Atomic Numbers - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how atomic numbers organize the periodic table and define chemical elements
What is Atomic Number?
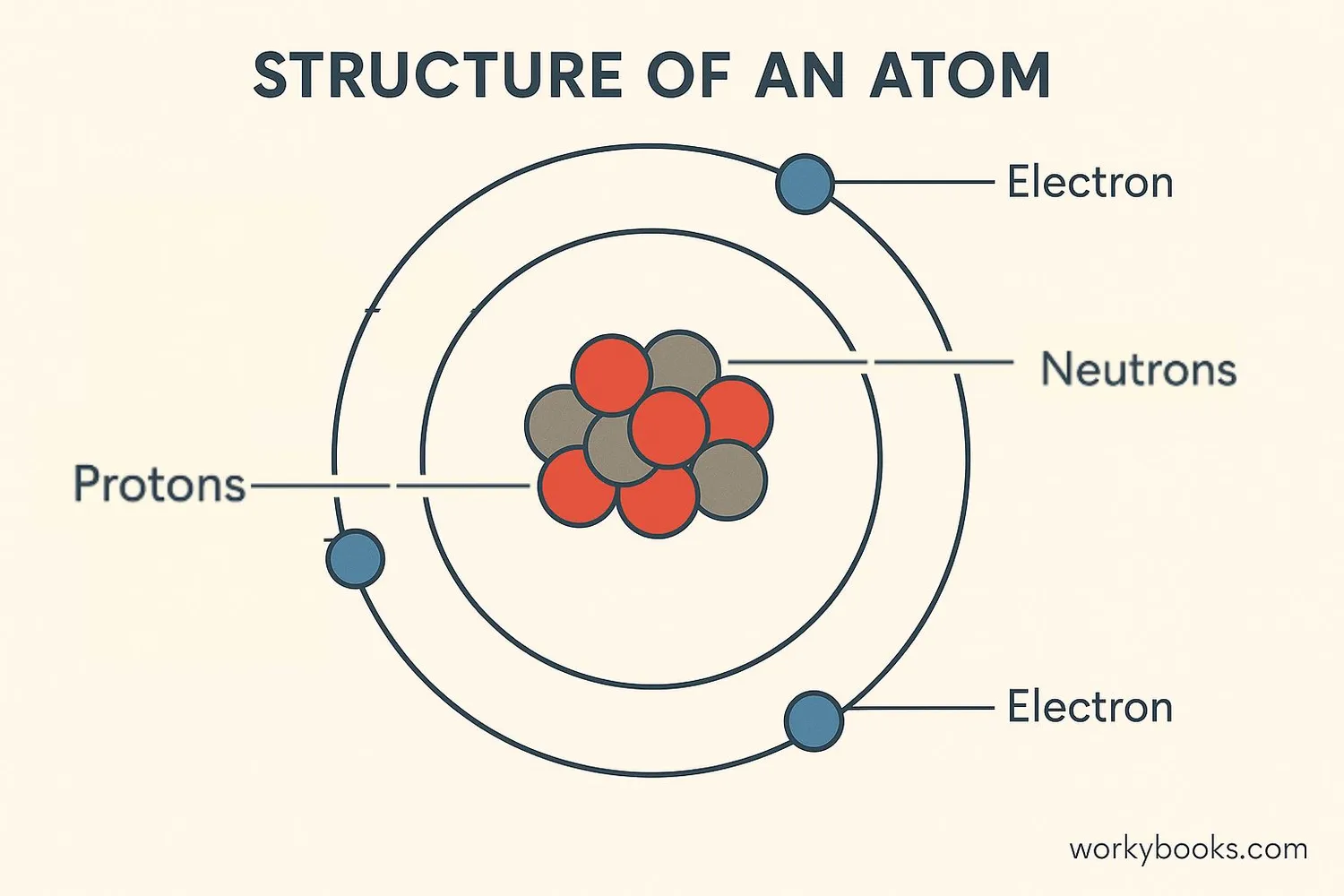
The atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom. It's like the atom's ID card - each element has its own unique atomic number that never changes!
Think of it as an element's fingerprint. For example:
- Hydrogen has atomic number 1 (1 proton)
- Carbon has atomic number 6 (6 protons)
- Oxygen has atomic number 8 (8 protons)
Key Fact!
In a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the number of protons, so the atomic number also tells us how many electrons an atom has!
