Acid Rain - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about how pollution creates acidic rain and its effects on our environment
What is Acid Rain?
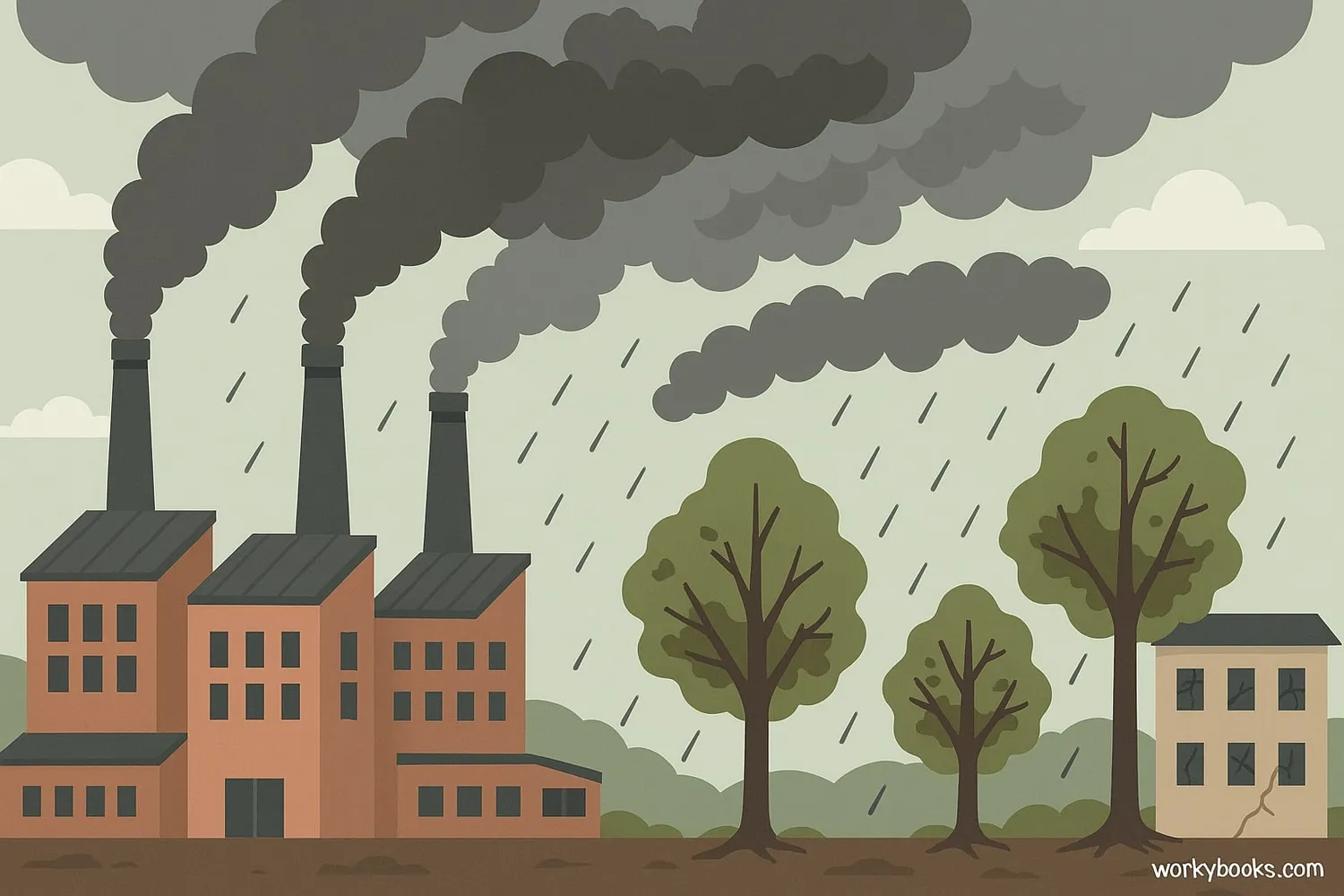

Acid rain is rain or any other form of precipitation that is unusually acidic. This means it has elevated levels of hydrogen ions (low pH). Normal rain has a pH of about 5.6, while acid rain usually has a pH between 4.2 and 4.4.
Acid rain occurs when sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) are released into the atmosphere and react with water molecules to produce acids. This pollution comes mainly from human activities like burning fossil fuels in power plants and vehicles.
Did You Know?
The term "acid rain" was first used by Scottish chemist Robert Angus Smith in 1852! He discovered the connection between pollution and acid rain while studying rain chemistry near industrial cities.
