Buoyancy - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover why some objects float and others sink!
What is Buoyancy?
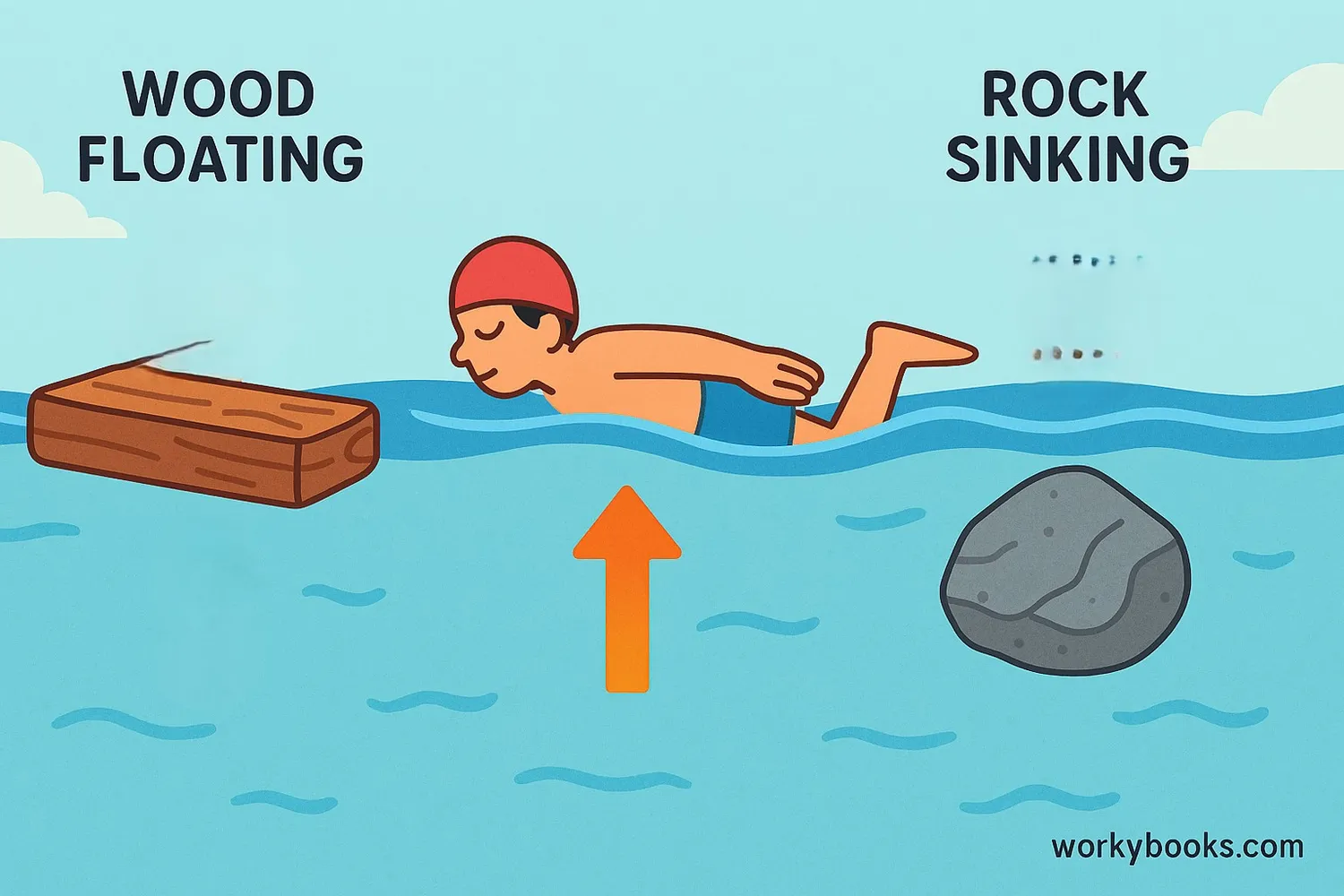
Buoyancy is the force that makes objects float in liquids like water! It's an upward force that pushes against gravity. When an object is placed in water, the water pushes up on the object with a force called the buoyant force.
Think of it like this: When you jump into a swimming pool, you feel lighter in the water. That's buoyancy helping to hold you up! Whether an object floats or sinks depends on how its weight compares to the buoyant force pushing upward.
Science Fact!
Buoyancy works in all fluids - liquids and gases! That's why hot air balloons float in the air and ships float on water.