Element Examples
Hydrogen
1 proton
Helium
2 protons
Lithium
3 protons
Carbon
6 protons
How Atomic Numbers Work
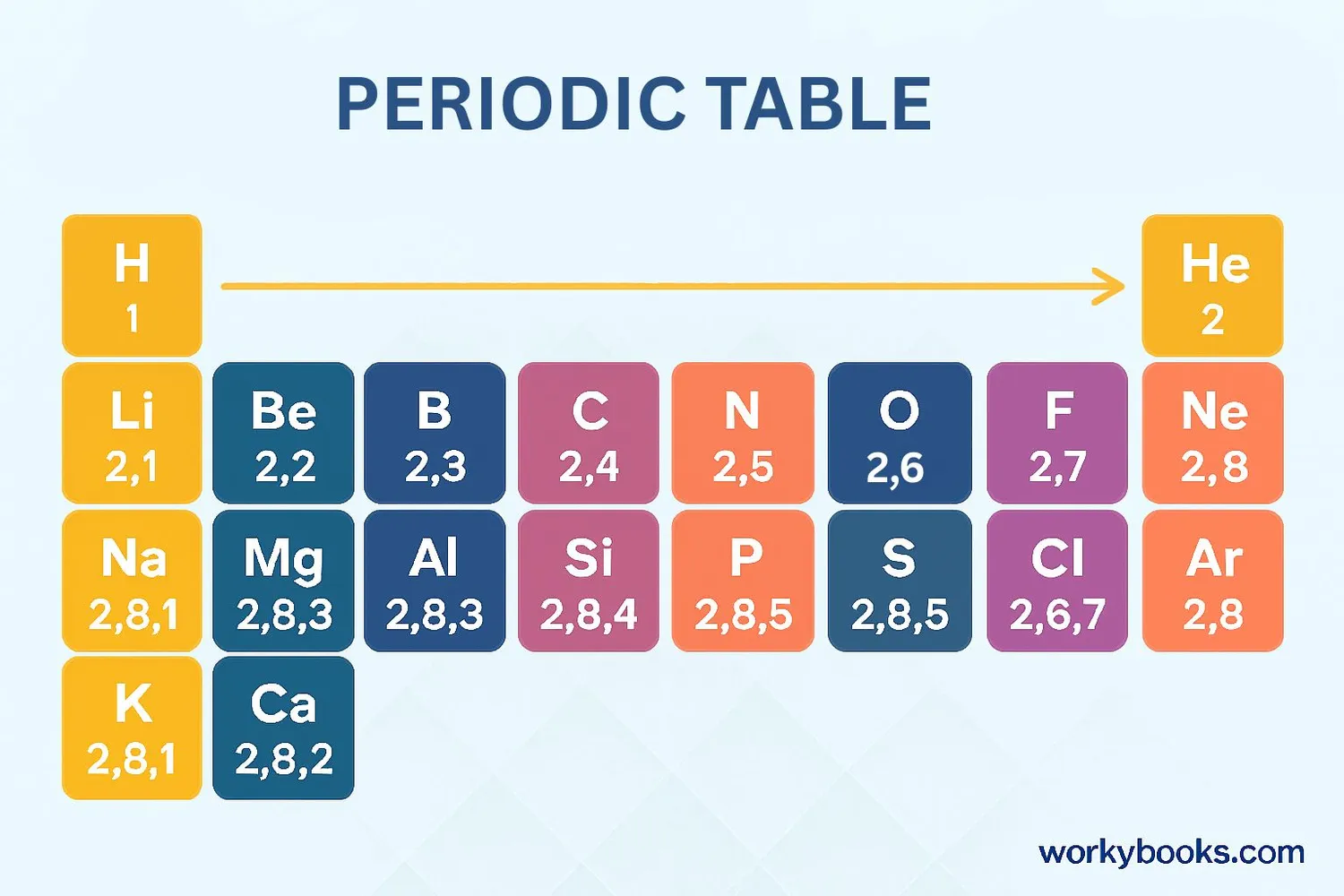
Atomic numbers are the key to organizing the periodic table. Here's how they work:
Protons Define Elements
The number of protons determines which element an atom is
Periodic Table Order
Elements are arranged by increasing atomic number
Electron Configuration
Atomic number determines how electrons are arranged
Chemical Properties
Elements in the same column have similar properties
Isotopes
Atoms with same protons but different neutrons
Dmitri Mendeleev created the first periodic table by arranging elements by atomic weight, but today we use atomic number because it more accurately reflects an element's properties. The atomic number tells us:
- The number of protons in the nucleus
- The number of electrons in a neutral atom
- The element's position in the periodic table
- The element's chemical behavior
Mendeleev's Genius!
Mendeleev left gaps in his periodic table for elements that hadn't been discovered yet. He predicted their properties based on where they would appear!