Causes of Acid Rain
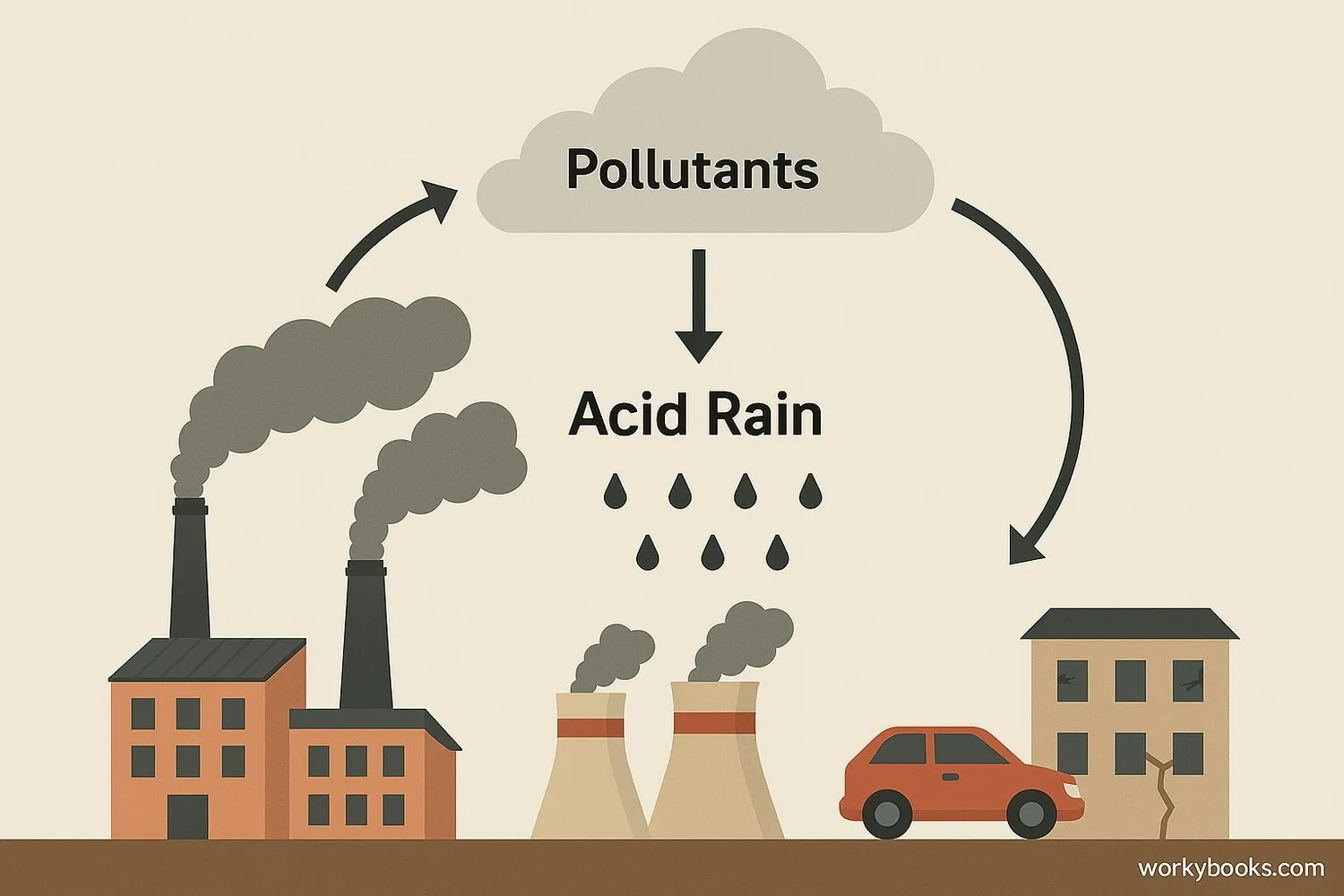
Acid rain is caused by chemical reactions that begin when compounds like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides are released into the air. These substances can rise very high into the atmosphere, where they mix and react with water, oxygen, and other chemicals to form more acidic pollutants, known as acid rain.
Pollution Sources
Burning fossil fuels in factories, power plants, and vehicles releases SO₂ and NOₓ
Chemical Reactions
Pollutants mix with water vapor and oxygen in the atmosphere
Acid Formation
Form sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) and nitric acid (HNO₃)
Precipitation
Acids fall to earth as rain, snow, fog, or dry particles
Natural Causes Too!
While human activities cause most acid rain, natural sources like volcanoes and decaying vegetation also release chemicals that can contribute to acid rain.