Archimedes' Principle
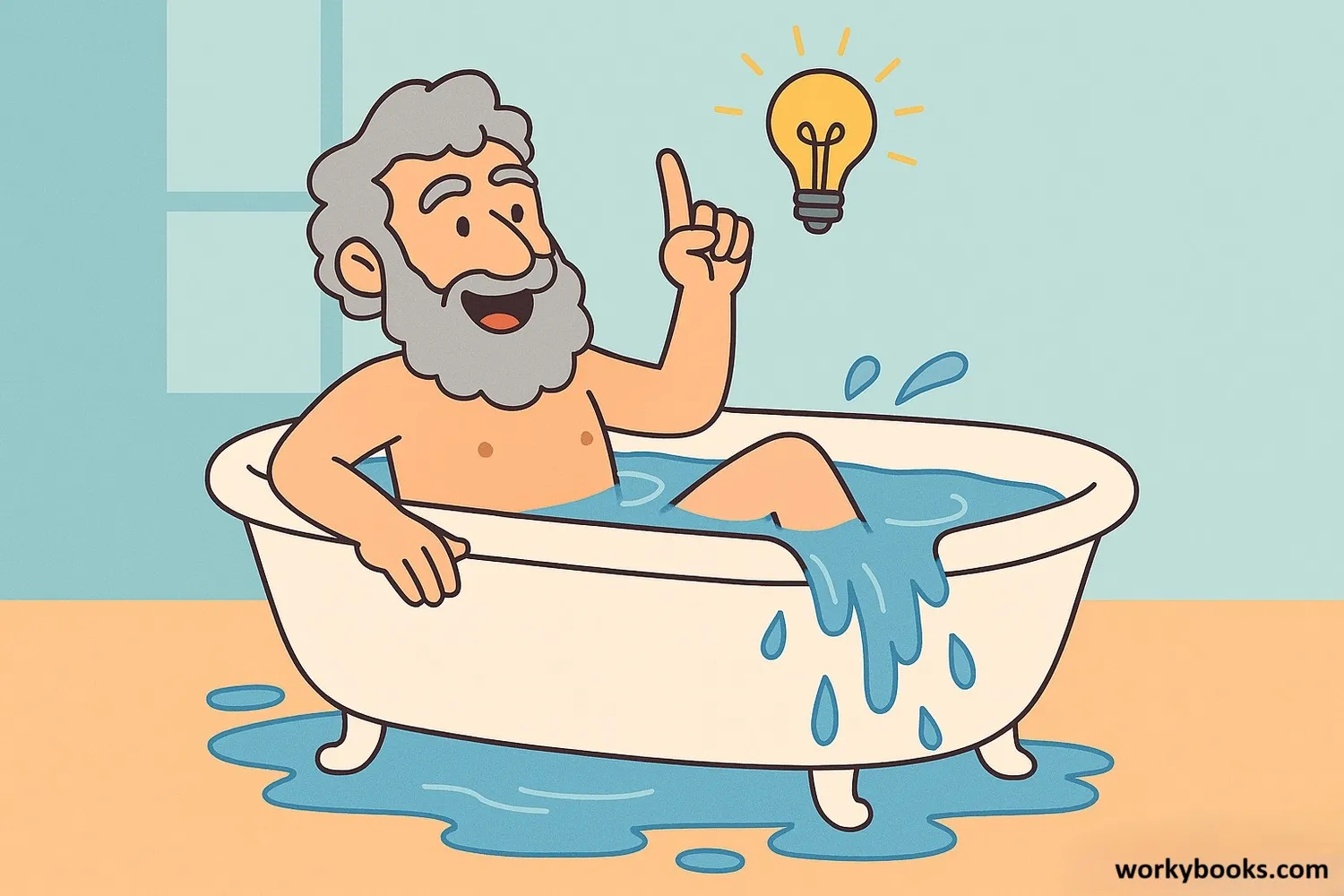

The story goes that a scientist named Archimedes discovered buoyancy while taking a bath! He noticed that when he got into the bath, the water level rose. He was so excited he ran through the streets shouting "Eureka!" which means "I found it!" in Greek.
Archimedes' Principle states: "The buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid it displaces." This means:
Displacement
When you put something in water, it pushes water aside
Weight Comparison
The water pushed aside has weight
Buoyant Force
The upward force equals that weight
So if an object weighs less than the water it displaces, it will float. If it weighs more, it will sink!
Displacement Fact!
Large ships float because they displace a huge amount of water. The weight of that displaced water is greater than the ship's weight!