Why Atomic Numbers Matter
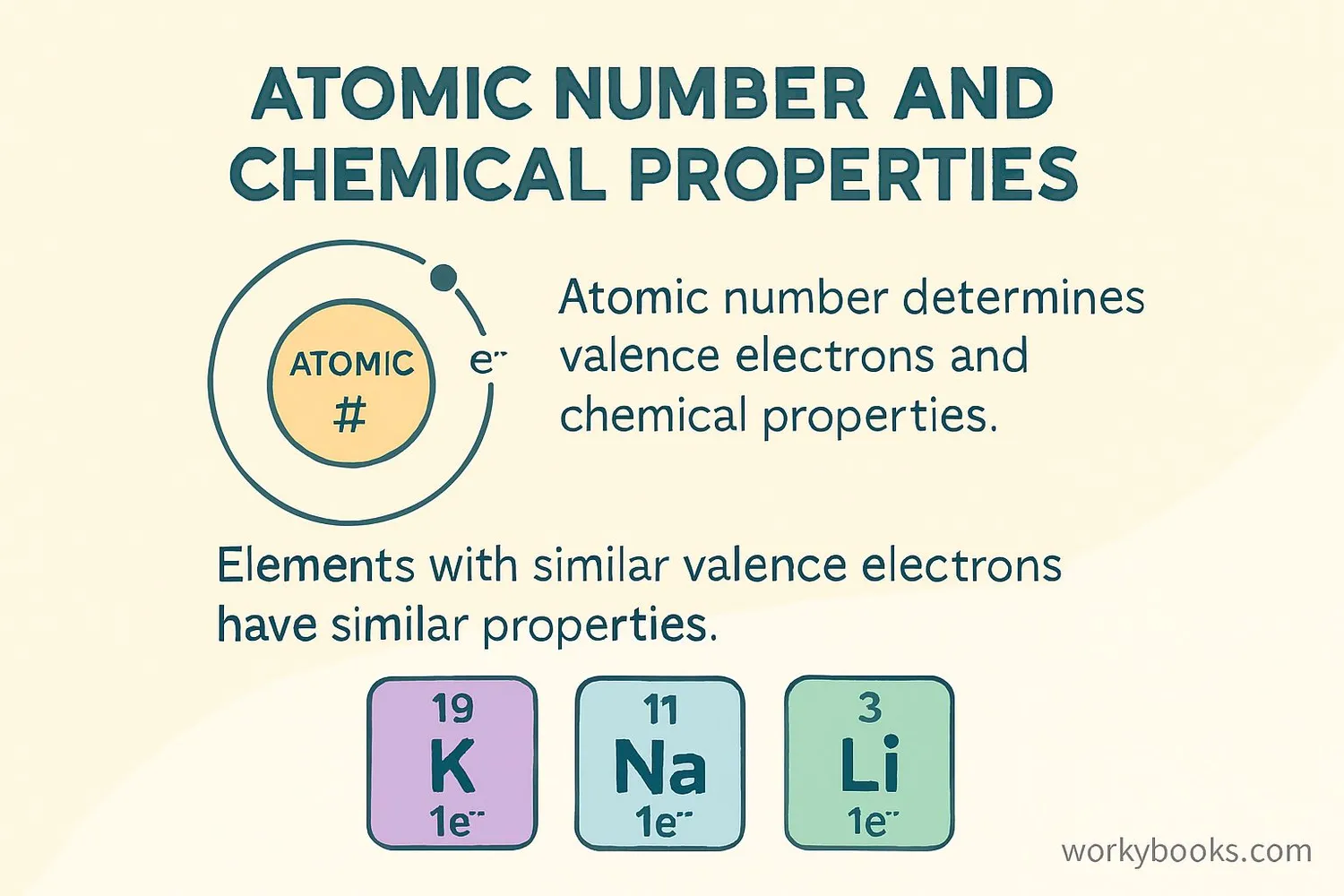
Atomic numbers are fundamental to understanding chemistry. Here's why they're so important:
Element Identity
Atomic number uniquely identifies each chemical element
Periodic Organization
The periodic table is organized by atomic number
Chemical Behavior
Determines valence electrons and chemical properties
Without atomic numbers, we wouldn't understand:
• Why elements behave differently
• How to predict chemical reactions
• The relationship between elements
• How to create new materials
The atomic number also tells us about the nuclear charge - the positive charge in the nucleus that holds electrons in place. This charge determines how tightly electrons are bound to the atom, which affects how atoms interact with each other.
Valence Electrons
The atomic number determines how electrons are arranged in shells. Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons, which is why they have similar chemical properties!
Atomic Number Quiz
Test your knowledge about atomic numbers with this 5-question quiz!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about atomic numbers:
Fun Atomic Number Trivia
Discover some fascinating facts about atomic numbers:
The Smallest Number
Hydrogen has the smallest atomic number (1) with just one proton. It's the most abundant element in the universe!
Golden Atomic Number
Gold has atomic number 79. Its chemical symbol Au comes from "aurum," the Latin word for gold.
Mendeleev's Prediction
Dmitri Mendeleev left gaps in his periodic table for undiscovered elements. He accurately predicted properties of elements like germanium (atomic number 32) before they were discovered!
Carbon's Isotopes
Carbon (atomic number 6) has several isotopes. Carbon-12 has 6 neutrons, Carbon-13 has 7, and radioactive Carbon-14 has 8 neutrons. All have 6 protons!