Effects of Acid Rain
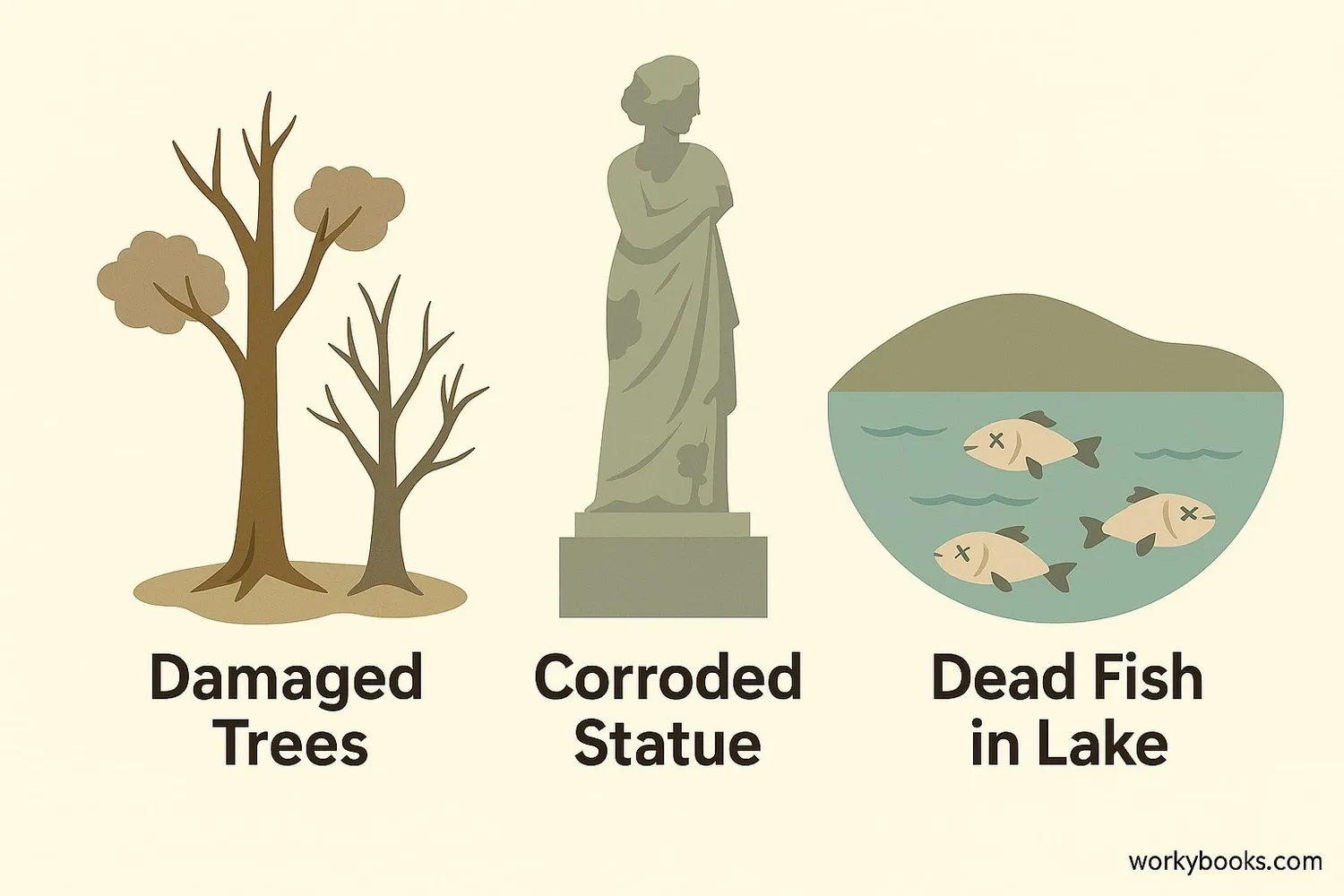
Acid rain has many harmful effects on the environment:
Forest Damage
Weakens trees by damaging leaves, depleting soil nutrients, and making trees more vulnerable to disease
Aquatic Ecosystems
Lowers pH in lakes and streams, harming fish and other aquatic life
Material Damage
Corrodes buildings, statues, and monuments made of stone and metal
Acid rain affects soil chemistry by dissolving and washing away nutrients that plants need to grow. It also releases aluminum from the soil, which can be toxic to both plants and aquatic life. When acid rain flows through soil, it can leach aluminum from soil clay particles and then flow into streams and lakes.
Solutions to Acid Rain

There are several ways to reduce acid rain:
Cleaner Energy
Switch to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower
Pollution Controls
Install scrubbers in smokestacks to remove SO₂ before it's released
Energy Conservation
Reduce electricity use and improve energy efficiency
Cleaner Vehicles
Use electric vehicles or those with better emission controls
The Clean Air Act of 1990 in the United States helped reduce acid rain by requiring power plants to reduce their SO₂ emissions. Since then, SO₂ emissions have decreased by over 80%, showing that regulations can make a big difference in fighting acid rain.
Acid Rain Quiz
Test your knowledge about acid rain with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about acid rain:
Acid Rain Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about acid rain!
Extreme Acidity
The most acidic rain ever recorded fell in Wheeling, West Virginia with a pH of 1.5 - that's more acidic than lemon juice and almost as acidic as stomach acid!
Forest Damage
In Germany's Black Forest, acid rain damaged about 50% of the trees in the 1980s. Many trees lost their needles or leaves, weakening the entire forest ecosystem.
International Problem
Pollution from the United States causes acid rain in Canada, and UK pollution causes acid rain in Scandinavia. Winds can carry pollution hundreds of miles before it falls as acid rain.
Recovery Success
After pollution controls were implemented in the 1990s, lakes in New York's Adirondack Mountains began recovering. Some fish species have returned to lakes that were too acidic for them for decades.