Types of Buoyancy
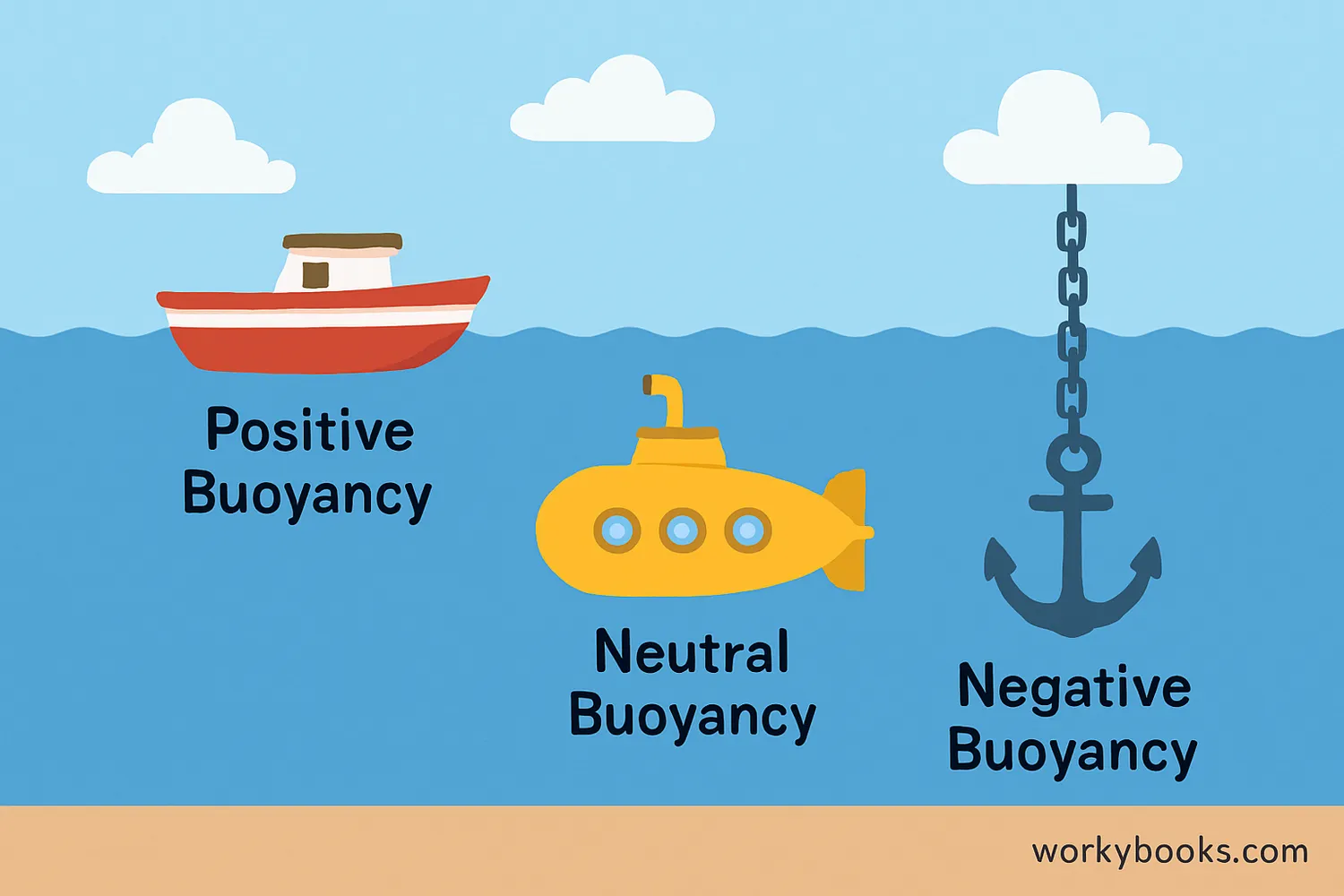
There are three different types of buoyancy that determine whether an object floats, sinks, or stays suspended in fluid:
Positive Buoyancy
The object floats because buoyant force is greater than its weight. Examples: Wood, boats, balloons.
Neutral Buoyancy
The object stays suspended at a certain depth because buoyant force equals weight. Examples: Submarines, scuba divers, fish.
Negative Buoyancy
The object sinks because its weight is greater than buoyant force. Examples: Rocks, anchors, metal weights.
Many objects can change their buoyancy. Submarines take in water to become heavier (negative buoyancy) or pump it out to become lighter (positive buoyancy). Fish use swim bladders to control their buoyancy!
Buoyancy Examples

Buoyancy is all around us! Here are some common examples you see every day:
Ships and Boats
Even heavy metal ships float because their shape displaces enough water to create strong buoyant force
Life Jackets
Help people float by increasing their volume without adding much weight
Fish
Use swim bladders to control buoyancy and stay at different depths
Hot Air Balloons
Float in air because hot air is less dense than cool air
Icebergs
Float with most of their mass underwater because ice is less dense than water
Buoyancy Quiz
Test your buoyancy knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about buoyancy:
Fun Buoyancy Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about buoyancy!
The Floating Sea
The Dead Sea has so much salt that people float effortlessly! Its salinity is about 34% - nearly 10 times saltier than the ocean!
Titanic Mistake
The Titanic sank because its watertight compartments weren't sealed at the top. As water filled one compartment, it overflowed into the next.
Fish Technology
Submarines were inspired by how fish control buoyancy! The first successful submarine used water tanks to sink and air to rise, just like fish bladders.
Density Matters
The world's largest ship, the Seawise Giant, weighed over 650,000 tons but floated because it displaced more than 650,000 tons of water!





