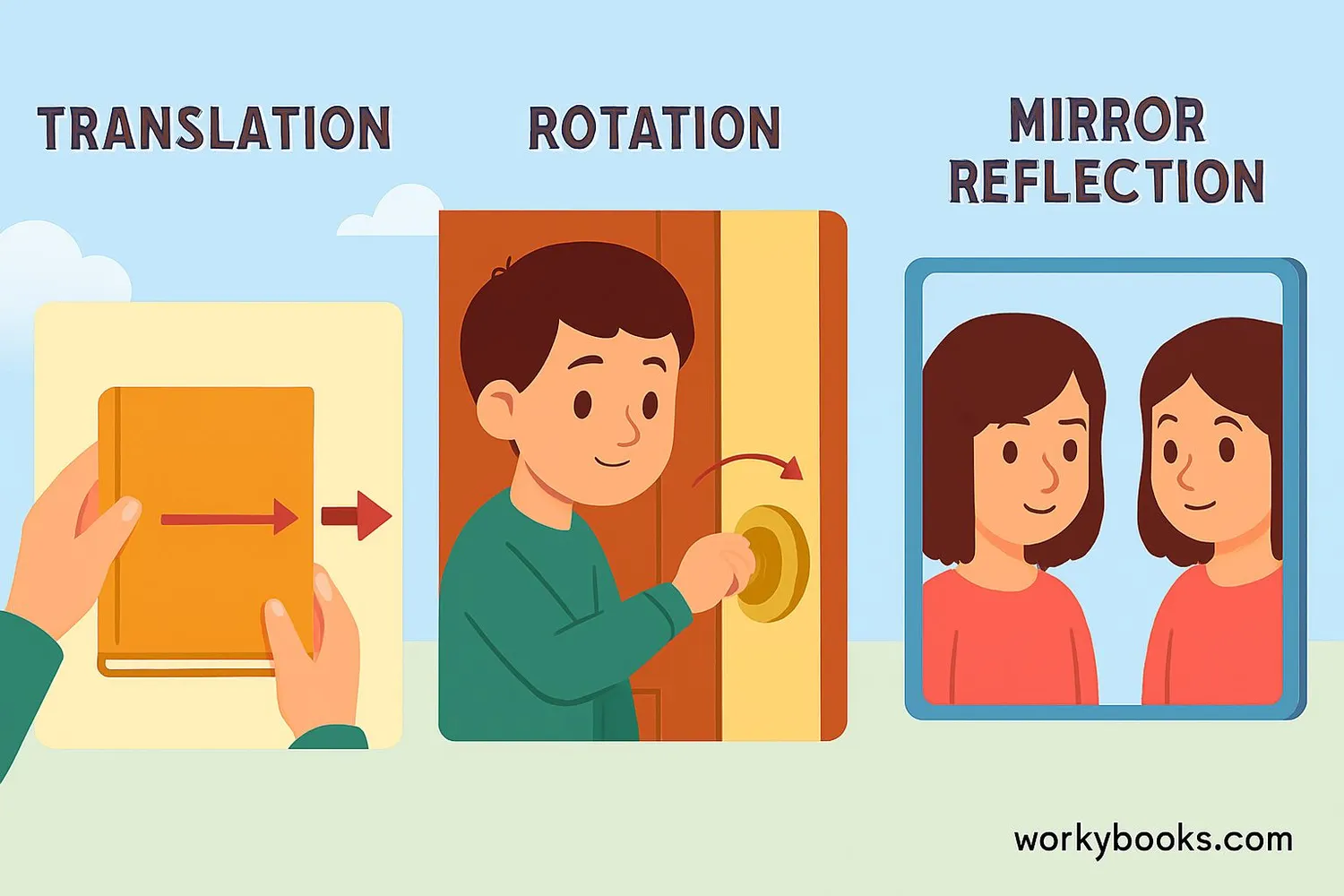
Rigid transformations are all around us! Here are some examples you might recognize:
Translation Examples:
- Sliding a book across a table
- Pushing a shopping cart straight ahead
- Moving a chess piece to a different square
- Turning a door knob
- Hands moving on a clock
- Spinning a bicycle wheel
- Your image in a mirror
- Butterfly wings (symmetrical patterns)
- Reflection on a calm lake
Math Connection
Rigid transformations are the foundation of congruence in geometry. When two shapes can be transformed into each other using rigid motions, we say they are congruent.
Rigid Transformation Quiz
Test your knowledge with these 5 questions about rigid transformations. Choose the best answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about rigid transformations:
Geometry Trivia
Discover fascinating facts about transformations and geometry:
Ancient Origins
The study of rigid transformations dates back to ancient Greece. Euclid, known as the "Father of Geometry," described transformations in his famous book "Elements" around 300 BC.
Crystal Symmetry
In nature, rigid transformations create the symmetrical patterns in snowflakes and crystals. The six-fold symmetry of snowflakes comes from rotational transformations at 60° angles.
Space Exploration
NASA uses rigid transformations to calculate spacecraft trajectories. When planning missions to Mars, engineers use rotations and translations to map the journey through space.
Mathematical Groups
The set of all rigid transformations forms a mathematical structure called the Euclidean group. Special subgroups include translations alone (translation group) and rotations alone (rotation group).




